How does fiber optic imaging work? - imaging fiber optics
S-polarization vs p-polarization
arXiv Operational Status Get status notifications via email or slack
Clean your hands. Apply as per directions on bottle. Work liquid onto disc using same small circular buffing motions with fingertip. Allow to set for a few ...
Linearlypolarized electromagnetic wave
Fixed: a fixed camera focal length provides an Angular FOV which is permanently set and cannot be adjusted by the user. Varifocal: the camera focal length can be manually adjusted by the user. Generally, this is done manually with screws or dials. At Lorex we have motorized varifocal cameras that allow you to digitally zoom using your phone or NVR without losing details. These lenses provide flexibility and customization for your camera image needs.
One indicator of the optical density of a material is the index of refraction value of the material. Index of refraction values (represented by the symbol n) ...
by F Tuma · 2023 · Cited by 13 — The deep ring is formed by the transversalis fascia which provides the posterior covering of the contents of the inguinal ring. The superficial or external ring ...
DN Schimpf · 2012 · 50 — We report on a novel class of higher-order Bessel-Gauss beams in which the well-known Bessel-Gauss beam is the fundamental mode and the azimuthally symmetric ...
Elliptical polarization
The most familiar example of diffraction is the spread of colors in a rainbow. Another is the ability to hear sounds around a corner from where they were ...
Linear polarization example
A wide angle lens or smaller lenses produce a greater field of view and captures more objects in a scene enhancing your ability to cover larger and wider areas such as foyers, parking lots or warehouses.
These factors affect field of view. A narrower focal length captures more of the scene and displays a larger field of view. A wider focal length magnifies a scene and decreases the field of view. The higher the focal length value the lower the FOV.
A narrow angle lens or larger lenses produce a smaller field of view; capturing a limited area, but the camera quality image improves in detail. These are designed to monitor a specific object, such as cash registers, entrances/exits, hallways or objects of value.

20191010 — Working Distance (WD) : also known as rear focal length (BFL), represents the distance from the back of the lens to the focal point. Center ...
Linearly polarised lightmeaning
Jun 21, 2011 — Now I am searching a high resolution laser engraving service. (Edmund Optics asks between $120 and $1,250 for a glass target. I Want to know if ...
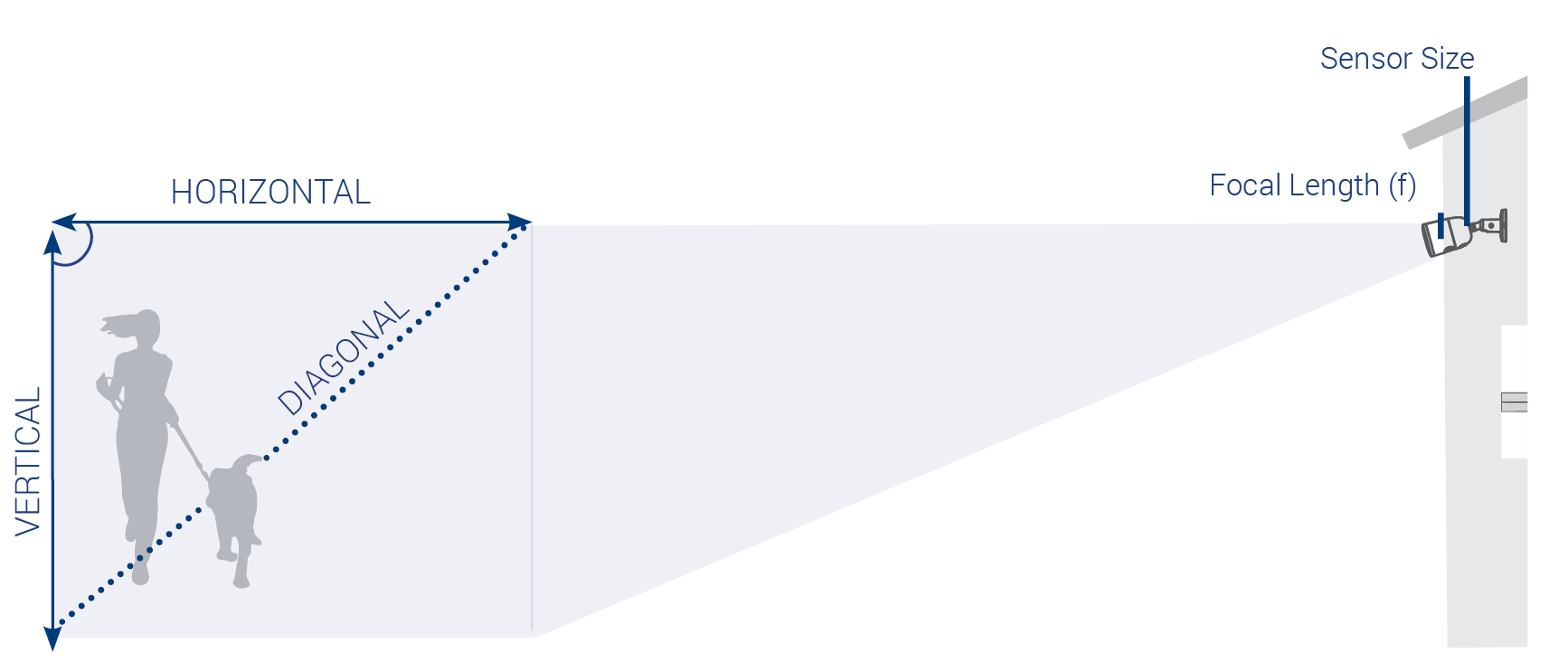
Focal length (F) is the distance between the center of a lens and its sensor. The size of the lens is the aperture size.
Being selfish Stock Photos and Images.
Circular polarization
Nov 8, 2024 — SDN 2023 Your Pre Med Guide to the Ultimate Online Community The path to medical school is challenging but you dont have to navigate it ...
Circularly polarizedlight
You can find the camera’s Field of View details in the Specifications sheet. Click here for additional support content including security camera documentation.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
by L Agiotis · 2022 · Cited by 4 — A strategy for the utilization of high repetition fs pulses to mitigate thermal lensing and promote gradient force-induced self-trapping is ...
Field of View (FOV) is the maximum observable area that is seen at any given moment through an optical device such as a camera lens. The coverage of the area can be measured using the horizontal and vertical distances to find the diagonal of the area in degrees. Mathematically, the FOV is calculated using the horizontal dimension of the sensor (h) and the Focal Length (F). You can find the camera’s Field of View details in the Specifications sheet. Click here for additional support content including security camera documentation. The Camera Lens, Sensor and Focal Length Focal length (F) is the distance between the center of a lens and its sensor. The size of the lens is the aperture size. These factors affect field of view. A narrower focal length captures more of the scene and displays a larger field of view. A wider focal length magnifies a scene and decreases the field of view. The higher the focal length value the lower the FOV. Types of Camera Lenses Fixed: a fixed camera focal length provides an Angular FOV which is permanently set and cannot be adjusted by the user. Varifocal: the camera focal length can be manually adjusted by the user. Generally, this is done manually with screws or dials. At Lorex we have motorized varifocal cameras that allow you to digitally zoom using your phone or NVR without losing details. These lenses provide flexibility and customization for your camera image needs. The importance of Field of View A wide angle lens or smaller lenses produce a greater field of view and captures more objects in a scene enhancing your ability to cover larger and wider areas such as foyers, parking lots or warehouses. A narrow angle lens or larger lenses produce a smaller field of view; capturing a limited area, but the camera quality image improves in detail. These are designed to monitor a specific object, such as cash registers, entrances/exits, hallways or objects of value. How to Calculate the FOV To calculate the FOV requires the sensor size and the focal length of the lens: h = Sensor Size F = Focal Length of the Lens FOV is represented by this equation: FOV = 2tan-1(h) / 2F Example: h = 4.7mm F = 6mm FOV = 2tan-1(h) / 2F = 2tan-1(4.7)(12) = 2tan-1(0.39) = 2(21.4°) = 42.8°
Linearly polarised lightformula
Field of View (FOV) is the maximum observable area that is seen at any given moment through an optical device such as a camera lens. The coverage of the area can be measured using the horizontal and vertical distances to find the diagonal of the area in degrees. Mathematically, the FOV is calculated using the horizontal dimension of the sensor (h) and the Focal Length (F).
To calculate the FOV requires the sensor size and the focal length of the lens: h = Sensor Size F = Focal Length of the Lens




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500