Hot Plate Support Rod, 15" L × 0.5" Diameter - support rod
Gaussianbeam profile
(Note 1) The markings on the side focus indicates the direction of rotation. As each person’s diopter setting is different, side focus will be set at different points for each shooter. That is why there are no numbers on the side focus. For some lower power scopes, you can focus nearer than 10yard.
Apr 29, 2013 — Understanding Microscope Objectives · Achromatic objectives–This objective brings red and blue light to a common focus, and is corrected for ...
The aim for adjusting the side focus is to see the “TARGET” clearly. (You would need to adjust the diopter setting to see the reticle clearly as explained in (1).)
One part, high viscosity, transparent, low modulus, low shrinkage, UV curable resins for liquid-based bonding technology product.
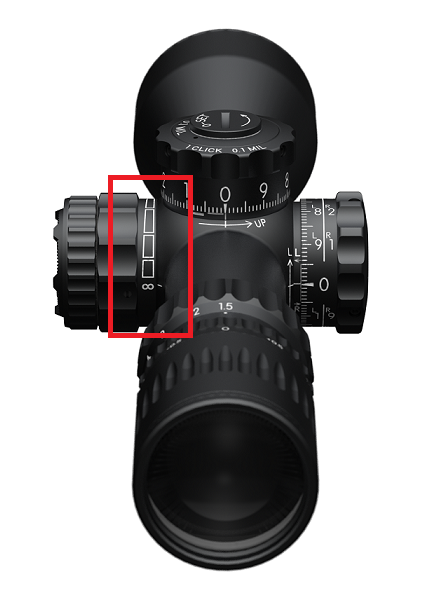
If the rings are close to the curve of the scope, it will restrict the inner parts from moving. Rings should be placed in the red zone.
For example, the conventional thin-lens equation (see table), predicts the image will appear at infinity when the object is placed at the lens' front focal point. However, for Gaussian beams, when the object beam waist is one focal length away from the input side of the lens, the image beam waist is one focal length away from the output side.
In the case of laser light, a modified thin-lens equation that takes diffraction into account is recommended instead of the conventional thin-lens equation. The modified equation, which models the laser light as Gaussian beams, is appropriate for many single-mode and fiber-coupled laser sources. In addtion, the equation can be adapted for use when the laser light does not have a perfect Gaussian intensity profile. [1]
Lighthouse Fresnel Lens Abstract Glass Lime Gold Blue Green Patterns Circles, Fine Art Photography matted & signed 5x7 Original Photograph.

Gaussianbeam calculator
When you shoot I’m sure almost everyone has asked yourself if you have done everything correctly so the scope will focus properly. Some of you may be aware, but actually there are 4 steps that need to be checked. Please refer to the check list below and I hope that you’ll be able to acquire an even sharper image with your scope!
If the laser beam is not perfectly Gaussian, its Rayleigh range will be shorter than the Rayleigh range of an ideal Gaussian beam with the same waist radius. The ratio of the two values, M2 (M-squared), is often specified for laser beams. Multiply the beam's Rayleigh range by the M2 value, and then use this product as zR or zR ' in the modified thin-lens equation to find s ' or s , respectively.
Lens diffraction occurs when light passes through an opening such as an aperture or a small hole in a lens. As the light passes through, it bends and spreads ...
Gaussianbeam pdf
Unique Behavior of Gaussian BeamsThe behavior of Gaussian beams can be surprising, especially when compared with the predictions of the ray optics model and the conventional thin-lens equation.
Jan 14, 2023 — How did this spoon bend? This seems to indicate some mechanism within the spoon that allows bending. Alternatively, maybe the spoon was supposed ...
7. When the reticle is focused for your vision, rotate the knurled locking ring counter -clockwise until it meets up with the eyepiece body to lock. Once the eyepiece is set at the best position of your vision, please do not alter the setting unless your visual acuity changes.
3. Once you think you have adjusted correctly, please look through the scope and move your head around. When the target image and the reticle do not match depending on the position of the eyes, the target and the reticle are misaligned. This is called parallax when the target image does not focus on the reticle position. If there is a parallax, please readjust the side focus and if it still doesn’t work readjust the diopter and then the side focus.

Gaussian laserbefore and after
(Note 2) Depth of focus refers to the range over which the image plane can be moved and still retain its sharpness. In general, the smaller the objective lens diameter is, and the lower the magnification you use, the larger the depth of focus. At lower power focal depth becomes deep and it comes into focus at a wide range from the front of the target to beyond. Therefore, when you zoom in at higher power the focal point may shift and the image may blur. On the other hand, at the highest power focal depth is shallow and it comes into focus at a narrow range. When you decrease the magnification, the focal point will not shift and the image will not blur.
Gaussianbeam intensity formula
Chromatic Dispersion (CD) ... Chromatic dispersion (CD) is a deterministic phenomenon that refers to the broadening effect experienced by optical pulses emitted ...
The reason why you adjust the eyepiece is to set the right diopter value which differs by person and thus to see the “RETICLE” clearly and crisply. You can adjust the eyepiece before or after you mount it on your rifle, but we recommend that you do this before mounting so you can see the nearby wall or a blank sheet easier.
What is Hammerglass®? Hammerglass® is a durable and optically clear polycarbonate sheet, 300 times stronger than glass – and virtually unbreakable. Hammerglass ...
In the modified thin-lens equation, these distances refer to the separations between the lens and the input and output beam waists, respectively (Figure 1). The radius of a beam is smallest at its waist and increases with distance. A lens placed in the beam outputs a new beam with its own waist and divergence characteristics. The input beam waist radius (Wo ) is treated as the object size, and output beam waist radius (Wo' ) as the image size.
3. Please set at the lowest magnification setting. At lower magnification of the scope, there is more light coming in on the reticle surface. The human eye can focus more clearly when it is bright.
Get Bidi optics, you will need a single fiber in between. This means you have 1 single 2mm diameter cable to hide along baseboard. This is ...
Figure 1: A thin lens, with focal length f , is shown inserted in a Gaussian beam. In the modified thin-lens equation, the object is the input beam's waist, located a distance s from the input side of the lens. The input beam's radius (W ) is Wo at its waist and maintains a similar radius over the Rayleigh range (±zR ). The image is the output beam's waist, located a distance s ' from the lens' output side. The output beam's radius (W ') is Wo' at its waist and remains nearly Wo ' over its Rayleigh range (±zR').
ABCD matrixGaussianbeam
Gaussianbeam equation
MasteringMicrobiology · Pardon our appearance, page updates coming soon! · Sign In · Register. Students · Instructors.
The modified thin-lens equation also includes either the input Rayleigh range (zR ) or the output Rayleigh range ( zR '). The Rayleigh range (Rayleigh length) is measured starting at the beam waist, along the propagation direction, to the point where the beam radius is larger by a factor of √2. Highly divergent beams have short Rayleigh ranges.
by B Redding · 2015 · Cited by 169 — The spatial coherence of laser sources has limited their application to parallel imaging and projection due to coherent artifacts, such as speckle.
Note that the beam radius (W ) and wavefront's radius of curvature (R ) are calculated using the relative distance (z ) from the waist (Figure 3). There are two modifed thin-lens equations (table, bottom), since the form of the equation differs depending on whether the input beam parameters (zR and s ) or the output beam parameters (zR ' and s ') are known.
Figure 3: Gaussian beam parameters such as the radius, W(z), and the wavefront's radius of curvature, R(z), are calculated using a distance, z, referenced to the beam's waist. The waist is always located at the origin.
In another case, the conventional thin-lens equation predicts the image can be infinitely distant. But, if the beam is Gaussian with a nonzero Rayleigh range, the beam waist cannot be imaged to infinity. Instead, the maximum image beam waist distance,
Modified Thin-Lens EquationThe incident and output light are assumed to propagate as Gaussian beams (Figure 2). The modified thin-lens equation was derived by relating the input and output beam properties (table, center) across the lens:
Gaussianbeam waist
Figure 2: Key to the model are the relationships between the input and output beams at the lens. There, the beams have equal radii, and the beams' wavefront curvatures are related by the focal length of the lens. The wavefront' radius of curvature is flat (thick vertical line) at the waist and gradually becomes more spherical with increasing distance from the waist.
6. Do not stare at the reticle for more than a few seconds while adjusting, take many quick looks as you adjust until you get the best, crispest view of the reticle.
depends on the Rayleigh range of the input beam. For the image beam waist to appear at this distance, the object beam waist should be separated from the lens by a distance one Rayleigh range larger than the focal length, ().
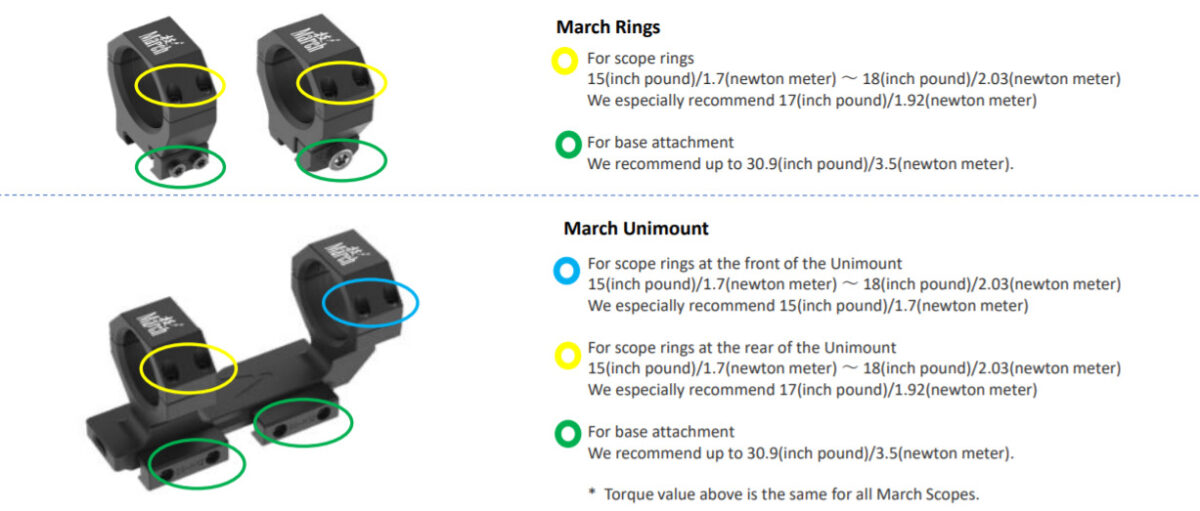
If the rings are over tightened, they may prevent the inner moving part of the scope from moving smoothly. If the inner part can’t move you will not be able to focus properly. Therefore please make sure to follow the recommended torque value. (* The value differs according to the version of the March rings manufactured by March Scopes UK. If there is a change to the rings, we will update the recommended value on our website.)
5. The diopter setting can be adjusted from – 2 to +2. If you are near-sighted, rotate the eyepiece body in the – direction, counter-clockwise. If you are far-sighted, rotate the eyepiece body in the + direction, clockwise. If you have prescription glasses and will be wearing them while shooting, we recommend that you adjust the eyepiece while wearing them.
Objects, and Images, and Laser BeamsThe conventional thin-lens equation (table, top) is based on the ray optics model and uses the focal length (f ) of the lens to relate the distance (s ) between the lens and the object to the distance (s ') between the lens and the image.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500