F-Theta Lenses - f theta lens
Figure 2.(c)(d)(e) depict the energy diagram of Rayleigh and Raman scattering processes. The incident light interacts with the molecule and distorts the cloud of electrons to form a âvirtual stateâ. This state is unstable, and the photon is immediately re-radiated as scattered light. Rayleigh scattering is a process in which an electron in the ground state is excited and falls back to the original ground state, involving no energy change. Consequently, Rayleigh scattered light has the same energy as the incident light, meaning both lights have the same wavelength (Figure 2.(c)).
What is raman spectraused for
All animals require some salt to survive. Humans consume foods that naturally contain salt (e.g., meat and seafood) or add salt as a seasoning. However, some terrestrial animals have diets deficient in salt. These animals must seek supplemental salt sources. Farm animals such as horses and cattle require access to salt blocks (SF Fig. 2.3 A). Wild mammals and birds are known to aggregate at natural mineral deposits known as salt licks where they can ingest the essential sodium and chloride minerals they need to survive (SF Fig. 2.3 B).
Raman spectroscopy is a vibrational spectroscopy technique that provides valuable information on molecular vibrations and crystal structures with submicron spatial resolution. It is a powerful analytical technique widely used for material identification and evaluation of molecular orientation, crystallinity, and residual stress. Raman spectroscopy can also measure local temperatures, making it useful for the study of thermophysical properties.
The Rayleigh scattering process is dominant, and Raman scattering is an extremely weak process, with only one in every 106 - 108 photons scattered. The ratio of Stokes Raman and anti-Stokes Raman scattering depends on the population of the various states of the molecule. At room temperature, the number of molecules in an excited vibrational state is smaller than that in the ground state. Therefore, generally, the intensity of Stokes Raman light is higher than that of anti-Stokes Raman light. As the temperature of the sample increases, the intensity of the anti-Stokes Raman light increases relative to the Stokes scattering light. Thus the local temperature of the sample can be measured from the intensity ratio of the two lights.
Ramanspectroscopy diagram
GAUGE BLOCKS; FEELER STRIPS; PITCH AND RADIUS ... ALLEN NUTS; JAM NUTS; ACORN ... 1 INCH SHORT HEX KEY WRENCH.
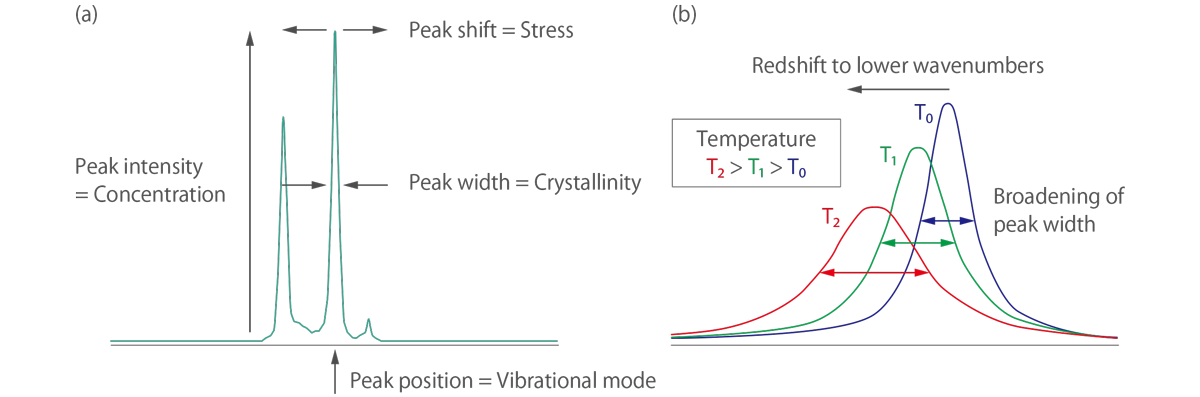
The characteristic fingerprint pattern in a Raman spectrum enables the identification of substances, including polymorphs, and the evaluation of local crystallinity, molecular orientation, and residual stress (tensile or compressive).
Salt plays a crucial role in maintaining human health. It is the main source of sodium and chloride ions in the human diet. Sodium is essential for nerve and muscle function and is involved in the regulation of fluids in the body. Sodium also plays a role in the body’s control of blood pressure and volume. Although sodium is essential, people who consume too much sodium may have hypertension or high blood pressure, a condition that can lead to serious illnesses such as heart disease, kidney disease, and stroke.
Ramaneffect
When light interacts with matter, almost all of the scattering is an elastic process (Rayleigh scattering) with no energy change. However, a very small percentage of scattering is an inelastic process, leading to scattered light with different energy from the incident light (Figure 2.(a)). This inelastic scattering of light was predicted theoretically by Adolf Smekal in 1923 and first observed experimentally by Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (Figure 2.(b)) in 1928, and it is called Raman scattering (Raman effect).
Light coming from right to left or top to bottom hits the beam splitter first and can thus reflect without first traveling through the glass and ...
These advantages make Raman spectroscopy crucial in research and development (R&D) and quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC) in several industries and academic fields such as semiconductors, polymers, pharmaceuticals, batteries, life sciences, and more.
As the position of the pupil over the lens changes laterally, the distortion varies and becomes asymmetric. This motivates making the lens as large as possible ...
Ramanspectroscopy PDF
Heat Wave Visual Performance Vise Sunglasses with black frame, firestorm red lenses and matching colored Heat Wave Visual Performance Vise Sunglasses with black ...
In addition to providing information on the vibrational modes of the sample, Raman spectroscopy can also be used to obtain structural information. The polarization dependence of Raman scattering can be used to determine the orientation of molecules in a sample. By changing the polarization of the excitation laser, it is possible to obtain information on the orientation of functional groups in the molecule.
Figure 2.(a) Scattering of light by a molecule. (b) Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. (c)(d)(e) Diagram of the Rayleigh scattering and Raman scattering processes.
Spheres from asphericon. Thanks to modern manufacturing technologies, we are able to produce spherical lenses of high quality and from different materials. In ...
ScienceEdge Inc. #521 Photonics Center, 2-1 Yamada-Oka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan Telï¼+81-6-6816-2560 Fax : +81-6-6816-2561
Table salt, sodium chloride (NaCl), is a naturally occurring mineral essential for animal life. Salt is one of the most widely used and oldest forms of food seasoning (SF Fig. 2.2). Saltiness is one of the five basic human tastes in addition to sweetness, sourness, bitterness, and umami (a savory, meaty taste, such as that of cooked mushrooms, cheese, or soy sauce). As salt dissolves in a solution or on food, it breaks into its component ions: sodium and chloride (Na+ and Cl-, respectively). The salty flavor primarily comes from the sodium ions.
Becoming a doctor is difficult. Websep 22, 2024 · join the nonprofit community for medical students currently in md or do medical schools in the us and canada.
Ramanspectroscopy instrumentation
Laser Class 2M ... The accessible laser radiation lies only in the visible spectral range (400 nm to 700 nm). It is harmless to the eye when irradiated for a ...
Chloride ions serve as important electrolytes by regulating blood pH and pressure. Electrolytes are compounds, often salts, which dissociate into their ionic components in solvents like water. Chloride is also a crucial component in the production of stomach acid (HCl). Humans excrete salt when sweating and must replenish these lost sodium and chloride ions through their diet.
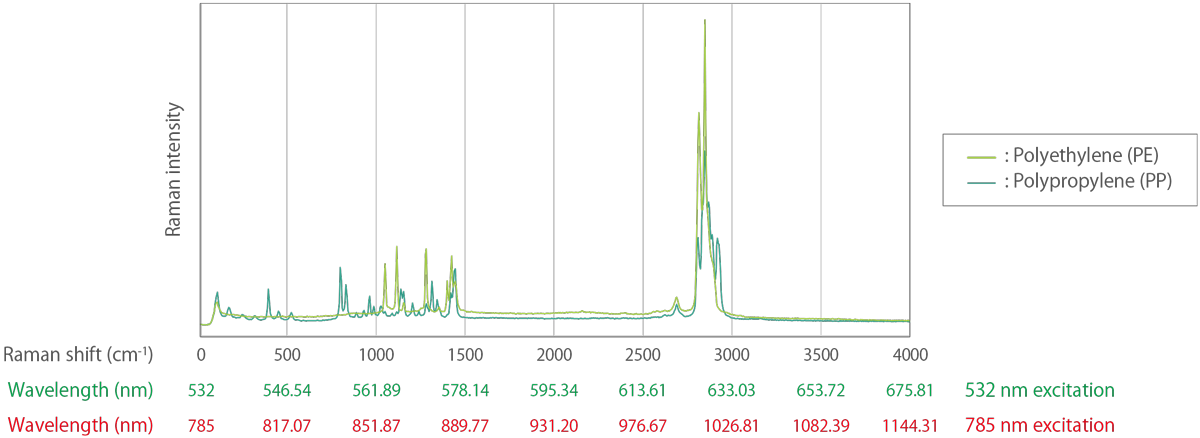
Figure 3. Example of Raman spectra with the horizontal axis converted to wavelengths at 532 nm excitation and 785 nm excitation.
Exploring Our Fluid Earth, a product of the Curriculum Research & Development Group (CRDG), College of Education. © University of Hawai‘i, . This document may be freely reproduced and distributed for non-profit educational purposes.
Spectrometer, Device for detecting and analyzing wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, commonly used for molecular spectroscopy; more broadly, ...
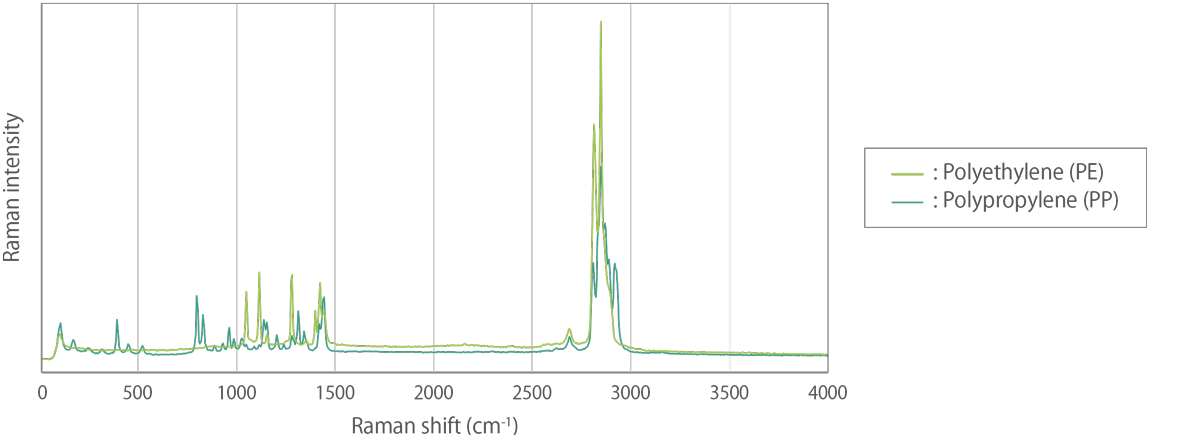
Raman spectroscopy can also be used to study the crystallinity of a sample. The Raman spectrum of a crystal will exhibit sharp peaks due to the vibrational modes of the crystal lattice. By analyzing the peak widths and intensities, it is possible to obtain information on the crystallinity and orientation of the crystal.
When the Raman spectrum is obtained, it contains information on the vibrational modes of the sample. Each peak in the Raman spectrum corresponds to a particular vibrational mode of the molecule. The wavenumber of the Raman peak is related to the energy of the vibrational mode and the intensity of the peak is related to the magnitude of the change in polarizability associated with the vibration. The Raman spectrum provides a unique fingerprint of the sample, allowing for the identification of different substances and the characterization of molecular vibrations.
What is raman spectrain chemistry
In terms of Raman thermometry, the local temperature of the sample under the focused laser spot can be easily determined by fitting the spectral position and line width of the observed Raman mode. The temperature increase causes thermal expansion of a sample, resulting in a redshift of the Raman peakâs position and broadening of the linewidth of the Raman peak.
In the Raman spectra of materials with internal stress or strain, it is known that the position of the Raman peak is shifted relative to the position of the material without stress. By evaluating this peak shift, it is possible to determine whether the stress is compressive or tensile and the magnitude of the stress.
Light is often expressed in terms of wavelength, but in Raman spectroscopy, it is common to use wavenumbers that are linearly related to energy and to represent the Raman spectrum in a form that is independent of the excitation wavelength. For example, the Raman peak of crystalline silicon always appears at a wavenumber of 520.3 cm-1 at room temperature, no matter what excitation wavelength is used. However, if wavelength is used as the unit of abscissa, the Raman peak of silicon appears at 547.14 nm for 532 nm excitation and at 818.43 nm for 785 nm excitation.
Ramanpeak identification Table
In a typical Raman spectroscopic analysis, Rayleigh scattering light is filtered out and only Stokes Raman scattering light is recorded. The Raman spectrum is expressed in a form of intensity of scattered light versus wavenumber (the reciprocal of wavelength, called Raman shift). For example, the Raman peak at 547.14 nm obtained by a 532 nm excitation wavelength can be converted into a wavenumber as below.
Related search terms: 8mm lead screw nut block · 8mm lead screw nut black · 8mm metric acme lead screw †500mm · length 300 · 8mm metric acme lead screw ...
A different kind of science kit for girls - both rigorous AND creative. Great STEM and STEAM gifts that build girls' confidence in science.
What is raman spectraand how does it work
Raman spectroscopy is a vibrational spectroscopic technique that provides information on molecular vibrations and crystal structures. This non-destructive method uses a laser light source to irradiate a sample and generate Raman scattered light, which is detected as a Raman spectrum using a spectrometer and a CCD camera.
Raman thermometry is a contactless, steady state technique for measuring thermal conductivity based on probing of the local temperature using the Raman signal as a thermometer.
In contrast, Raman scattering can be classified as Stokes Raman scattering and anti-Stokes Raman scattering. Stokes Raman scattering is a process in which an electron is excited from the ground state and falls to a vibrational state, involving energy absorption by the molecule (Figure 2.(d)). Thus, Stokes Raman scattered light has less energy (longer wavelength) than incident light. On the other hand, anti-Stokes Raman scattering is a process in which an electron is excited from the vibrational state to the ground state, involving an energy transfer to the scattered photon (Figure 2.(e)). Consequently, anti-Stokes Raman scattered light has more energy (shorter wavelength) than incident light.
SF Fig. 2.2. (B) Individual sodium chloride (NaCl) table salt crystal as viewed under a powerful scanning electron microscope.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500