Focal Length: Formula & Uses in Optics - formula focal length
Pot plants benefit from diffuse glass. A wide range of flowering and green pot plants performs better under ReduFuse. For some types the increase in ...
Revolving nosepiecemicroscopefunction
Objectives of high numerical aperture are particularly sensitive to changes in coverglass thickness, including thickness of mounting medium. In Experiment 24 it was mentioned that spherical aberration due to coverglass/mountant thickness variation could be corrected by using the so-called “correction collar” of specially-constructed objectives in which a knurled ring surrounding these objectives is used to alter the position of key lens elements within the objective itself. Altering the lens position introduces spherical aberration that is of equal magnitude, but opposite sign, so as to cancel the aberration from the specimen slide. Objectives with correction collars are, however, very expensive, and here is where the adjustable drawtube comes in!
The CCD sensor in the Atik 414EX is pretty small with an 11mm diagonal, and on a refractor with a focal length of 509mm it produces a field of view of 1º by 0.75º. Nonetheless, what the chip may lack in size, it certainly makes up for in terms of its sensitivity.
Testing the camera out, we were very pleased with its capability in collecting photons without too much thermal noise. Also, because the field of view is quite small, only the central portion of the light cone is intercepted. This is the area with fewest optical distortions, so correction is often not required.
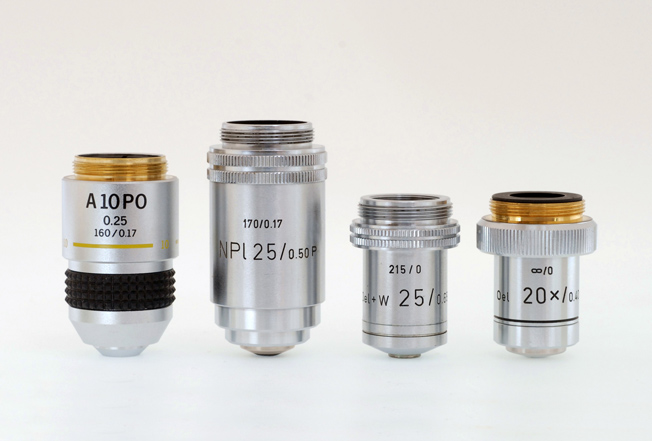
The reason for the move to “infinity corrected” systems is because of the trend today to use multiple modules stacked for polarized light and various contrast enhancement systems, and also for epi-fluorescence (see Experiment 23). Figure 28-1 illustrates four objectives, each requiring a different mechanical tube length; from left to right, 160 mm, 170 mm, 215 mm, ∞. If these objectives are used at mechanical tube lengths other than that for which they were designed, the resulting images will be severely degraded.
We've reviewed a lot of CCD cameras at BBC Sky at Night Magazine over the years, and below is our pick of some of the best CCDs available to buy, ranging from the best value up to more high-end models.
Body tubedefinition
21 definitions of CW. Definition of CW in Slang/Internet Slang. What does CW stand for?
Our images showed little noise over the long exposures, which was great to see. There were some small, squiggly artefacts, but these were easily removed by stacking multiple images.
The KAF-8300 sensor responds very well to cooling. We used its set point cooling feature to reach –20°C and found there were no bad columns but typical of this sensor, some hot pixels.
Figure 28-3 shows the adjustable graduated drawtube removed from the main body tube of a Zeiss microscope; its range of tube length is 154 mm to 200 mm; it just slides into the main body tube.
Almost all student-grade microscopes today come equipped with a fixed mechanical tube length. In the past, the most common tube lengths were 160 mm (most manufacturers) and 170 mm (Leitz). Metallurgical-type microscopes required a longer tube length so as to accommodate a light source reflecting system above the objective; mechanical tube lengths for these systems included, for example, 185 mm and 215 mm. More recent microscopes, including metallographs (those with built-in epi-brightfield illumination made for looking at opaque specimens, such as polished metal and ore samples) have tended to be corrected for an infinitely long tube length, indicated with an infinity symbol, ∞.
PoE (Power over Ethernet) ; MX00119023 · U-POE-at 802.3AT PoE Injector, 30W · $24.99 ; MX00120352 · UniFi Lite 8 PoE Gigabit Ethernet Switch w/ 4 PoE+ 802.3at Ports.
With pixels just 3.69x3.69µm in size, the Trius-H814 is ideal for use with short focal length telescopes. When we used it with our 500mm focal length refractor it produced a high sampling rate of 1.6 arcseconds per pixel.
Function of objective lens inmicroscope
They come in a range of sensor sizes and, like DSLRs, capture colour in a single shot, which is ideal for the UK’s fickle weather.
Designed for relatively short exposures, the Infinity has no active cooling, yet we found its passive cooling was acceptable for relatively noise-free results.
Spinell, B. M. and Loveland, R. P. (1960). Optics of the Object Space in Microscopy. Journal of the Royal Microscopical Society 79 Pt 1, 59-80.

In all, we loved the 414EX. It worked straight out of the box with minimal setup and we were imaging before we knew it. We'd definitely recommend this to deep-sky imagers making the leap from DSLR to cooled CCD.
The Trius Pro 694 bundle has something for everyone, while generally a deep-sky camera, it can be used for imaging the Sun and Moon as well. The camera is Windows and Mac compatible and the included Starlight Live software allows you to stack images live as you capture them.
Fine adjustment knobmicroscopefunction
The camera was very sensitive and we had a very pleasant imaging session with it performing perfectly throughout. We were impressed with the performance and would recommend to both astrophotography beginners and those upgrading from a DSLR to their first CCD.
Jun 10, 2023 — When you compare it to High Reflective White, you can see that Pure white is much softer. High Reflective White has more of a blue undertone, ...
What the Atik Infinity really has going for it is its image quality and dedicated control software, which makes group or broadcast outreach sessions a breeze.
The small size also means your 1.25-inch filters will be perfectly suitable for this CCD, making the move to full astro-CCD camera a little easier on the purse strings.
Body tube microscopefunction
In video mode the camera exposes in a continuous loop, sending two or three full frames to its host computer every second.The Infinity software checks image quality and, if good enough, adds it to a stacked result to produce a cleaner image.
This much is taken for granted: that the user of any microscope will make sure that the objectives being used correspond to the microscope’s mechanical tube length. Now, if you will review the Discussion in Experiment 24 on Coverglass Thickness, you will recall that use of incorrect coverglass thickness will introduce spherical aberration into the final image; the image will be “soft.” Notice that the required coverglass thickness for any particular objective is always engraved on it. In Figure 28-1, the two objectives on the left require a coverglass that is 0.17 mm thick—this is indicated after the slash following the mechanical tube length; the two objectives on the right require no coverglass, indicated by the “0”, because they are intended for viewing polished metal and ore specimens by reflected light; a coverglass would reflect the incident light right back up, causing nothing but glare.
First Light Optics - Suppliers of Astronomy telescopes, binoculars and accessories from Skywatcher, Celestron, Meade, William Optics, Atik, Imaging Source, ...
What a CCD camera is, what sort of astrophotography it's best suited to, and some of the best models currently available on the market.
The Celestron Skyris 445C is a colour CCD camera featuring USB 3.0 connectivity and a 1280x960 pixel Sony ICX445AQA chip at its core. This great little CCD is aimed at hi-res imaging of the brighter planets of the Solar System, and can also be used to capture images of the Sun and Moon.
Getting going is simple because the guide camera and filter wheel are already assembled in the case. All you need to do is open the filter wheel, install the filters and then screw the camera on the back.
The QHY9S is in many ways firmly in the function over form category. Having said that, it's certainly more robust in design than unattractive, typified by its large and clunky looking cooling fan. The advantage of this is a relatively low price, but of course the CCD still need to perform to appeal to astro imagers,
If you've already got your camera sorted but need a decent scope to go with it, discover our pick of the best telescopes for astrophotography.
Fine adjustment knobmicroscopedefinition
In the past, Hooke College of Applied Sciences offered a microscopy workshop for middle school and high school science teachers. We thought that these basic microscope techniques would be of interest not only for science teachers, but also for homeschoolers and amateur microscopists. The activities were originally designed for a Boreal/Motic monocular microscope, but the Discussion and Task sections are transferable to most microscopes. You may complete these 36 activities in consecutive order as presented in the original classroom workshop, or skip around to those you find interesting or helpful. We hope you will find these online microscope activities valuable.
One-shot colour CCD cameras are designed for deep-sky imaging. They sport a filter-free sensor with a Peltier cooling system to reduce 'noise' generated by the electronics.
CCDs are optimally suited for long-exposure deep-sky imaging. They're capable of imaging the Moon and Sun and have basic planetary capability, but are also good for picking out faint moons around other planets.
The most important use of the adjustable drawtube is to correct for spherical aberration in the image that is due to incorrect coverglass thickness. You will know how to choose correct coverglass thickness to begin with, after performing Experiment 24, Coverglass Thickness. But if you are looking at a commercially prepared specimen, or any specimen prepared by someone else, you do not know if the correct thickness coverglass has been used. You will also recall from Experiment 24 that lower magnification objectives with their lower numerical apertures are not particularly affected by incorrect coverglass thickness; it is the high numerical aperture objectives that are particularly affected.
Using tube length adjustment to change magnification is self-explanatory. When viewing your image on a screen or within framing lines, if you would like the image a bit bigger, but the next objective up in magnification is too much, you may increase the tube length to increase the image size.
We would sincerely recommend this camera for those astro imagers who are wanting to produce detailed and crisp images of our celestial neighbours, not least nor its large colour chip and USE 3.0 connection.
For example, the Skyris 445C produced smooth images showing good detail over large regions of the Moon, with the 1280x960 chip running at 30 frames per second.
A CD supplied includes a user manual in PDF format, camera drivers, ASCOM drivers and two camera control programs, CCDCap and EZCap.All drivers loaded quickly and easily onto our computer.
The Atik 16200 is a heavy duty and capable camera for deep-sky imaging and it has excellent low-noise ability. Its almost industrial cooling capabilities allow it to take remarkable large format astrophotos.
It's by no means an exhaustive list, but hopefully gives you an idea as to what you should be looking out for, and what you can expect to get for your money.
The Trius-H814 is impressive and its high-resolution sensor neatly fills the gap between the popular Sony ICX285 and Kodak/Truesense KAF-8300 sensors.
If you've ever taken a group of people to gaze up at the night sky through a telescope, or if you've ever wanted to share your telescope view with the rest of the world online, chances are you'll love the Atik Infinity.
High definition lenses also enable patients to enjoy up to 20 percent wider vision channel for both intermediate and near distances, this makes computer use ...
Obtain a microscope that has an adjustable graduated drawtube, install a high numerical aperture objective, and practice finding the optimum tube length for some very fine structure in any specimen. Change the tube length, and repeat the operation to get an idea of the reproducibility of your findings. These are advanced tasks that require some practice, but they will result in making you a critical observer.
KBr is hygroscopic, deliquescent, highly soluble in water, and soluble in some polar organic solvents like glycerol, ethylene glycol, liquid ammonia, and ...
Not all drawtubes are graduated; ungraduated drawtubes are used in the same way described for neutralizing image error due to incorrect coverglass thickness; they just cannot be used for micrometry. Ungraduated drawtubes still have a simple line engraved all around them at e.g., 160 mm.
The Trius-H814 comes in a custom-fitted case and is finished in the standard Starlight Xpress gloss black.It has a low-profile, cylindrical body with integral cooling fans, making it suitable for use on a wide range of telescopes.
Armmicroscopefunction
A more accurate method of determining the focal length of a positive lens is to measure the image distance corresponding to a suitable and known object distance ...
Coarse adjustmentmicroscopefunction
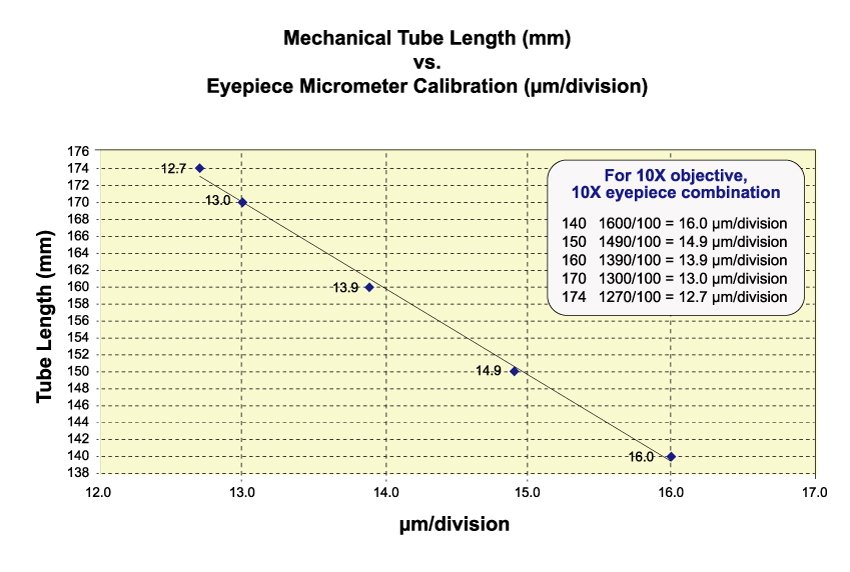
Figure 28-4 shows the resulting graph; note that there is approximately a 1 µm difference in calibration for each 10 mm change in tube length. What is commonly done is that a tube length is selected that results in some even number of µm/div to facilitate measurements of structures, or for particle size analysis.
Astrophotography cameras produce cleaner images if the sensor is chilled. The Atik 16200 aims to provide cooling capability up to 50°C below ambient temperature.
We set the cooling to maximum and kept our eye on the readout as the temperature fell, and within about 5 minutes the sensor had cooled from 10°C to –37°C. The camera then held that temperature steadily.
The Revolution Imager comes in a soft case including the camera, a 12V rechargeable battery plus charger, a 7-inch colour monitor with an adjustable stand and a number of accessories: a 1.25-inch nosepiece, a 0.5x focal reducer and a 1.25-inch infrared-cut filter.
This involves taking different sets of exposures using red (R), green (G) and blue (B) filters and then combining them in software to produce a final RGB colour image.
Mono CCD cameras take great greyscale images. If you want to take colour images with mono CCDs, things get a little more complicated.
So, say you are looking for Barr bodies in the leucocytes in a stained blood film, or any fine structure within any tissue section, or live microorganisms using a 40X/0.95 NA objective. Here is how you proceed: with one hand on the fine focus knob, and the other hand on the drawtube, concentrate your view on some tiny, tiny structural feature, and adjust the fine focus carefully for best critical focus. Now change the tube length slightly—it does not matter if you lengthen it or shorten it a little—and you will discover that you have to re-adjust the fine focus for sharp focus. Evaluate the tiny fine feature you were concentrating your view on, and ask yourself if the change in mechanical tube length results in a better, sharper image, or has the image become “softer.” If the resulting image was improved, continue to lengthen or shorten the tube length as you did before. Again refocus and evaluate. Continue the procedure as long as image quality improves. When the image starts to degrade, reverse direction of the drawtube. The object is to find that tube length that results in the very best quality image. When you have done so, you will have corrected the system for spherical aberration; it does not matter what the actual tube length reads, as long as the image quality is perfect. This use of the drawtube is particularly necessary for those microscopists who desire to resolve the fine lines and “puncta” of diatoms. As for the actual, final tube length reading, it is immaterial, but you will find that tube length must be shortened for too-thick coverglass, and lengthened for too-thin coverglass.
The choice of objective lens greatly influences the level of detail and clarity in observing cellular structures. Lower power objective lenses provide a broader ...
With the set-point cooling adjusted to –20°C and an ambient temperature of 16.6°C, the camera took three minutes 55 seconds to reach target temperature, and then we were ready to image.
by R Abbasi · 2021 · Cited by 13 — Ultra-luminous infrared galaxies (ULIRGs) have infrared luminosities L_{\mathrm{IR}} \geq 10^{12} L_{\odot}, making them the most luminous ...
In the fully-closed position, this drawtube gives a total tube length of 140 mm; when fully extended, the total tube length can be increased to 174 mm. There is a reference line at 160 mm that goes all the way around the drawtube to indicate that this is the correct starting position setting for the vast majority of observations made with objectives corrected for 160 mm tube length. (Note that you could mix a Leitz objective on the nosepiece, but you would have to remember to re-set the tube length to 170 mm when that objective is being used).
An adjustable drawtube allows the user to change the overall length of the body tube so as to correct spherical aberration due to use of too-thick or too-thin coverglasses. In the past, adjustable graduated drawtubes were offered as an option with every monocular microscope. Figure 28-2 is a composite photograph of a Bausch & Lomb Microscope fixed-length eyepiece tube (right) having been replaced with an optional adjustable graduated drawtube screwed into the main body tube.
As soon as we opened the case we were impressed by the attention given to the quality and design. The Starlight Xpress Trius Pro 694 is solid with a nice tough coat of paint and all the threads screw together nicely.
The Revolution Imager R2 is a complete camera and monitor kit. The great thing about it is that it enables you to observe the view through your telescope on screen and in real time. You can also see details in your selected target that would be impossible to see with an eyepiece alone.
There is an important use of the graduated drawtube in micrometry. The eyepiece micrometer is normally calibrated with a fixed tube length body. With an adjustable tube length, the calibration of each eyepiece micrometer division will continuously change with tube length because of the continuous magnification change. So, what you do is prepare a graph in which you plot mechanical tube length against eyepiece micrometer calibration. For example, the set-up in Figure 28-2 was used; the tube was fully closed to 140 mm, and the eyepiece micrometer was calibrated using a stage micrometer, and found to be 16.0 µm per division. Next, the drawtube was successively set to 150 mm, 160 mm, 170 mm, and 174 mm (the maximum extension), and the value of each eyepiece micrometer division was determined for each tube length setting.
It's an exceptionally comprehensive package that includes everything needed to get imaging straight out of the box. It is also a great introduction to astro imaging, not to mention one that provides wonderful enjoyment and entertainment.
The type of celestial target and the detail you can photograph in the night sky depend - among other variables - on which kind of camera you are going to use, and in this guide we'll be looking at some of the best CCD cameras currently available on the market.
With a weight of 553g, the camera has a purposeful feel and we found it simple to attach to a 2-inch filter wheel lent to us for the purpose of our review.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500