How To Choose A Good Magnifying Glass? | E-Tay - buy magnifying glass
LaserMirror
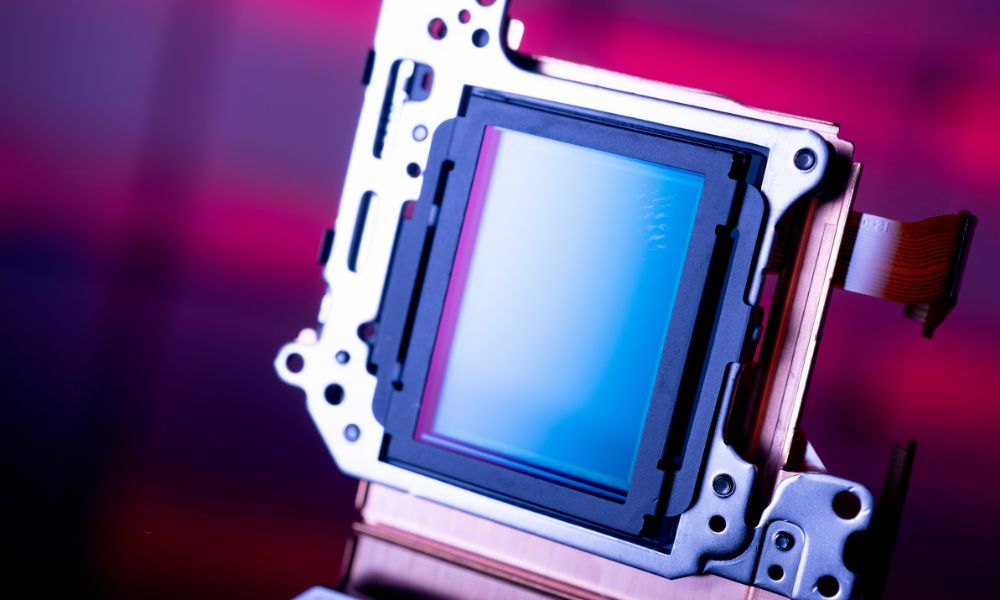
We understand that image sensors take in light from the camera’s lens. But what happens after that? Once an image sensor registers incident light, it transfers the information to its next stage, either digital signal or voltage, depending on the sensor type in your camera.
Image sensors are crucial to capturing beautiful pictures. That alone is enough to make them a benefit to any digital camera system. But there’s also more to it than that. Image sensors don’t just convert light into images. They do so with impressive precision—so much so that we get to enjoy crystal-clear, colorful photographs that wouldn’t have been possible in the past.
Right AngleMirror
There are two different types of image sensors that can be found in most equipment: CMOS and CCD. These two are slightly different but in essence perform the same task within a camera system.
An image sensor is a tiny piece of optical technology within a digital camera system. They receive photons or incident light that’s focused through the lens of a camera or other piece of optical equipment. In other words, the image sensor is the part of your camera that takes in light.
Mirror flatbathroom
This crucial part of the digital camera known as the image sensor makes it possible for digital cameras to create high resolution, clear, and colorful images with just the click of a button. We’ll talk about how image sensors work within a camera and why they’re beneficial to the advancement of camera technology.
The 10Q00UF.25 ultrafast flat mirror is a 1.0 inch (25.4 mm) mirror. Low GDD dielectric coated ultrafast mirrors can be used with ultrafast lasers like Spitfire, Mai Tai, etc. to route and focus the laser beams. This mirror is designed to work between 700-930 nm for S-polarized and 730-870 nm for P-polarized light. The uncoated surface of this mirror is commercially polished to allow leaked light to be used for various pulse measurement purposes.
Once it hits this next stage, your camera’s processor will read the voltage or digital signals as color. From there, all the data your image sensor initially gathered is converted into a high-resolution image. In other words, the image sensor collects the information necessary to create the pictures you love.
Referenceflat mirror
Yes, opt-in. By checking this box, you agree to receive our newsletters, announcements, surveys and marketing offers in accordance with our privacy policy
From beloved smartphones to the professional-grade cameras you’d find in a photographer’s studio, digital cameras allow us to capture the beauty of the world around us. Being able to aim a lens, push a button, and get the perfect shot may seem like magic. Numerous mechanical and optical parts of a camera come together to bring us these crystal-clear depictions of our most cherished moments.
Contact us at Gamma Scientific if you work with image sensors or optic technologies and are looking for high-quality image sensor calibration.
Wallmirror flat
Choose products to compare anywhere you see 'Add to Compare' or 'Compare' options displayed. Compare All Close
In short, digital cameras need an excellent image sensor to work properly and provide us with impeccable images. That said, image sensors must be tested, characterized, and calibrated for quality assurance.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500