Determining the Depth of an Earthquake - focal depth
In ophthalmic instruments, to eliminate strong reflection from a patient's cornea, the phenomenon polarization of light is used.
Finger weg davon – verschiedene Kameras (besonders im Consumer-Bereich) bieten einen Zoom, der rein digital errechnet wird. Das Foto wird kameraintern groß gerechnet. Die Qualität ist einfach nicht vorhanden – woher auch – es wird hier nur gerechnet und interpoliert.
Also immer mit einem echten optischen Zoom arbeiten und den digitalen Zoom deaktivieren. Hat Ihre Kamera nur einen digitalen Zoom, dann schauen Sie sich einmal genau die Qualität der Bilder an. Machen Sie ein Bild mit Zoom und ein zweites ohne Zoom mit dem gleichen Ausschnitt (ja, man muss sich dann ein Stück näher an das zu fotografierende Objekt heran bewegen). Die Qualität bei Fußarbeit dürfte sichtbar besser sein.
Polarization by Transmission- In this method, involves the use of filter materials that have special chemical composition. They are known as Polaroid filters. These polaroid filters can block one of the two planes of electromagnetic waves. When the unpolarized light is transmitted through these polaroid filters, it filters out one-half of the vibrations of the light in a single plane. This polarized light has one half of the intensity.
Qualität hat aber deutlich ihren Preis – besonders wenn man Fotografie als Hobby betreibt, schmerzen Preise von 1000 Euro allein für ein Objektiv. Und es geht auch noch teurer.
For longitudinal waves, the displacement of the particles is parallel to the wave propagation direction. Particles do not move in the tube with the waves. They simply rock back and forth around individual equilibrium positions. Choose a single particle and watch it move. The waves appear to move from left to right in the compressed area (that is, the pressure wave).
Objektiv BrennweiteVergleich
Polarization by Scattering- When light travels through a medium, atoms of the medium (also the dust present in the medium) vibrate and produce electromagnetic waves. These waves are radiated outwards and thus the light is scattered. In this entire process, absorption and remission of light waves occur throughout the material. The scattered light is also known as partially polarized. Transmission of these partially polarised lights causes glare.
Und es gibt Zoomobjektive, die alle Bereiche umschließen, z. B. 18–250 mm. Allerdings erkauft man sich diese „Freiheit“ meistens mit einer Verschlechterung der Abbildungsqualität.
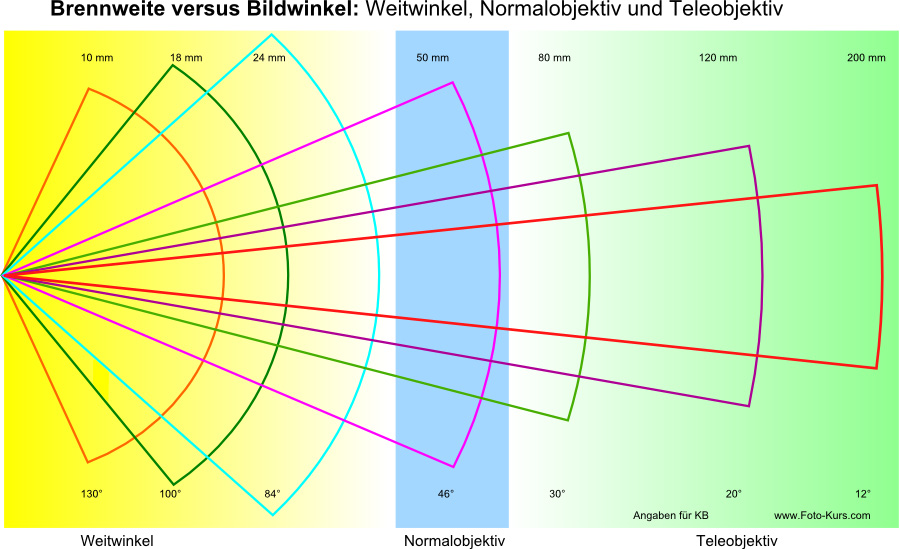
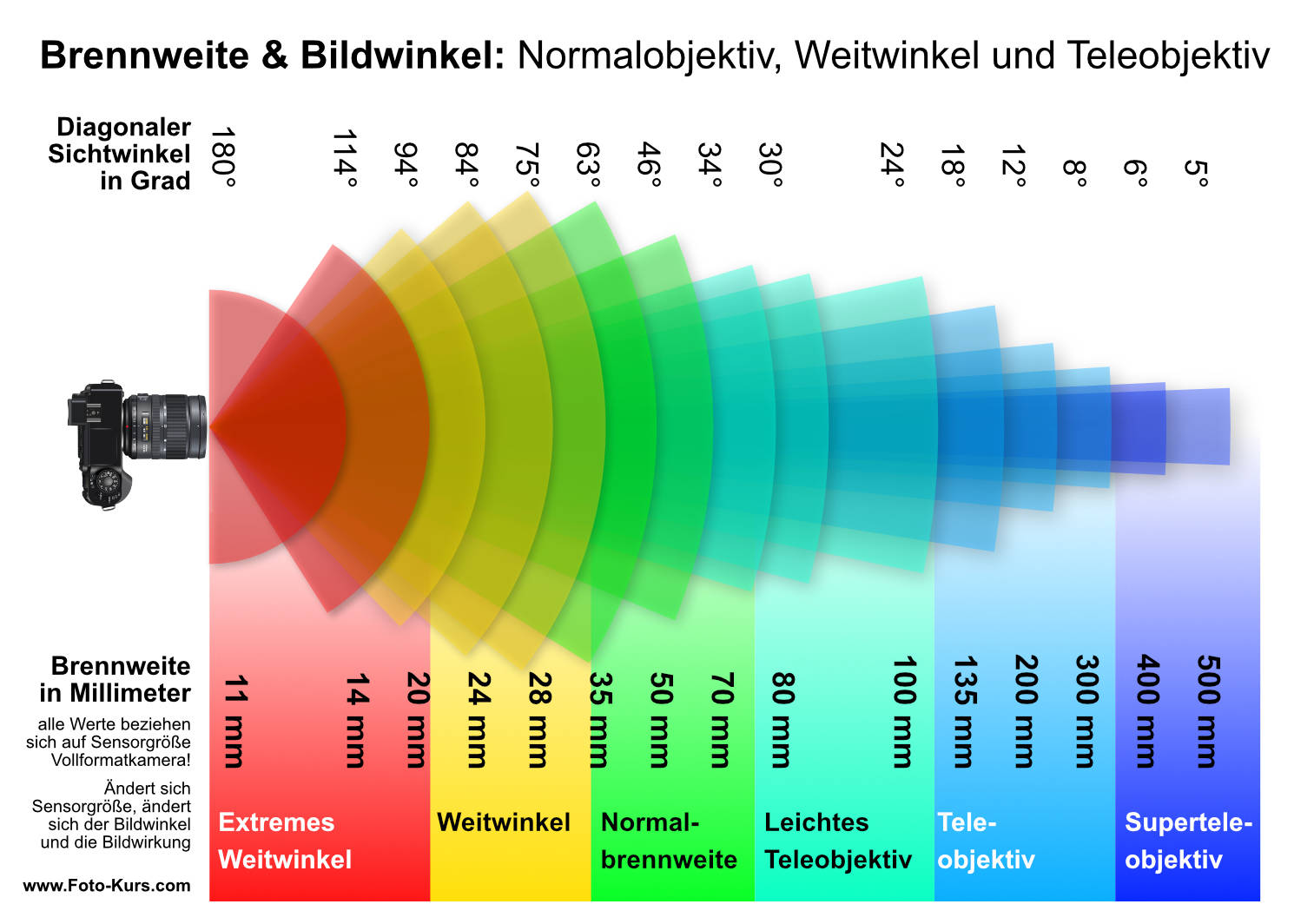
Wird in einem breiten Winkel gesehen, spricht man von einem Weitwinkelobjektiv – dazu muss der Mensch schon seinen Kopf drehen, bzw. die Augen hin- und herbewegen.
Viele Objektive gibt es als Festbrennweite – sprich: mit nur einem festen Wert. Das hat den Vorteil, dass ein Objektiv mit Festbrennweite exakt auf die eine Brennweite optimiert ist und so die maximale Qualität möglich ist.
Das folgende abgebildete Objektiv hat einen Zoombereich von 24 bis 70 mm mit einer konstanten Lichtstärke von f/2,8. Die konstante Lichtstärke hat den großen Vorteil, dass ein eingestellter Blendenwert von f/2,8 durchgängig zur Verfügung steht, egal ob man sich im Bereich 24 mm oder 70 mm befindet.
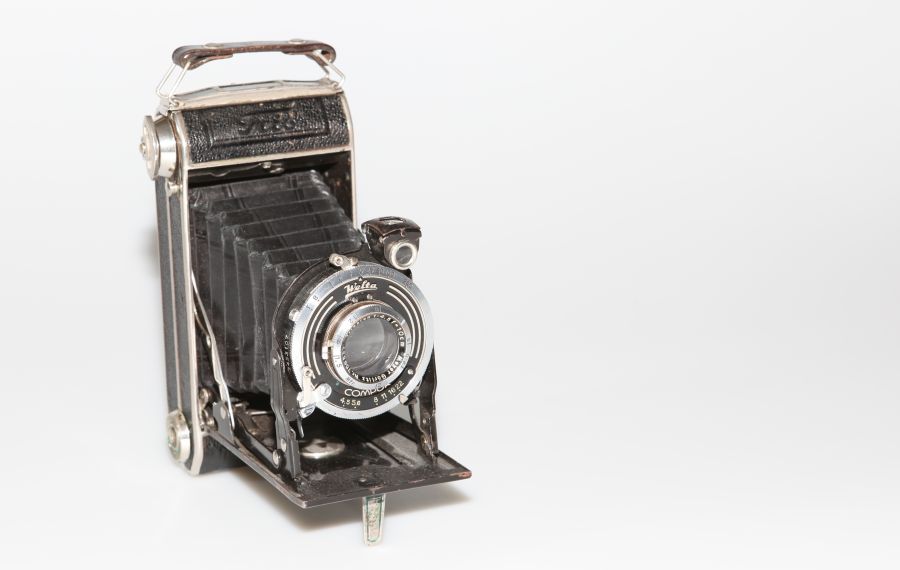
Dieses Objektiv hat also eine Lichtstärke von f/4,5 - je kleiner der Wert ist, desto mehr Licht kann auf den Film oder Bildsensor fallen. Für das Alter der Compur ist das schon ein guter Wert.
Elliptical Polarization- It is the type of polarization where the tip of the electric field vector defines an ellipse in any fixed plane traversing and is normal to the direction of propagation. An elliptically polarized wave may be bifurcated into two linearly polarized waves with their polarization planes perpendicular to each other. As the electric field can rotate clockwise or anti-clockwise while propagating, elliptically polarized waves show chirality.
Je nachdem, mit welchem Bildwinkel ein Objektiv genutzt wird bzw. welchen das Objektiv zur Auswahl bietet, spricht man von:
BrennweiteKamera einfach erklärt
Dagegen hat folgendes Objektiv einen Zoombereich von 18 bis 250 mm und eine Lichtstärke von f/3,5 bis f/6,3. Das bedeutet, dass man bei der 18 mm-Einstellung eine Blende von f/3,5 verwenden kann, aber sobald man zu zoomen anfängt, der Anfangsblendenwert deutlich schlechter wird. Bei 250 mm ist der Anfangsblendenwert dann bei f/6,3.
Allerdings hat sich mit der digitalen Fotografie die verfügbare Anzahl an verschiedenen Größen von Bildsensoren enorm erhöht – neben dem Vollformatsensor (der mit seinen Maßen dem Kleinbild entspricht) gibt es noch APC-C, Four Thirds 4/3 und einiges mehr.
To cut the refractions, Fishermen, Skiers, motorists, sportsmen need special sunglasses. In the production of these special sunglasses polarization of light is used.
Flexible Waves: Waves where particle movements depend on the direction of wave motion. For example, when you throw a stone, it creates waves in the water and sounds like air.
In impact, polarized mild waves having their vibration instructions oriented parallel to every different can integrate to provide interference, while those which can be perpendicular do not intervene.
Hierbei ändert sich nicht der Bildwinkel – dieser bleibt konstant für alle Formate. Aber je nach Sensorgröße entspricht ein Objektiv mit einem Bildwinkel von 46° dann 50 mm oder durch die Ausschnittvergrößerung, die ein kleiner Sensor mit sich bringt, dann eher 80 mm. Von „Brennweitenverlängerung“ (was man oft liest) zu sprechen, ist falsch. Es wirkt wie eine Verlängerung der Brennweiten, weil das Bild „größer“ abgebildet wird – in Wirklichkeit ist es aber nur eine Ausschnittvergrößerung.
Im folgenden Bild sieht man eine Detailaufnahme der 1932 gebauten Kamera „Welta Compur“. Bereits hier findet man schon die Angabe 1:4,5 f.
Brennweite ObjektivBeispiel

Electronic polarization: The displacement occurring in dielectric elements and minerals between a positive charge and negative charge results in Electronic polarization.
Brennweitein Meter umrechnen
Flexible Waves: Waves where particle movements depend on the direction of wave motion. For example, when you throw a stone, it creates waves in the water and sounds like air.
Man hat z. B. mit einem 50 mm-Objektiv an einer Kamera mit APS-C-Sensor dann den Ausschnitt eines 80 mm-Objektivs – aber nicht die Vorzüge eines 80 mm-Objektivs. Das 80 mm-Objektiv hat in der Porträtfotografie den Vorteil, dass es eine kissenförmige Verzeichnung hat, was Gesichter schlanker abbildet. Dazu mehr im Kapitel über Porträtfotografie.
Linear Polarization- Linearly polarized light wave means that the electric field vibrates in a certain linear direction perpendicular to the wave axis, and the magnetic field vibrates in a direction that is perpendicular to both, the advancement axis and direction of the electric field. The direction of polarization is considered to be the direction of the electric field vibration. The polarization can take place in any other direction perpendicular to the wave axis. Rotation of the polarization by 180° does not lead to a rationally different state.
Im Folgenden wird hauptsächlich von Objektiven gesprochen – damit sind auch eingebaute Objektive von Kompaktkameras gemeint.
Von Zoomobjektiven spricht man, wenn das Objektiv variable Brennweiten bietet. Es gibt reine Weitwinkel-Zoomobjektive – diese bieten z. B. eine Bandbreite von 10–24 mm. Es gibt reine Zoom-Teleobjektive, z.B. mit einem Bereich von 70–200 mm.
It means that the light emitted by the sun travels in all the given directions i.e in different planes. And while being transmitted through a distance it gets semi polarized and only gets polarized when its angle of reflection is equal to the angle of polarization. Because the light of the sun takes all directions, it is said to be unpolarized light. When unpolarized light falls on the transparent surface at an angle of incidence equal to the polarization angle also called Brewster's angle, it is called plane-polarized. When the unpolarized light is passed through a polarizing sheet, it becomes polarized.
Polarization additionally takes place when light is scattered even as touring via a medium. while light moves the atoms of a material, it'll regularly set the electrons of these atoms into vibration. The vibrating electrons then produce their electromagnetic wave that is radiated outward in all instructions.
BrennweiteKamera einstellen
Aber egal welche Kameraart man sich ansieht – das dahinter liegende Grundprinzip ist dasselbe, und auch die verschiedenen möglichen Vorteile und Probleme sind identisch.
Brennweite Objektivablesen
Kurz: Wir finden die Angaben der Brennweite bei Objektiven – sollten uns aber des Formatfaktors (siehe Kapitel Bildsensor) unserer Kamera bewusst sein.
Sunlight and other natural, as well as artificial sources, give rise to light. Truly, light is a wave phenomenon. It can bend around objects. It can diffract and interfere. The light waves travel through the vacuum to reach us and because of Earth’s magnetic field, it becomes an Electromagnetic wave. These light waves are transverse. It exhibits the phenomenon of reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, double refraction and polarisation. The electric and magnetic field vectors of the light wave travel in all directions. If the movement of these vectors is restricted to a single plane then the effect is called Polarization of light. Specialized materials are used to filter these beams, according to the direction of propagation.
Jede Kamera benötigt eine Optik, also das Objektiv – in Kompaktkameras ist dieses fest integriert, bei Spiegelreflexsystemen wechselbar. Es gibt kein ideales Objektiv, das für alle Anwendungsfälle die optimalen Eigenschaften besitzt. Daher ist die Möglichkeit zum Auswechseln der Objektive bei Spiegelreflexkameras vorteilhaft, um die bestmögliche Qualität zu erhalten.
Je lichtstärker ein Objektiv ist, desto mehr Freiheit hat der Fotograf. Diese Angabe auf dem Objektiv gibt die größtmögliche Blendenöffnung an, was der maximalen Lichtstärke des Objektivs entspricht. Auf dem Bild ist zu sehen, wie bei der alten Kamera noch die Blende durch den unteren Regler eingestellt werden kann. Gerade steht der Pfeil nicht ganz auf dem Blendenwert f/22 - möglich sind Blendenwerte von f/4,5 bis f/22.
An event caused by the vibration of light waves limited to a specific plane is known as polarisation. With normal light from the feed, vibration usually occurs in the distribution path across all active aircraft. This kind of soft beam is known as incandescent light. If with the help of several methods (reflection, refraction or dispersion) a beam of light is produced when vibration is limited to one highly efficient aircraft, then it is called far-flung polarized light. Therefore, polarization is the process of producing a polarized mild aircraft from non-coating.
Circular Polarization- It is the type of polarization in which at every point, the electromagnetic field has a constant magnitude but its direction rotates with a constant value in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in two ways, either the electric field vector rotates according to the direction of propagation in a right-hand direction or according to the direction of propagation in a left-hand sense. The phenomenon of polarization rises as a result of the fact that light acts as a 2 Dimensional transverse wave.
BrennweiteTabelle
Polarization by Reflection- When unpolarized light is made to fall on a non-metallic surface, at a particular angle, the surface reflects the polarized light. In this process, the angle of incidence and the non-metallic surface plays an important role to regulate the magnitude of polarization.
Due to the three dimensions, there are two directions perpendicular to the propagation direction. Therefore, if the wave is propagating in the Z direction (that is, if the Z-axis is selected as the direction of travel of the wave), the wave can oscillate in the X or Y direction, or a combination of these overlay directions. Therefore, the shear wave has two polarizations, one for each direction of propagation. If you have a polarized light-sensitive medium (such as a polarizing element for eyeglasses), you can detect the polarized light. For example, consider two polarisations. Align one to the X-axis, then rotate the other. You can see that the light intensity is cos2θ. Where θ is the relative angle between the preferential directions of the modulator.
Die Angabe der Brennweite stammt noch aus den analogen Zeiten der Fotografie. Hier war der Film genormt – i. d. R. im Kleinbildformat (Abkürzung KB), man hatte 24 x 36 mm.
Brennweiteberechnen
Als zweite Angabe ist die Brennweite wichtig bzw. bei Zoomobjektiven die möglichen Bereiche inklusiv der zugehörigen Lichtstärke.
The combination of electrical and magnetic fields that travel through space is known as light. The electric current and the magnetic field of light waves depend on each other. The magnetic field travels one way and the electric field in another but remains perpendicular. So we have an electric field in one plane, a magnetic field in which to fly, and a direction in the direction of both. Electrical and magnetic vibrations can occur on a variety of aircraft.
In a polarized mild aircraft, an aircraft that has a vibration and soft distribution system is called a vibration aircraft. The plane associated with the vibration plane is called the polarization plane.
The P wave (primary wave) of an earthquake is an example of a longitudinal wave. The P wave moves fastest and arrives first.
In transverse waves, the displacement of the particles is perpendicular to the wave propagation direction. Particles do not move with the waves. They only sway up and down around their equilibrium positions as the waves pass. Choose a single particle and watch it move. The S wave (secondary wave) of an earthquake is an example of a transverse wave. The S wave travels slower than the P wave and arrives in a few seconds.
An event caused by the vibration of light waves limited to a specific plane is known as polarisation. With normal light from the feed, vibration usually occurs in the distribution path across all active aircraft.
Die Wahl der Brennweite hängt immer vom bevorzugten Bereich der Fotografie ab! Hier finden sich in den Kapiteln über die verschiedenen Bereichen der Fotografie bei jedem einzelnen Bereich Hinweise zu empfehlenswerten Brennweiten. Autor: Axel Pratzner WhatsApp teilen Facebook teilen pin it mitteilen teilen teilen teilen Das E-Books zum Foto-Kurs.com E-Book mit über 290 Seiten Umfang als PDF. Alle Details und Download NEU E-Book kaufen Sucher der Kamera Crop-Faktor - Formatfaktor
Polarization by Refraction- Refraction is when a light wave travels from one medium to another, it changes its direction and speed. This refracted beam attains some degree of polarization. In the majority of the cases, polarization by refraction occurs in the plane which is perpendicular to the surface.
Polarization is a crucial property of light that affects even the optical systems that don't explicitly measure it. The polarization of light influences the point of interest of laser beams affects the reduced-off wavelengths of filters and can be critical to saving you unwanted returned reflections.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500