How to correctly set-up and focus a stereo microscope - how to focus a microscope
The size of the camera sensor affects how much light it can capture, impacting image quality, especially in low-light conditions.
It’s very common for each of your eyes to be a little different. If you have glasses, you’re probably aware of this – your prescription compensates for the difference in the ‘strength’ of your vision in each eye.
Rolling shutters capture am image in a sequence from top to bottom, which can lead to distortions in fast-moving scenes.
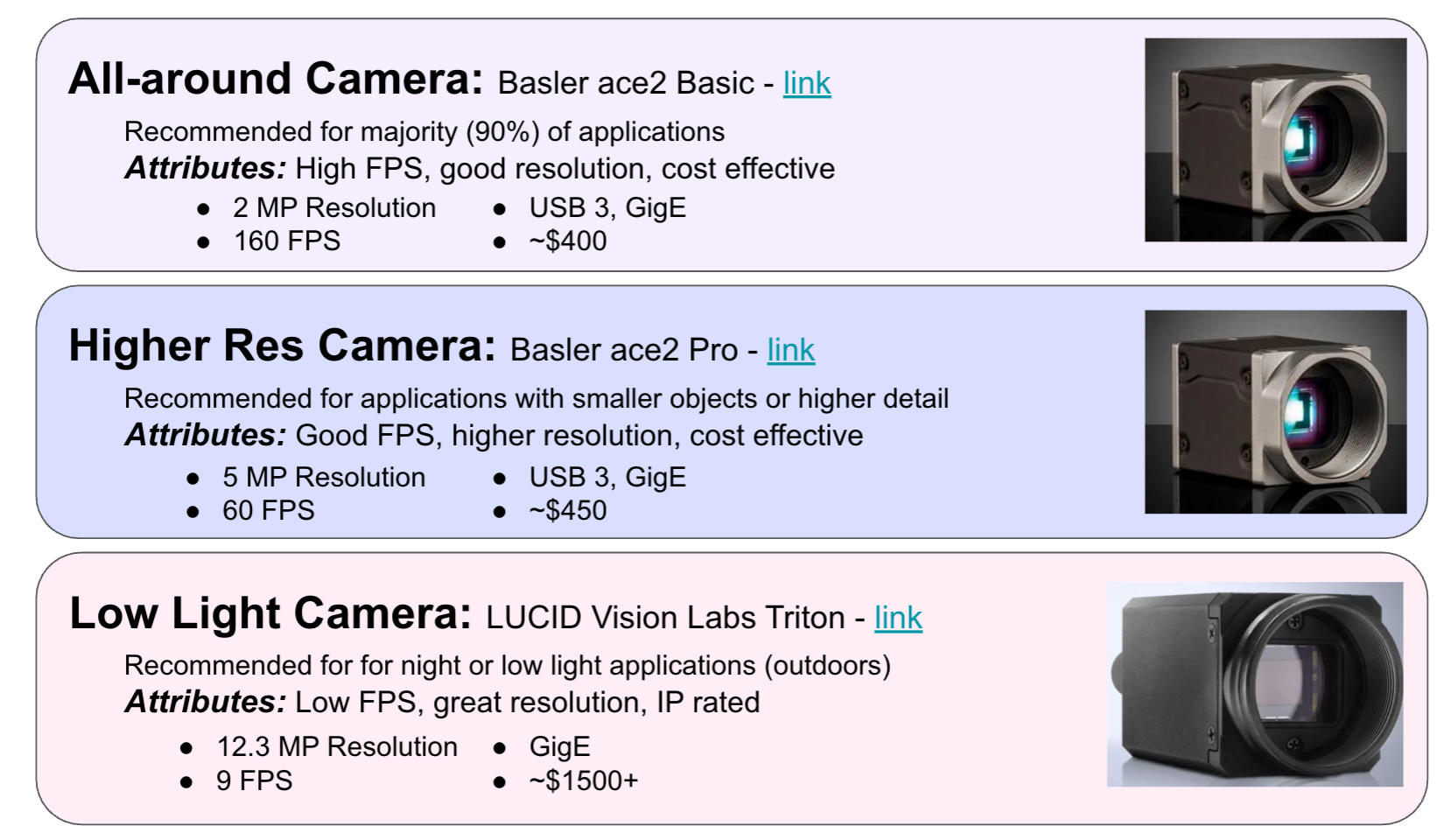
With its high resolution and excellent low-light performance, the LUCID Vision Labs Triton ensures that you capture clear and detailed images even in the darkest conditions.
Before diving into the technical specifications of cameras, it's crucial to first identify and understand the specific requirements of your computer vision application. Different tasks will demand different capabilities from a camera, and what works for one application may not be suitable for another.
Consideration: For applications like outdoor surveillance or vehicle navigation, where exposure to varying lighting conditions is common, HDR capability is beneficial.
The camera should be capable of handling the data throughput necessary for real-time analysis, which involves both the camera’s interface and the processing unit’s capability to handle the incoming data stream.
Consideration: Ensure the camera supports interchangeable lenses if flexibility or specific lens characteristics are required for your application.
Computer vision cameraapp
Some microscopes have a single adjustable eyepiece with the other fixed in place, while others let you adjust both. The process is virtually identical either way, so don’t worry.
Third, consider the operational environment in which your project will be deployed. Consider if the camera needs to withstand harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or vibrations.
Computer Vision Cameraprice
The Basler ace2 Pro is ideal for detailed inspections, precision measurement, and other applications where capturing fine details is crucial.
If your lab or classroom uses shared microscopes, the first thing you should do before getting down to work is adjust your eyepieces.
GigEVision camera
Higher resolution cameras capture more detail, which is vital for accurately identifying features in an image, especially in applications like precision measurement or defect detection.
Next, note the number settings written around the side of the eyepieces. Once they are memorised, you can be ready to go with a simple adjustment the next time you sit down at a microscope.
When considering which camera to select for a computer vision project, asking the right questions can guide your decision-making process effectively. Here are some helpful questions to consider:
Consideration: Determine the minimum resolution needed based on the smallest object feature you need to detect or the finest detail required for analysis.
The choice of lens affects the field of view, depth of field, and potential for zoom, which are essential for framing your subject correctly.
Machinevision cameramanufacturers
Whether you’re working on object detection, facial recognition, or motion tracking, the Basler ace2 Basic provides reliable performance without breaking the bank.
Consideration: Choose global shutter cameras for high-speed applications like traffic monitoring or automated inspection systems where motion blur can be a concern.
If you are working in an environment where frames are captured less frequently – for example, a security monitoring system – you may not need to invest as much in a low-latency camera.
These specialized features can dramatically affect the performance of a computer vision system by enhancing the camera's ability to capture high-quality images under various conditions. When selecting a camera, consider these features in the context of your specific application needs to ensure optimal performance.
Frame rate, measured in frames per second (fps), is critical for applications involving motion, such as tracking moving objects or video analysis.
By carefully evaluating each of these factors, you can make an informed decision that balances technical capabilities with practical constraints and budget considerations. Remember, the ideal camera not only meets today's needs but also accommodates future expansions and technological advancements.
The ability of a camera to seamlessly integrate with existing systems and handle data efficiently is crucial for the success of computer vision applications. This section explores the various connectivity options and integration considerations that are essential when selecting a camera.
When selecting a camera for computer vision applications, certain technical specifications are crucial to consider. These specifications directly impact the performance of the camera in capturing images that are suitable for analysis by computer vision algorithms. Here’s a detailed look at the key camera specifications you need to evaluate:
Fortunately, microscope manufacturers are aware of this, and most microscopes let you easily compensate for the differences.
The first thing to do is to adjust for how far apart your eyes are (sometimes known as the interpupillary or interocular distance).
Cameras with larger sensors, better noise reduction algorithms, and advanced image processing capabilities tend to perform better in low light conditions.
It's crucial to know if the camera will operate in harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or dusty environments. This affects the choice of camera housing and any additional protective measures.
We encourage you to use the outlined questions and recommendations as a starting point to carefully assess each option. With the right camera, your computer vision system will be better equipped to perform its intended tasks efficiently and accurately, thereby enhancing the overall value and effectiveness of your technological solutions.
Understanding the specific use case, such as inspection, measurement, or identification, helps in selecting a camera with the appropriate capabilities and specifications.
For most people, the difference is usually very slight and may be unnoticeable in everyday life, but when using a microscope for lengthy periods you can sometimes end up with headaches and dizziness.
Cameraforcomputer visionapplications
For computer vision applications, beyond basic specifications like resolution and frame rate, there are specialized camera features that can significantly enhance performance in specific scenarios. Understanding these features can help tailor your camera selection to meet the unique demands of your computer vision project.
Fourth, consider the required processing time for your system. Are you deploying a model that will run on an assembly line or in another environment where video is processed in real time? If so, you will need a low-latency camera.
Understanding the speed at which the camera needs to capture images (frames per second) is vital, especially for applications involving moving objects or high-speed processes.

Cognexcamera
Everyone’s eyes are different – the distance between your eyes will be different from other people's and your left eye often sees a little differently from your right eye.
Second, cameras must be capable of performing under the lighting conditions prevalent in the application area, whether it’s indoor, outdoor, or variable lighting.
Computer vision camerasoftware
By thoroughly understanding these requirements, you can better evaluate which camera specifications are most critical for your computer vision application.
Different sensors perform differently under various lighting conditions. Knowing whether the camera will be used in low light, bright light, or fluctuating conditions helps in choosing a sensor with suitable sensitivity and dynamic range.
The appropriate camera can drastically enhance the performance of computer vision algorithms by providing high-quality images that are crucial for accurate analysis and decision-making. Conversely, the wrong camera can lead to poor system performance, regardless of the sophistication of the software algorithms.
Consideration: Higher frame rates are necessary for capturing fast-moving objects without blur, ensuring smooth video playback and effective motion analysis.
Global shutters capture an entire image simultaneously, eliminating motion artifacts. Ideal for capturing fast-moving objects.
For applications that require higher detail and resolution, the Basler ace2 Pro is an excellent choice. This camera is perfect for tasks involving smaller objects or where higher image fidelity is necessary.
(If you wear your prescription glasses while you work, you shouldn’t need to do any further steps because your vision is already corrected)
First, no matter what application you are building, image quality is essential. High-quality images with low noise are crucial for accurate analysis, especially in low light conditions.
• GigE (Gigabit Ethernet): Offers high data rates and long cable lengths, making it suitable for industrial environments where cameras may be far from the processing unit.
Bestcomputer vision camera
In this article, we will start with our top three camera recommendations. We will then analyze key factors you should consider when making a choice about what camera to buy, from shutter types to interfaces through which you can interfact with a camera.
Consider the physical size and mounting options of the camera to ensure it fits within your setup, especially in constrained spaces or where specific mounting options are necessary.
It’s very easy to do – simply try to look down the eyepiece with both eyes. The goal is to be able to see a single image. If you can see 2 images, you need to move the eyepieces closer or further apart until they merge into a single image.
• USB: Common and easy to use, suitable for low to moderate speed requirements. USB cameras are plug-and-play, making them ideal for desktop applications and simple setups.
It’s worth remembering that eyepiece distances are often adjusted by moving them in a vertical motion (a bit like how a bird flaps its wings), rather than horizontally, so make sure not to accidentally pull your eyepieces apart.
If you can remember the distance (you can usually see it on a scale on the central area between the eyepieces), you can be ready to go on any microscope in seconds.
Choosing the right camera for your computer vision project is a critical decision that can significantly influence the success of your application. Throughout this blog, we have explored various aspects of camera technology—from understanding the specific requirements of your computer vision tasks and key camera specifications, to considering specialized features and practical considerations relevant to your industry and application environment.
Choosing the right camera for your computer vision application can be challenging, given the myriad of options available. To simplify this process, we’ve identified three standout cameras that cater to a wide range of scenarios, from general-purpose applications to specialized tasks requiring high resolution or low-light performance. Here’s a closer look at our top picks:
In addition, check if the camera can be powered through the interface (like PoE - Power over Ethernet) or if it requires a separate power supply, which could affect the setup and maintenance complexity.
Consideration: Evaluate the ISO range and noise levels at higher ISOs to ensure the camera can capture usable images in dim environments.
Asking about the required interfaces (e.g., USB, GigE, Camera Link) and compatibility with existing systems ensures the camera can be integrated smoothly into the customer’s current setup.
The resolution necessary for the application determines the level of detail the camera needs to capture. Field of view requirements help determine the sensor size and resolution needed.
The Basler ace2 Basic is our top recommendation for the majority of computer vision applications, covering a vast majority of use cases. This camera strikes an excellent balance between performance and cost, making it ideal for a wide range of tasks.
Reed Johnson. (Sep 19, 2024). Best Cameras for Computer Vision. Roboflow Blog: https://blog.roboflow.com/best-cameras-for-computer-vision/
Ensure the camera is supported by readily available drivers. This compatibility is crucial for facilitating development and integration into existing systems.
When it comes to night or low-light applications, the LUCID Vision Labs Triton stands out. This camera excels in environments with poor lighting conditions, making it suitable for outdoor surveillance and other challenging scenarios.
Check if the camera manufacturer provides a robust software development kit (SDK) or application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow for extensive customization and control over camera functions.
HDR cameras can capture multiple exposures of a scene and combine them to enhance detail in both shadows and highlights.
Many computer vision applications operate in less than ideal lighting conditions. Effective low light performance is crucial for maintaining image quality.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500