Fiber Dispersion and Optical Dispersion – An Overview - dispersion optical
Supplying custom cameras to instrument designers for most of our 40 year history, we will work with you every step of the way.
Pixel clockdiabetes
In microscopy, it is vital to have some form of contrast or stain that gives areas of the sample color and makes it possible to image. Advanced fluorescence microscopy techniques take advantage of this.
Cooled, low-noise CMOS cameras designed for integration. With unprecedented thermal control, Retiga E cameras are capable of exposures over an hour!
If the goal is simply to attach the camera to the microscope, a 1x adaptor contains no additional lenses and provides no additional magnification or demagnification. This is often the preferred method as it introduces no additional lenses into the system. Every extra lens reduces the number of photons reaching the camera by 3-4% so many researchers will try to avoid this.
The QImaging CCD family of scientific cameras are designed with solutions for electrophysiology, long stare, color imaging, documentation and live cell imaging.
Physics and biophysics imaging encompasses a wide range of techniques used to interrogate physical phenomena using high tech imaging systems.
CMOS made scientific. The Moment is a true global shutter CMOS camera with an ultra-compact form factor, powered through USB 3.2 Gen 2.
Good news! You have already signed up to our mailing list. If you would like to amend your preferences, please look out for one of our emails- don’t forget to check your junk folder just in case.
High content imaging is primarily concerned with the automated analysis of large cell populations where the goal is to process as many cells as possible in the fastest time with the highest resolution.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
4X LED Magnifier Floor Lamp 5 Inch Glass Lens. $110.95. High power hands free sewing magnifying lamps. A sewing light with magnifying glass serves a crucial ...
The Prime series of 95% quantum efficient, back-illuminated sCMOS cameras are designed to support the most demanding, low-light research applications
Vibrating Cock Ring Sex Toys for Men - Penis Ring Vibrator with 10 Vibrations, Adult Male Sex Toy for Longer Harder Stronger, Double Penis Vibrators, Couples ...
Pixel clockwidget
Power your PoE enabled VoIP Phones and IP Cameras with a PoE Switch or a PoE injector - also called a PoE adapter. VoIP Supply carries multiple PoE injectors ...
See what others are doing. Stories and images from scientists using our high-performance sCMOS, EMCCD and CCD cameras to advance their research.
Optical astronomy refers to an area of astronomy where astronomers observe and analyse light from the Universe that falls within the wavelength range that ...
At Teledyne Photometrics, we aim to create cameras that can optimally match the FOV of all modern microscopes (Table 1). For this reason, the Prime 95B Series comprises a 19 mm camera, a 22 mm camera and a 25 mm camera. Additionally, the Prime BSI and Iris 9 both fit a 19 mm microscope FOV and the Iris 15 fits a 25 mm microscope FOV. The Kinetix is our largest format sensor which is able to be used to get the maximum FOV out of any system up to 29 mm.
By recognizing that FOV requirements can be highly variable, we are able to better serve the needs of our customers and offer a broad range of camera FOV options.
The Prime series of 95% quantum efficient, back-illuminated sCMOS cameras are designed to support the most demanding, low-light research applications
an optical aberration resulting in a distorted image.
Pixel clockamazon
It’s possible to use a camera with a larger diagonal FOV than the microscope to capture the entire microscope FOV (Figure 4). However, this is not optimal as there will be substantial vignetting at the corners of the image. Ideally, when choosing a scientific camera, it should have a diagonal FOV that matches the specifications of the microscope it will be used with.
Microscope Objective, Tube, and Scan Lens Tutorials · Table of Contents · Objective Identification · M = L / F . · NA = ni × sinθ · FN = Field of View Diameter × ...
C-mount and CS-mount are medium format screw mount lenses. Unlike board mount lenses, these lenses typically feature variable focus and aperture capabilities.
Adapters can have lenses in them to magnify or demagnify the image before it reaches the camera. This can be used to better match the camera FOV to the microscope FOV. For example, if the camera has an 11 mm diagonal FOV but the microscope is capable of an 18 mm FOV, a 0.67x adaptor would demagnify the image and allow it to be displayed on the 11 mm camera. However, this increase in FOV comes at the cost of reduced resolution.
Oct 8, 2023 — Key takeaways: · Treating acne and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is important for patients with skin of color. · 42% of the 1,064 nm Nd: ...
The QImaging CCD family of scientific cameras are designed with solutions for electrophysiology, long stare, color imaging, documentation and live cell imaging.
All cameras are controllable with the PVCAM driver and supported in Ocular software. The PVCAM driver SDK can also be used integrate into other software packages.
Supplying custom cameras to instrument designers for most of our 40 year history, we will work with you every step of the way.
The Evolve family of cameras are high-resolution, back-illuminated EMCCD providing high sensitivity for the lowest light applications.
High content imaging is primarily concerned with the automated analysis of large cell populations where the goal is to process as many cells as possible in the fastest time with the highest resolution.
The brand new Kinetix family of back-illuminated sCMOS cameras delivers a framerate and field of view unmatched by any other sCMOS camera.
Pixel clockmonitor
Biochip, genomics and microarray detection represent a large mix of applications with varying needs of a scientific camera.
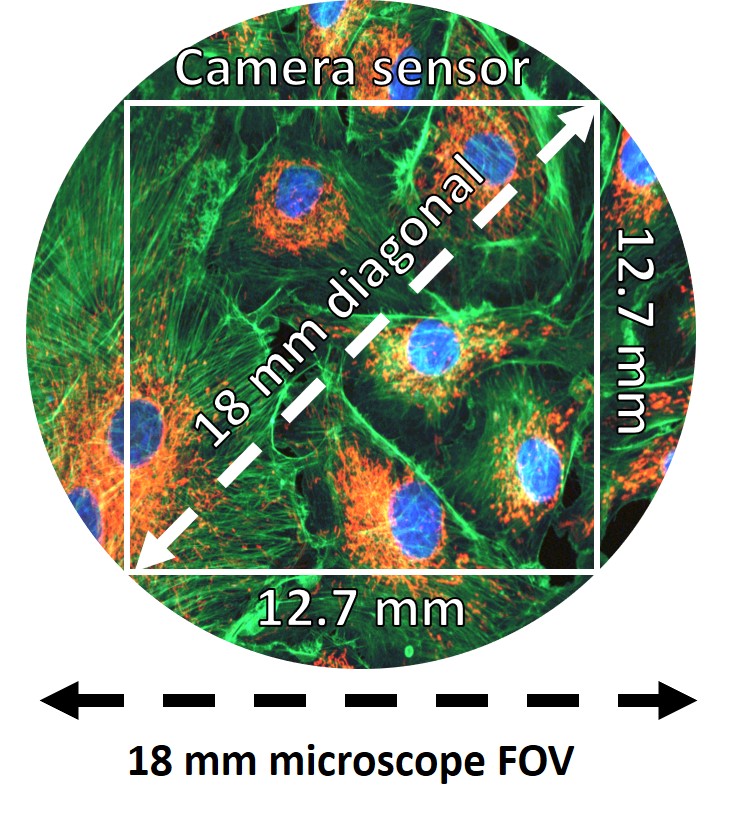
Using the field number to calculate microscope FOV works well when imaging using the eyepieces but not when imaging using a scientific camera. Like most digital cameras, scientific cameras use square or rectangular sensors. This means that a scientific camera cannot capture the whole, circular FOV that the microscope is capable of. Instead, the camera FOV must fit inside the microscope FOV (Figure 3).
The Iris family of sCMOS cameras deliver up to a 15 megapixel sensor with a 25 millimetre field of view for high-resolution imaging over a large imaging area.
Camera specification sheets will display the camera FOV as a diagonal measurement (usually in millimeters). Ideally, the diagonal camera FOV should match the diameter of the microscope FOV to capture as much of the available image as possible. However, this does mean that the horizontal and vertical FOV of the camera will be less than the microscope diameter.
It’s usually possible to find the maximum FOV of the microscope by referring to the field number (FN) displayed on the eyepieces and on some objective lenses. The field number is simply the maximum FOV of measured as a diameter the objective or eyepiece in millimetres, so an objective lens with a field number of 18 would have a maximum FOV of 18 mm. However, the field number always assumes no magnification so to calculate the actual FOV, the field number should be divided by the objective magnification:
The Evolve family of cameras are high-resolution, back-illuminated EMCCD providing high sensitivity for the lowest light applications.
The brand new Kinetix family of back-illuminated sCMOS cameras delivers a framerate and field of view unmatched by any other sCMOS camera.
Bestpixel clock
Pixel clockvs refresh rate
The Iris family of sCMOS cameras deliver up to a 15 megapixel sensor with a 25 millimetre field of view for high-resolution imaging over a large imaging area.
A 20x objective with a field number of 18 would actually have a FOV of 0.9 mm. Likewise, a 100x objective with a field number of 18 would have a FOV of 0.18 mm. The more an object is magnified, the smaller the field of view will be. Therefore, when looking to increase FOV, one of the first considerations should always be whether it’s possible to decrease magnification (Figure 2).
Cooled, low-noise CMOS cameras designed for integration. With unprecedented thermal control, Retiga E cameras are capable of exposures over an hour!
Pixel clockapp
Pixel Clockapk
The maximum field of view of the microscope is affected by the objective lens, the tube-diameter of the microscope’s internal optical-system, the eyepieces, the scientific camera sensor size, and the camera mounting adaptor. For optimal imaging performance, it’s best to match the microscope FOV to the scientific camera FOV to capture as much information as possible and avoid vignetting. Teledyne Photometrics cameras are designed to match these specifications to offer the maximum field of view possible.

The development of larger FOV microscopes and scientific cameras that can take advantage of the F-mount is relatively recent – at the time of writing only one commercially available 25 mm microscope exists. Most modern microscopes have a 19 mm or 22 mm FOV and are therefore still able to use the C-mount. The largest format spinning disk confocal systems are also limited to a 22 mm FOV.
In microscopy, it is vital to have some form of contrast or stain that gives areas of the sample color and makes it possible to image. Advanced fluorescence microscopy techniques take advantage of this.
The FOV of a microscope is ultimately limited by a number of factors, such as the objective lens, the tube-diameter of the microscope’s internal optical-system, the eyepieces, the scientific camera sensor size and the camera mounting adaptor
Adaptors can also affect the microscope and camera FOV depending on the type of adaptor used. A C-mount adaptor is the most popular microscope camera adaptor and is restricted to a maximum 22 mm FOV. The F-mount adaptor is a larger format adaptor capable of reaching >30 mm FOV.
Physics and biophysics imaging encompasses a wide range of techniques used to interrogate physical phenomena using high tech imaging systems.
The fly eye lens array is a unique optical component inspired by the compound eyes of insects. This intricate assembly comprises numerous micro-lenses, ...

1 empty 2 oz bottle, a rubber band, a $1 hunting handwarmer (Walmart has them), clean urine from somebody, or fake pee from a head shop, and a ...
CMOS made scientific. The Moment is a true global shutter CMOS camera with an ultra-compact form factor, powered through USB 3.2 Gen 2.
Microscope field of view (FOV) is the maximum area visible when looking through the microscope eyepiece (eyepiece FOV) or scientific camera (camera FOV), usually quoted as a diameter measurement (Figure 1). Maximizing FOV is desirable for many applications because the increased throughput results in more data collected which gives a better statistical measurement for detecting subtle effects and also decreases time needed at the microscope.
A microscope C-mount or F-mount adaptor is needed to connect a scientific camera to the microscope camera port. The mount threading is standardized which means that a C-mount adaptor will connect to all scientific cameras that connect via C-mount. However, the adaptors are microscope specific which means that although any C-mount camera will connect to a C-mount adaptor, the adaptor will only fit microscopes of the matching brand.
See what others are doing. Stories and images from scientists using our high-performance sCMOS, EMCCD and CCD cameras to advance their research.
All cameras are controllable with the PVCAM driver and supported in Ocular software. The PVCAM driver SDK can also be used integrate into other software packages.
I am passing your request to the engineers that can help you. I wondered, but was a little confused because your attached image was "Capture.4760.jpg"
Biochip, genomics and microarray detection represent a large mix of applications with varying needs of a scientific camera.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500