GVM F60 Fresnel Attachment for LED Light Spotlight ... - fresnel lens spotlight
Convert your millimeters to micrometers swiftly and accurately at Examples.com. Enter your measurement for instant results.
Parabolic reflectorTelescope
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal. This law when used along with a parabola, helps the beam focus. The shape of the
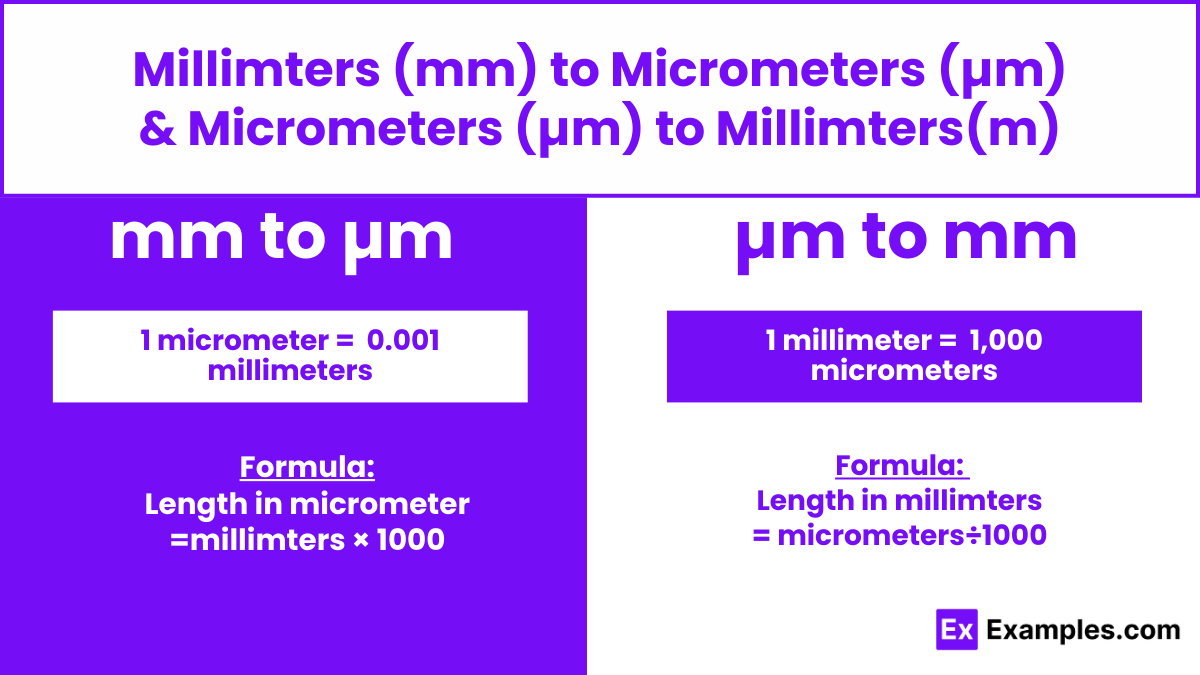
Calculating micrometers usually involves converting from another unit of measurement to micrometers. For example, if you have measurements in millimeters and you want to convert them to micrometers, you multiply by 1,000.
If a Parabolic Reflector antenna is used for transmitting a signal, the signal from the feed, comes out of a dipole or a horn antenna, to focus the wave on to the parabola. It means that, the waves come out of the focal point and strike the Paraboloidal reflector. This wave now gets reflected as collimated wave front, as discussed previously, to get transmitted.
Micrometers are used to measure very small distances such as the thickness of a cell or a thin film layer in scientific and industrial contexts.
Parabolicmirror examples
The standard definition of a parabola is - Locus of a point, which moves in such a way that its distance from the fixed point (called focus) plus its distance from a straight line (called directrix) is constant.
Tutorials Point is a leading Ed Tech company striving to provide the best learning material on technical and non-technical subjects.
Usually a wave guide horn antenna is used as a feed radiator for the paraboloid reflector antenna. Along with this technique, we have another type of feed given to the paraboloid reflector antenna, called as Cassegrain feed.
Tutorials Point is a leading Ed Tech company striving to provide the best learning material on technical and non-technical subjects.
Parabolic reflectordiagram
Hence, of all the types of reflector antennas, the simple parabolic reflectors and the cassegrain feed parabolic reflectors are the most commonly used ones.
The same antenna is used as a receiver. When the electromagnetic wave hits the shape of the parabola, the wave gets reflected onto the feed point. The dipole or the horn antenna, which acts as the receiver antenna at its feed, receives this signal, to convert it into electric signal and forwards it to the receiver circuitry.
Some of the power that gets reflected from the parabolic reflector is obstructed. This becomes a problem with small dimension paraboloid.
Parabolicmirror concave or convex

: To convert micrometers (µm) to millimeters (mm), you divide the number of micrometers by 1,000. This is because one millimeter equals 1,000 micrometers.
Parabolicmirror uses
1 µm (one micrometer) is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one millionth of a meter (0.000001 meter). It’s a standard unit used primarily in science and engineering to measure very small distances, such as the dimensions of bacteria, or the wavelength of infrared radiation.
When the antenna acts as a transmitting antenna, the energy from the feed radiates through a horn antenna onto the hyperboloid concave reflector, which again reflects back on to the parabolic reflector. The signal gets reflected into the space from there. Hence, wastage of power is controlled and the directivity gets improved.
The gain of the paraboloid is a function of aperture ratio (D/λ). The Effective Radiated Power (ERP) of an antenna is the multiplication of the input power fed to the antenna and its power gain.
Parabolic dishcollector
This is another type of feed used. A pair of certain configurations are there, where the feed beamwidth is progressively increased while antenna dimensions are held fixed. Such a type of feed is known as Gregorian feed. Here, the convex shaped hyperboloid of casssegrain is replaced with a concave shaped paraboloid reflector, which is of course, smaller in size
Parabolic Reflectors are Microwave antennas. For better understanding of these antennas, the concept of parabolic reflector has to be discussed.
All the waves originating from focus, reflects back to the parabolic axis. Hence, all the waves reaching the aperture are in phase.
The reflected wave forms a colllimated wave front, out of the parabolic shape. The ratio of focal length to aperture size (ie., f/D) known as “f over D ratio” is an important parameter of parabolic reflector. Its value varies from 0.25 to 0.50.
The frequency range used for the application of Parabolic reflector antennas is above 1MHz. These antennas are widely used for radio and wireless applications.
To convert a measurement from micrometers (µm) to millimeters (mm), you divide the number of micrometers by 1,000 because one millimeter is equivalent to 1,000 micrometers.
The figure clearly depicts the working pattern of all the types of reflectors. There are other types of paraboloid Reflectors such as −
Parabolic reflectorantenna PDF
The following figure shows the geometry of parabolic reflector. The point F is the focus (feed is given) and V is the vertex. The line joining F and V is the axis of symmetry. PQ are the reflected rays where L represents the line directrix on which the reflected points lie (to say that they are being collinear). Hence, as per the above definition, the distance between F and L lie constant with respect to the waves being focussed.
To convert a length from millimeters (mm) to micrometers (µm), you multiply the number of millimeters by 1,000 because one millimeter equals 1,000 micrometers.
Parabolic dish reflectorfor sale
When the same antenna is used for reception, the electromagnetic waves strike the reflector, gets reflected on to the concave hyperboloid and from there, it reaches to the feed. A wave guide horn antenna presents there to receive this signal and sends to the receiver circuitry for amplification.
parabola when used for the purpose of reflection of waves, exhibits some properties of the parabola, which are helpful for building an antenna, using the waves reflected.
Casse grain is another type of feed given to the reflector antenna. In this type, the feed is located at the vertex of the paraboloid, unlike in the parabolic reflector. A convex shaped reflector, which acts as a hyperboloid is placed opposite to the feed of the antenna. It is also known as secondary hyperboloid reflector or sub-reflector. It is placed such that its one of the foci coincides with the focus of the paraboloid. Thus, the wave gets reflected twice.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500