How the Helium-Neon Laser Works? - he-ne laser
How manytypes ofprism are there
Total internal reflection alters only the mutual phase between s- and p-polarized light. Under well chosen angle of incidence, this phase is close to π / 4 {\displaystyle \pi /4} .
By shifting corrective lenses off axis, images seen through them can be displaced in the same way that a prism displaces images. Eye care professionals use prisms, as well as lenses off axis, to treat various orthoptics problems:
Types ofprism with examples
Spectral dispersion is the best known property of optical prisms, although not the most frequent purpose of using optical prisms in practice.
Opti-Coat ceramic coatings are backed by Optimum Polymer Technologies, Inc. Opti-Coat Pro Warranty is valid for Five (5) years, and Opti-Coat Pro Plus Warranty is valid for Seven (7) years.
Rectangular prism
Prisms made of isotropic materials like glass will also alter polarization of light, as partial reflection under oblique angles does not maintain the amplitude ratio (nor phase) of the s- and p-polarized components of the light, leading to general elliptical polarization. This is generally an unwanted effect of dispersive prisms. In some cases this can be avoided by choosing prism geometry which light enters and exits under perpendicular angle, by compensation through non-planar light trajectory, or by use of p-polarized light.

Opti-Coat enhances the mirror effect, glossiness, color depth and clarity of the paint. With proper maintenance, the finish will shine for many years to come.
Opti-Coat increases the anti-water spotting, it repels dirt, brake dust, and tar to stick to the surface, and make it comes off with ease. Keeping the vehicle cleaner for longer, and wash less frequent.
Prism shape examples
Various thin-film optical layers can be deposited on the hypotenuse of one right-angled prism, and cemented to another prism to form a beam-splitter cube. Overall optical performance of such a cube is determined by the thin layer.
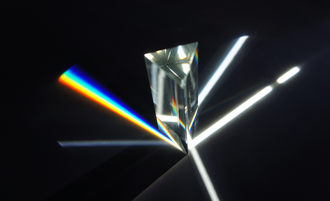
Dispersive prisms are used to break up light into its constituent spectral colors because the refractive index depends on wavelength; the white light entering the prism is a mixture of different wavelengths, each of which gets bent slightly differently. Blue light is slowed more than red light and will therefore be bent more than red light.
A dispersive prism can be used to break white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) to form a spectrum as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflect light, or to split light into components with different polarizations.
Prism spectacles with a single prism perform a relative displacement of the two eyes, thereby correcting eso-, exo, hyper- or hypotropia.
Types of prismsand their Formulas
Reflective prisms are used to reflect light, in order to flip, invert, rotate, deviate or displace the light beam. They are typically used to erect the image in binoculars or single-lens reflex cameras – without the prisms the image would be upside down for the user.
The long-lasting durability of Opti-Coat ceramic coating makes it highly cost effective. As opposed to applying thin coats of wax or sealant several times a year.
Types of prismsand pyramids
These are typically made of a birefringent crystalline material like calcite, but other materials like quartz and α-BBO may be necessary for UV applications, and others (MgF2, YVO4 and TiO2) will extend transmission farther into the infrared spectral range.

Reflective prisms use total internal reflection to achieve near-perfect reflection of light that strikes the facets at a sufficiently oblique angle. Prisms are usually made of optical glass which, combined with anti-reflective coating of input and output facets, leads to significantly lower light loss than metallic mirrors.
Prism formula
In contrast, spectacles with prisms of equal power for both eyes, called yoked prisms (also: conjugate prisms, ambient lenses or performance glasses) shift the visual field of both eyes to the same extent.[5]
Another class is formed by polarizing prisms which use birefringence to split a beam of light into components of varying polarization. In the visible and UV regions, they have very low losses and their extinction ratio typically exceeds 10 5 : 1 {\displaystyle 10^{5}:1} , which is superior to other types of polarizers. They may or may not employ total internal reflection;
Types ofprism in optics
Depolarization would not be observed for an ideal monochromatic plane wave, as actually both devices turn reduced temporal coherence or spatial coherence, respectively, of the beam into decoherence of its polarization components.
Resisting to chemical etching, harder than factory clear coatings to reduce swirl marks and scratches. It provides resists the damaging effects of bugs, bird droppings, tree sap, oxidization and UV rays fading.
In comparison with a usual glass substrate, the glass cube provides protection of the thin-film layer from both sides and better mechanical stability. The cube can also eliminate etalon effects, back-side reflection and slight beam deflection.
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite.
Opti-Coat is a permanent coating that will not wash away, or break down over time. Opti-Coat is more than 100 times thicker than the typical wax coating. It protects the surface for years, not months.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500