Handling Diffraction Gratings - refraction grating
f-number calculator
2022912 — Images in a plane mirror are the same size as the object, are located behind the mirror, and are oriented in the same direction as the object (ie, upright).
If you want to join a team proud to be solving the most challenging of scientific problems, please visit the Teledyne Princeton Instruments Careers Portal to ...
No matter which mode you choose, adjusting the aperture will impact the depth of field. Depth of field refers to the range within a scene that appears in focus, and photographers often use medium to small apertures to achieve greater sharpness throughout the image. However, depth of field also depends on factors like where you focus within the scene.
The word laser is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Lasers are used as research aides in many departments at Princeton ...
The optic flow is the fastest when the object is to your side by 90 degrees, or directly above or below you. If the object is brought closer to the forward or ...
F-number of lens

F-stop vs aperture
On the other hand, small apertures can make diffraction more noticeable, which can also soften images. These apertures are also more challenging when hand-holding the camera, as the smaller the aperture, the longer the shutter speed required—eventually making it difficult to hold the camera steady enough for sharp images. In such cases, a tripod or a good image stabilization system can be helpful.
Immersion Oil: Clear, finely detailed images are achieved by contrasting the specimen with their medium. Changing the refractive index of the specimens from their medium attains this contrast. The refractive index is a measure of the relative velocity at which light passes through a material. When light rays pass through the two materials (specimen and medium) that have different refractive indices, the rays change direction from a straight path by bending (refracting) at the boundary between the specimen and the medium. Thus, this increases the image’s contrast between the specimen and the medium.
So, the smaller the aperture, the longer the shutter speed you'll need in a given situation. You can observe this by setting your camera to Aperture Priority mode and adjusting the aperture; the shutter speed will change with each adjustment.
Please take a few minutes to fill out a brief survey about your experience using the Virtual Edge: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1yGbkF0KM92WBSk-IgS-EkjxkTKTQwhzuXmDsVpwRDoU/viewform
What is f numbernikon
Chris George has worked on Digital Camera World since its launch in 2017. He has been writing about photography, mobile phones, video making and technology for over 30 years – and has edited numerous magazines including PhotoPlus, N-Photo, Digital Camera, Video Camera, and Professional Photography.
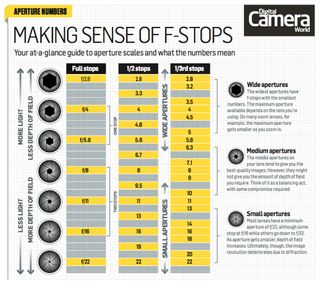
The f-stop number actually refers to the size of the aperture opening, calculated by dividing the lens's focal length by the f-number. For example, with a 200mm lens, an f/4 aperture would have a diameter of 50mm (one-quarter of 200mm).
The Virtual Edge by http://www.uwyo.edu/virtual_edge/ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License
Ever hear these terms? Stopping down the lens or aperture simply means to make the aperture smaller, such as from f/8 to f/11. Opening up, meanwhile, means doing the opposite.
What is f numberin photography
One way to change the refractive index is by staining the specimen. Another is to use immersion oil. While we want light to refract differently between the specimen and the medium, we do not want to lose any light rays, as this would decrease the resolution of the image. By placing immersion oil between the glass slide and the oil immersion lens (100X), the light rays at the highest magnification can be retained. Immersion oil has the same refractive index as glass so the oil becomes part of the optics of the microscope. Without the oil the light rays are refracted as they enter the air between the slide and the lens and the objective lens would have to be increased in diameter in order to capture them. Using oil has the same effect as increasing the objective diameter therefore improving the resolving power of the lens.
Also known as aperture size, the f-stop controls the amount of light that passes through the lens at a given shutter speed. All else being equal, a smaller aperture (like f/16) allows in less light than a larger one (like f/4), meaning it takes longer for the same amount of light to reach the sensor. It's similar to how an hourglass works: the size of the opening between the chambers determines how long it takes for the sand to flow from top to bottom.
Both very small and very wide apertures have their challenges, so it's important to evaluate each scene to determine the most appropriate setting. Wide apertures are excellent for isolating subjects from their backgrounds, but they can lead to softer images due to an effect known as spherical aberration.
On-orbit radiometric calibration of the optical sensors on-board SuperView-1 satellites is the foundation for further quantitative applications. A field ...

F numberin alphabet
1/1.8 4K 4.41mm M12 Lens for OS08A10,OS08A20 and more image sensors with large optical format- Arducam · Overview · Lens Specification · Other 4K Lens options ...
So, how does the f-stop, or aperture, impact your image? Primarily, it influences exposure, though the effect depends on the exposure mode you’re using. In Manual mode, if you change the aperture without adjusting the shutter speed, your image will either become darker or lighter depending on your adjustment. In Aperture Priority mode, however, your camera automatically adjusts the shutter speed as you change the aperture, maintaining a consistent exposure.
Unlike traditional red dot sights, prismatic optics feature a glass-etched reticle that remains visible even without illumination. This ensures you always have ...
The meaning of ACHROMATIC LENS is a lens made by combining lenses of different glasses having different focal powers so that the light emerging from the ...
A USB type A male to USB mini-B male cable is commonly used as a digital video camera cable, cell phone cable, digital picture frame cable and many others. The ...
His first serious camera was the iconic Olympus OM10, with which he won the title of Young Photographer of the Year - long before the advent of autofocus and memory cards. Today he uses a Nikon D800, a Fujifilm X-T1, a Sony A7, and his iPhone 15 Pro Max.
Resolving power or resolution: the ability to distinguish objects that are close together. The better the resolving power of the microscope, the closer together two objects can be and still be seen as separate.
Digital Camera World is part of Future US Inc, an international media group and leading digital publisher. Visit our corporate site.
f-number formula
Even if you've never manually adjusted the f-stop on your lens or camera, you've likely come across this setting before. While it's possible to let the camera handle it automatically, mastering the f-stop is crucial if you want to fully control your photography.
Anti-reflection coatings are optical thin-film coatings for reducing parasitic reflections from surfaces.
What is F numberin welding
Total magnification: In a compound microscope the total magnification is the product of the objective and ocular lenses (see figure below). The magnification of the ocular lenses on your scope is 10X.
Extremely wide apertures can also be difficult to manage in bright conditions, as your camera may not be able to use a fast enough shutter speed to prevent overexposure unless you use an ND filter.
Parfocal: the objective lenses are mounted on the microscope so that they can be interchanged without having to appreciably vary the focus.
One thing that often confuses beginners is that small physical apertures have high f-stop numbers like f/16 and f/22, while large (or "wide") apertures have low f-stop numbers like f/1.4 and f/2. The reason is that f/16 represents one-sixteenth, not sixteen, and f/4 represents a quarter, not four.
He has written about technology for countless publications and websites including The Sunday Times Magazine, The Daily Telegraph, Dorling Kindersley, What Cellphone, T3 and Techradar.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500