Generalized Risley Prism for Beam-Steering Transmit ... - risley prism
10 uses ofmagnifying glass
The ASTM subcommittee on Raman spectroscopy has adopted eight materials as Raman shift standards (ASTM E 1840). Raman spectra of eight common chemicals were obtained by at least six different labs, with both FT and dispersive Raman spectrometers. For each of the standards, peak frequencies with standard deviations of less than 1 cm-1 were tabulated and are available for viewing. These peak frequencies have been established as an ASTM standard for calibrating the Raman shift axis of Raman spectrometers.

How does magnifying glass worksphysics
Raman intensity standards were developed using both white light and luminescent standards for correction of Raman instrument response functions, as described in the following publications:
How doesamagnifying glasswork diagram
ASTM has established a series of Raman shift frequency standards (ASTM E 1840) for use in the calibrating of Raman spectrometers. Raman shift standards are easier to use than wavelength standards (such as atomic emission lines) and do not depend on laser wavelength. Standard Raman shifts for eight materials are included in the standard. The procedure is below and the standard spectra are available here.
The National Institute for Standards and Technology has developed Standard Reference Materials using similar techniques, which are available for purchase. An example is SRM 2241 for 785 nm excitation: https://www-s.nist.gov/srmors/view_detail.cfm?srm=2241
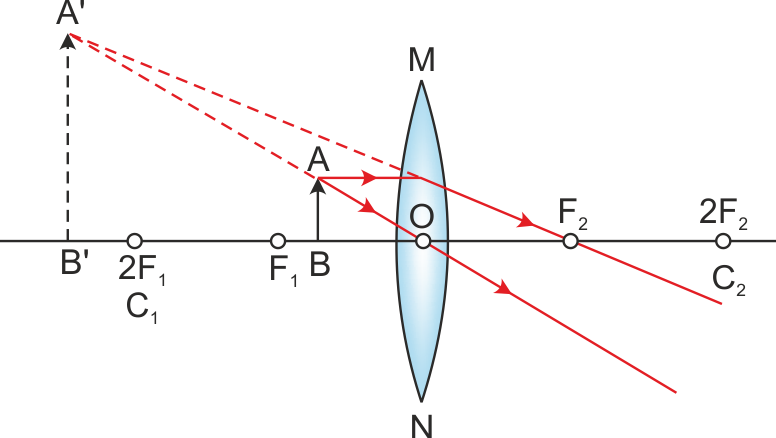
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image by a magnifying glass. State three characteristics of the image.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500