Euromex Asphärische Kondensorlinse pour LE.5224 p ... - kondensorlinse
Numerical aperture, magnification, optical tube length, degree of aberration correction, and other important characteristics are typically imprinted or engraved on the external portion of the barrel for easy reference. These specifications help researchers select the appropriate objective for their experiments, ensuring optimal performance and total magnification when combined with the ocular lens. Specifications like numerical aperture and magnification are typically labeled on the barrel for easy reference. These lenses are indispensable in scientific research providing high powered optics essential for research.
VIETNAM:Alpha Industrial Park, Tu ThonVillage, Yen My District, HungYen Province 17721+84 221-730-8668sales-vn@avantierinc.com
Fluorescence microscopy is a powerful imaging technique used primarily in biomedical research to visualize and study samples labeled with fluorescent dyes or proteins at the microscopic level. The method relies on the phenomenon of fluorescence, where materials absorb light at a specific wavelength (excitation light) and then emit light at a longer wavelength (emission wavelength). A focused light source, such as a laser, is used to selectively excite fluorescent molecules within the sample. The emitted fluorescence is captured to form detailed images, providing valuable information about the sample’s internal structure and composition.
Adding to these features, long working distance objectives allow ample space between the lens and the specimen, facilitating the manipulation of samples without compromising image quality. Infinity correction objectives utilize infinity-corrected optical systems, providing flexibility and compatibility with various microscopy accessories.
A simple microscope only uses one lens whereas a compound microscope uses multiple lenses to magnify the specimen. A simple microscope uses lenses with lower ...
Darkfield illumination directs light rays obliquely onto the object, avoiding direct entry into the objective. Despite this oblique angle, the rays still illuminate the object plane. The resulting darkfield illumination image achieves high contrast between the transparent object and the light source. In a darkfield setup, a light source forms an inverted cone of light that blocks central rays but allows oblique rays to illuminate the object (see Figure 3). This design effectively forces light to illuminate the object without entering the optical system, making darkfield illumination particularly suitable for transparent objects. In contrast, no rays are blocked in a brightfield illumination setup.
Enter a dark and brutal new gameplay experience from the creators of Bloodborne and the Dark Souls series. Sekiro: Shadows Die Twice is an intense, ...
Although today’s microscopes are usually far more powerful than the microscopes used historically, they are used for much the same purpose: viewing objects that would otherwise be indiscernible to the human eye. Here we’ll start with a basic compound microscope and go on to explore the components and function of larger more complex microscopes. We’ll also take an in-depth look at one of the key parts of a microscope, the objective lens.
What isthejobof theobjective lenses
Designs and manufactures machine vision cameras and components. Compact, high-performance GigE vision cameras are suited for a wide range of industrie...
A microscope is an optical device designed to magnify the image of an object, enabling details indiscernible to the human eye to be differentiated. A microscope may project the image onto the human eye or onto a camera or video device.
In the following content, we delve intensively into the various components and features of microscope objective lenses, exploring their construction, functionality, and specialized designs that enable researchers to gain deeper insights into the microscopic world.
Microscopes are usually complex assemblies that include an array of lenses, filters, polarizers, and beamsplitters. Illumination is arranged to provide enough light for a clear image, and sensors are used to ‘see’ the object.
What isthepurposeof theobjective lens inalightmicroscope
In terms of performance, it is positioned between the plan achromat objective lens and the plan apochromat objective lens. High Grade type.
Hello! If you’re in need of data scraping services, I’d be happy to assist you. As an expert in this field, I have the experience and tools necessary to provide fast and accurate data scraping that can help you make informed decisions and grow your business. Don’t hesitate to reach out to me for any of your data scraping needs. Joann
Microscope objectives are pivotal components in optical microscopy, especially in influencing image quality and resolution. Selecting the right objective is crucial for achieving optimal results in your microscopy applications. To guide you through the selection process, consider the following factors:
In many microscopes, backlight illumination is favored over traditional direct light illumination due to the latter’s tendency to over-saturate the object under inspection. One specific backlight illumination technique employed in microscopy is Koehler illumination. This method involves flooding the object with light from behind using incident light from a source like a light bulb (see Figure 2). Koehler illumination utilizes two convex lenses, the collector lens and the condenser lens(or called field lens) , to ensure even and bright illumination on both the object and image planes. This design prevents imaging the light bulb filament, a common issue with direct light illumination. Backlight illumination is also commonly referred to as brightfield illumination.
Both the objective lens and the eyepiece also contribute to the overall magnification of the system. If an objective lens magnifies the object by 10x and the eyepiece by 2x, the microscope will magnify the object by 20 times. If the microscope lens magnifies the object by 10x and the eyepiece by 10x, the microscope will magnify the object by 100x. This multiplicative relationship is the key to the power of microscopes, and the prime reason they perform so much better than simply magnifying glasses.
Aug 16, 2013 — You can resurface this menu to change your choices or withdraw consent at any time by clicking the Manage Preferences link on the bottom of the ...
In modern microscopes, neither the eyepiece nor the microscope objective is a simple lens. Instead, a combination of carefully chosen optical components work together to create a high quality magnified image. A basic compound microscope can magnify up to about 1000x. If you need higher magnification, you may wish to use an electron microscope, which can magnify up to a million times.
3D is the abbreviation of 'Three Dimensions' in English. In Chinese, it refers to Three Dimensions and Three coordinates, namely, length, width, and height. In the world, 3D films are used to represent three-dimensional films. Anaglyph is the film that two images are overlapped to produce three-dimensional effects. When the audience watches with three-dimensional glasses, they will feel immersive. A stereoscopic film is a film that can produce a stereoscopic effect by using the difference of visual angle and the convergent function of human eyes. There is a three-dimensional space in 3D movies, for example, we can see multiple sides. Compared with 2D planes, 3D movies have a stronger three-dimensional sense and more forcing effect, just like we are in the scene.
Sep 25, 2024 — When handled in a respectful and positive way, conflict provides an opportunity for growth. Learn the skills that will help.
Do polarized glasses work 3D movies? You can watch a 3D movie completely on the computer, and first prepare 3D glasses, and it can be left and right format of 3D glasses, red and blue 3D glasses. And then use the computer to download a 3D movie, and pay attention that if the formats are different, the use of glasses is different. Note that the format of the selection should not be wrong. Red and blue glasses can only see red and blue 3D movies and left and right formats can only see left and right 3D. You can't watch a polarization-type 3D movie on a computer, because the polarization-specific display just adds a horizontal and horizontal amplitude polarization plate, which is a physical property and cannot be realized through software. Polarized 3D uses the principle that light has the direction of vibration to decompose the original image. By adding a polarizing plate on the display screen, two images with different polarization directions can be transmitted to the viewer, and then the three-dimensional image can be synthesized by the brain.
What doesthestage doon a microscope
The majority of microscope objective specifications are conveniently displayed on the objective’s body, including information such as the objective design/standard, magnification, numerical aperture, working distance, lens to image distance, and cover slip thickness correction. Refer to Figure 5 for guidance on interpreting microscope objective specifications. This direct placement of specifications on the objective facilitates a clear understanding of its characteristics, a crucial aspect when integrating multiple objectives into an application. Any additional specifications, like focal length, field of view (FOV), and design wavelength, can be readily calculated or obtained from the vendor or manufacturer’s provided specifications.
There are pros and cons to breadboard ends. Breadboard Ends are 2 to 3-inch strips of wood attached to the ends of the table. The grain runs perpendicular ...
Which partof the microscopesupportstheslide that you are viewing
Clevere Aufbewahrung für mehr Zeit im Alltag · 2 UPPSNOFSAD Boxen in schwarz übereinander gestapelt. · Mehrere beige NOJIG Plastikboxen dienen als ...
Epi-illumination, a third form of illumination employed in microscopy, generates light from above the objective. This setup replaces the need for a Koehler illumination configuration, as both the objective and the epi-illumination source contribute to the illumination process. The compact structure of epi-illumination is a significant advantage, as the objective serves as a primary source for a considerable portion of the illumination. Figure 4 provides a depiction of a frequently used epi-illumination setup, particularly common in fluorescence applications.
Lasers find widespread applications, commonly employed to either (1) heat material onto a base or (2) ablate material off of a base. Laser ablation systems necessitate the integration of microscope components due to the precise manipulation of the laser beam, including focusing, bending, and reducing scattering. Typically, a laser ablation setup incorporates custom optics instead of off-the-shelf components, with the laser intricately designed into the system, as illustrated in Figure 14. The laser is strategically oriented in an epi-illumination design to leverage the microscope objective’s capacity to focus light at the object plane, generating exceptionally small spot sizes with minimal aberrations. Additionally, an eyepiece enables the user to visually locate the laser and ensure proper functionality. Filters are indispensable in shielding the user’s eyes from potential laser damage. Laser ablation setups, known for their superior precision compared to traditional surgical methods, find applications in medical and biological contexts.

Choosing the right microscope objective is pivotal for optimal imaging performance. Consider your specific application requirements, utilize the provided guide, and explore Avantier’s diverse objective offerings to ensure accurate and reliable results in your microscopy endeavors.
A 610nm longpass filter is an optical filter that transmits light with wavelengths greater than 610nm while blocking shorter wavelengths.
Hello! If you’re in need of data scraping services, I’d be happy to assist you. As an expert in this field, I have the experience and tools necessary to provide fast and accurate data scraping that can help you make informed decisions and grow your business. Don’t hesitate to reach out to me for any of your data scraping needs. Joann
Infrared microscopy, alternatively referred to as infrared microspectroscopy, is a form of light microscopy that employs a light source transmitting infrared wavelengths to observe a sample’s image. In contrast to conventional optical microscopes utilizing absorbent glass optics, an infrared microscope incorporates reflective optics, enabling it to encompass the complete spectral range of infrared light.
Objective lensmicroscope
A basic compound microscope could consist of just two elements acting in relay, the objective and the eyepiece. The objective relays a real image to the eyepiece, while magnifying that image anywhere from 4-100x. The eyepiece magnifies the real image received typically by another 10x, and conveys a virtual image to the sensor.
Best Prices on On Stage Stands RS7030 Table Top Rack Stand and other On Stage Stands products at Acclaim Sound and Lighting - Canada's Favourite Music ...
If you’re interested in acquiring in-stock microscope objective lenses, please visit our ‘Stock – Microscope Objective‘ page.
Thank you for your time in reading our passage “Can we watch 3d movies in laptop with polarized glasses?”. For more information about sunglasses, please continue to follow koalaeye.com. Also, it is welcome to share and forward to Facebook and Twitter.
This is the most common method, but if you focus on the center of the field of view, the periphery becomes blurred, so it is not suitable for inspection photography.
In the previous article, we discussed “Do polarized sunglasses block UV rays?”. In this article, let’s talk about “How can I watch 3D movies on a PC with polarized glasses?”.
So, how can I watch using polarized glasses? I have a projector that supports 3D, but do I need a polarizing screen or something?
While a magnifying glass consists of just one lens element and can magnify any element placed within its focal length, a compound lens, by definition, contains multiple lens elements. A relay lens system is used to convey the image of the object to the eye or, in some cases, to camera and video sensors.
Function ofeyepiece inmicroscope

Avantier is a premier manufacturer of high performance microscope objective lenses, and we produce a wide range of quality microscope objectives for applications ranging from research to industry to forensics and medical diagnostics. We carry many types of objectives in stock, including apochromat objectives, achromatic objectives, and semi apochromat objectives. We can also produce custom objectives designed to work as desired in your target spectral range.
For brightfield illumination to be effective, there needs to be a variation in opacity across the object. Without this variation, the illumination creates a dark blur around the object, resulting in an image with relative contrast between the object’s parts and the light source. Typically, brightfield illumination allows clear visualization of each part of the object unless it is extremely transparent. In cases where transparency hinders feature distinction, darkfield illumination becomes useful.
contrast · contrastcon‧trast2 /kənˈtrɑːst $ -ˈtræst/ ○○○ AWL verb · 1 [intransitive] if two things contrast, the difference between them is very easy to see ...
So, how can I watch using polarized glasses? I have a projector that supports 3D, but do I need a polarizing screen or something?
Microscope objective lenses, vital optical elements in microscopy, enable precise observation of specimens. Objective lens manufacturers offer a wide range of objective designs for specific needs: high power for detailed observation, scanning for broader views, oil immersion for high-resolution imaging, and long working distance for manipulation without compromising quality. Those objectives are designed with advanced construction techniques for high performance objectives with a spring loaded retractable nose cone assembly that protects the front lens elements and the specimen from collision damage.
There are two major specifications for a microscope: the magnification power and the resolution. The magnification tells us how much larger the image is made to appear. The resolution tells us how far away two points must be to be distinguishable. The smaller the resolution, the larger the resolving power of the microscope. The highest resolution you can get with a light microscope is 0.2 um, but this depends on the quality of both the objective and eyepiece.
What doestheobjective lens doon a microscope
The chromatic aberration of the three wavelengths, with a slight chromatic aberration remaining in the purple, and the curvature of the field have been corrected. Also called fluorite.
Opticalmicroscope
3D classification: Chromatic aberration 3D with passive red-blue (or red-green, red-blue) color filtering 3D glasses. The oldest technologies, which are relatively cheap to implement. And the other one is passively polarized 3D, which uses passive polarized glasses. The image effect of polarized 3D technology is better than that of chromatic aberration. At present, more cinemas use this kind of technology, but the brightness requirement of the display equipment is higher. Polarized 3D technology is now widely used in commercial cinemas and other high-end applications. It is also called passive 3D technology. The main reason for stereoscopic feeling is that the left and right eyes see different pictures, and the left and right eyes are different, so the picture will have some differences.
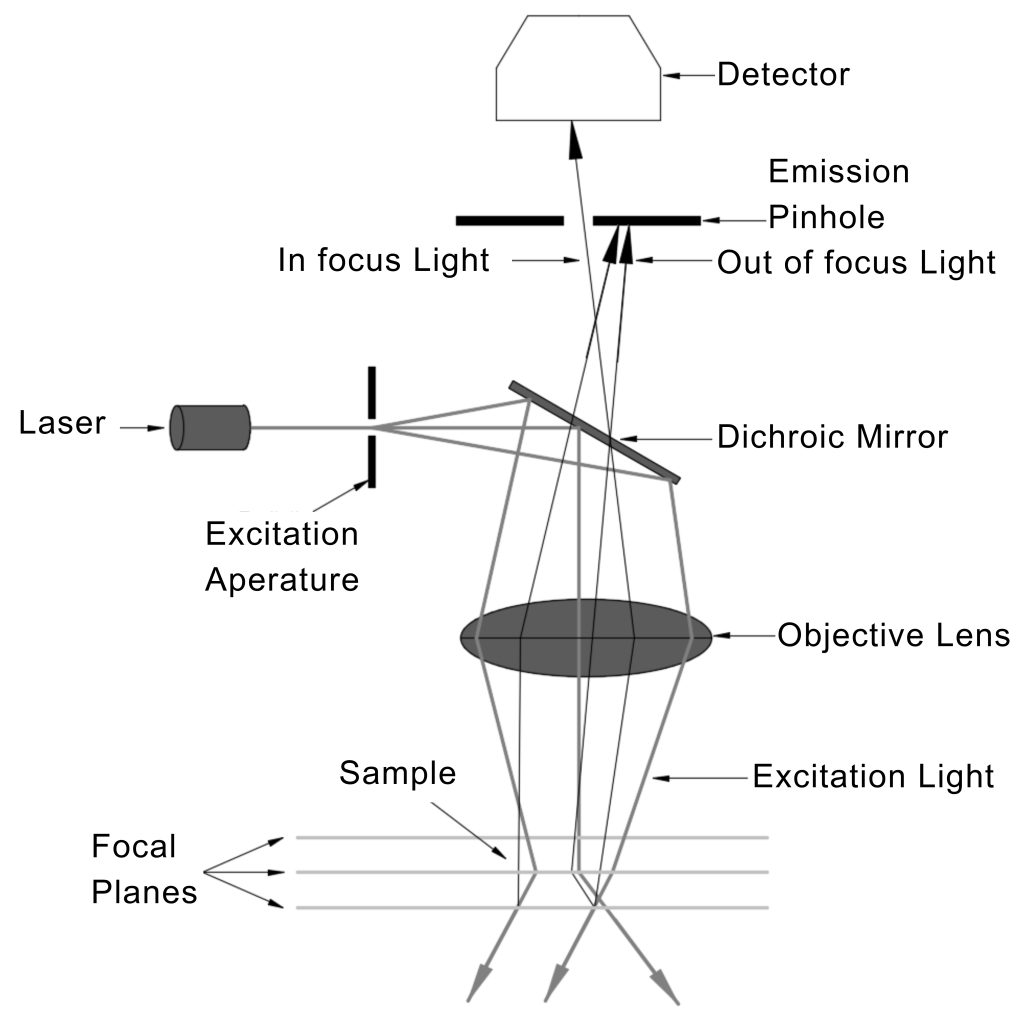
Confocal microscopy offers the capability to capture sharp images from a slender slice of a dense sample, minimizing background noise and reducing out-of-focus disturbances. Optical sectioning, widely employed in biomedical science and materials science, involves placing a sample on the microscope stage. An image is initially acquired at the primary focal plane, and subsequently, the stage or objective is adjusted vertically to capture images at successive focal planes.
In the projection of a three-dimensional film, two projectors are positioned in a certain way and project two frames point to point exactly in accord and synchronously on the same screen. The screen reflects different levels of polarized light to the viewer's eyes. Viewers should also wear polarized glasses when watching a movie. The polarization direction of the left and right lenses must be matched with the projector. In this way, the left and right eyes can filter out images that are not polarized and only see the corresponding polarized light image, that is, the left eye can only see the left screen and the right eye can only see the right screen. These images are combined by the brain to produce stereo vision.
It is suitable for inspection photography because it focuses not only on the center of the field of view but also on the periphery, producing a flat image.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500