How to Read Your Prescription for Glasses - cylindrical lens glasses
LASERfull form
In this way, the laser beam is generated in the direction of the fibre and is then emitted and transmitted via the fibre to the point of application.
In a carbon dioxide generator, a chamber is filled with carbon dioxide, helium, and nitrogen. The carbon dioxide is the medium used to generate the laser beam, and the other gases support and stabilise the process.
What islaserin Physics
Since this state is not a natural state for the atom, the electron eventually jumps back to its original level and emits the excess energy in the form of a photon in a random direction. This is called spontaneous emission.

Visualization of mitotic HeLa cells by advanced polarized light microscopy. Micron 39: 635-638 (2008). A nice example of using a conventional polarized light microscope to observe molecular order non-destructively in living cells without staining. The authors perform time-lapse imaging of dividing HeLa cells to visualize the mitotic spindles and kinetochore microtubules.
Pumping is done using relatively cheap diode lasers which insert laser light into the fibre. The light is directed towards and reflected against the outer sheath and repeatedly passes through the fibre core, which raises the electrons of the medium to a higher energy level (excitation), which are then stimulated to return to their basic state (emission), which releases the beams of light (photons).
This type of generator follows the basic principle of how a laser beam is generated, whereby a medium is “pumped” with energy to then emit photons when the medium returns to its natural state.
by V Moschos · 2020 · Cited by 22 — Overprediction is observed for 84 % of data points. The P25–P75 (P: percentile) total absorption reduction range at 370 nm vs. 660 nm is 11 %–18 ...
Jul 3, 2023 — A microscope is an optical device designed to magnify the image of an object, enabling details indiscernible to the human eye to be ...
Table of Contents · Objective Identification · M = L / F . · NA = ni × sinθ · FN = Field of View Diameter × Magnification · Magnification · Using an Objective with a ...
Although all laser generators work in this way, they have different ways of supplying energy, known as pumping, and different types of atoms used for the excitation, i.e. different laser media.
Several types of fibre generators are available. For example, in some cases the beam is bounced between mirrors at the ends, or the pumping is done by way of one or more inlets along the length of the fibre instead of from the end.
The photons let through form the laser beam that is then directed via optical mirrors and lenses to the point of application.
What are lasers used for
The polarized light microscope is designed to observe specimens that are visible primarily due to their optically anisotropic character. Polarizing microscopes must be equipped with both a polarizer, positioned in the light path somewhere before the specimen, and an analyzer (a second polarizer), placed in the optical pathway between the objective rear aperture and the observation tubes or camera port. Image contrast arises from the interaction of plane-polarized light with a birefringent (or doubly-refracting) specimen to produce two individual wave components that are each polarized in mutually perpendicular planes. The velocities of these components are different and vary with the propagation direction through the specimen. After exiting the specimen, the light components become out of phase, but are recombined with constructive and destructive interference when they pass through the analyzer.

In order to create a photon, with both wave and particle properties, external energy must be added to an atom. This raises the energy level of one or more electrons, resulting in their jumping up one or more electron shells. This is called excitation.
Pumping takes place by way of flashing light to raise the electrons of the medium to a higher energy level (excitation), which are then stimulated to return to their basic state (emission), which releases the beams of light (photons).
The photons bounce between a rear mirror and a front mirror to build the laser beam up to its full intensity. The front mirror is semi-transparent and allows a certain number of photons to pass through. However, the majority of the photons are reflected back to maintain the full intensity of the generator.
Quantitative polarized light microscopy. Journal of Microscopy 209: 13-22 (2003). The authors describe a confocal microscope modification that analyzes the polarization stte of light emerging from a specimen to permit quantitative polarized light microscopy. The system uses a rotating analyzer that enables images to be obtained where the image contrast corresponds to both specimen retardance and orientation.
Polarized light microscopy of spindles. Methods in Cell Biology 61: 175-208 (1998). The author describes the basic aspects of microscope configuration, such as contrast, noise, extinction factors, and retardation plates. This discussion is followed by examples of spindle birefringence in bundled and parallel microtubules, as well as individual spindle components.
M Xie · 2018 — Simultaneous measurement of refractive index and temperature by M-Z interferometer cascaded with a FBG. Mingyang Xie, Huaping Gong, Jun Zhang, and Yongxing ...
Departures in lens action from the ideal conditions of optics are known as aberrations. Optical trains typically suffer from as many as five common aberrations: ...
Rediscovering polarized light microscopy. American Laboratory 35: 55-61 (2003). Written by a research microscopist at the McCrone Research Institute, this nice review article covers the basic aspects of polarized light microscopy. Included are discussions of birefringence, indicatrix models, quantitative aspects, and classes of materials that can be used with polarized light microscopy.
A new view on polarization microscopy. Nature 381: 811-812 (1996). Dr. Oldenbourg discusses improvements to the traditional polarized light microscope, which have enhanced the direct analysis of the molecular architecture in living cells. Examined are electro-optical devices, polarization algorithms, and digital image processing of images captured using birefringent specimens.
This type of generator follows the basic principle of how a laser beam is generated, whereby a medium is “pumped” with energy to then emit photons when the medium returns to its natural state.
A simplified, low-cost method for polarized light microscopy. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 81: 782-783 (2009). An excellent description of how a conventional transmitted light microscope can be easily and cheaply converted for imaging using polarized light. The authors include examples of malaria parasites in thick blood films to demonstrate the capabilities of the modified instrument.
Laser light consists of parallel beams of light on the same wavelength. Compared with the light from a torch, this allows the beam to be focused down to an extremely small point.
This type of generator follows the basic principle of how a laser beam is generated, whereby a medium is “pumped” with energy to then emit photons when the medium returns to its natural state.
Laser basicsin dermatology
In simple terms, a laser uses light to transmit heat very precisely. The same principle applies to modern lasers as when laser technology was discovered almost sixty years ago. Over thirty years, Permanova has worked to refine the technology and make it easy and safe to use. For those who want to delve into the underlying physics and technology, there is a lot of information to feast on below.
Jul 26, 2021 — An aspherical lens is any lens that has an optical surface that is not spherical and may include cylindrical, toroidal, and general freeform ...
Laser basicsnotes
In a fibre laser, the medium is usually an erbium-doped fibre. The fibre itself consists of three layers – the inner ytterbium-doped core, a transparent middle layer, and the outer sheath.
Laserwavelength range
Enhanced polarizing microscopy as a new tool in aneuploidy research in oocytes. Mutation Research 651: 131-140 (2008). A comprehensive treatment of the use of polarized light microscopy in clinical diagnosis. The authors study human oocytes and provide a detailed discussion of the techniques and implications of this research. Included is an outstanding bibliography with numerous pertinent references.
The photons bounce between a rear mirror and a front mirror to build the laser beam up to its full intensity. The front mirror is semi-transparent and allows a certain number of photons to pass through. However, the majority of the photons are reflected back to maintain the full intensity of the generator.
Laserdiagram
Cost. In the 1990s, laser sources were bulky and relatively expensive to buy. A lot has happened since then. Modern industrial lasers are rarely bigger than a large refrigerator. The cost per kilowatt is a third of what it once was, and uptime is in excess of 99%.
Setze gezielte Highlights · Erfahrungsberichte unserer Kund:innen · Erfahrungsberichte in Deutsch für Sigma Beauty F42 - Strobing Fan ...
YTSWGKX07B Smart Audio Glasses ideal optics frames with Microphone, Anti-Blue Light Lens Open Ear Speaker with Bluetooth. Note: Please be cautious and check ...
The importance of polarized light microscopy in the analytical setting. Microscopy and Microanalysis 14: 1032-1033 (2008). A short review of how polarized light microscopy can provide information on a wide range of specimens. The author includes examples of plane-polarized images, dispersion staining of fibers, and stereoscopic images of wood, chemicals, and plant material.
The word LASER is the acronym of Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, which is essentially an explanation of the process.
Plastic Fresnel lenses are used as magnifiers when a thin, light lens is needed. The quality of the image is not nearly as good as that from a continuous glass ...
Laser Basicspdf
Quantitative image analysis of birefringent biological material. Journal of Microscopy 187: 62-67 (1997). Interference color contrast in polarized light microscopy is adapted for quantitative image analysis based on a linear relationship between color intensity and birefringence. Included are examples of collagen ribbons in the dogfish egg case.
Polarization microscopy. Current Protocols in Cell Biology Unit 4.9: 4.91-4.9.22 (2002). Professor Inoué, a recognized pioneer in polarized light microscopy, provides an introduction to the topic, the optics involved, and practical considerations for observing submicroscopic structures. Specific examples of microtubules in the mitotic spindle, chromatin in maturing spermatids, and the skeletal spicules in larvae are included.
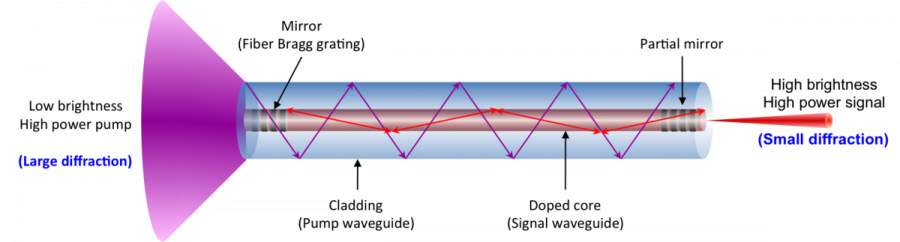
Pumping takes place by way of electrical discharges to raise the electrons of the medium to a higher energy level (excitation), which are then stimulated to return to their basic state (emission), which releases the beams of light (photons).
This type of emission is not desirable in the context of lasers as, ideally, photons with a parallel direction are required. This can be achieved by “pushing” the electron down to its original level using another photon. This is called stimulated emission and results in the photons emitted having exactly the same direction as the one that pushed the electron down. These in turn push down additional excited electrons, which creates a chain effect of emissions and subsequently builds up the energy in the laser beam.
Get the best deal for Laser Safety Goggles from the largest online selection at eBay.ca. | Browse our daily deals for even more savings!




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500