Element Medical Imaging, 9778 N Ash Ave, Kansas ... - element medical imaging
ZoomOptics Reviews Amazon
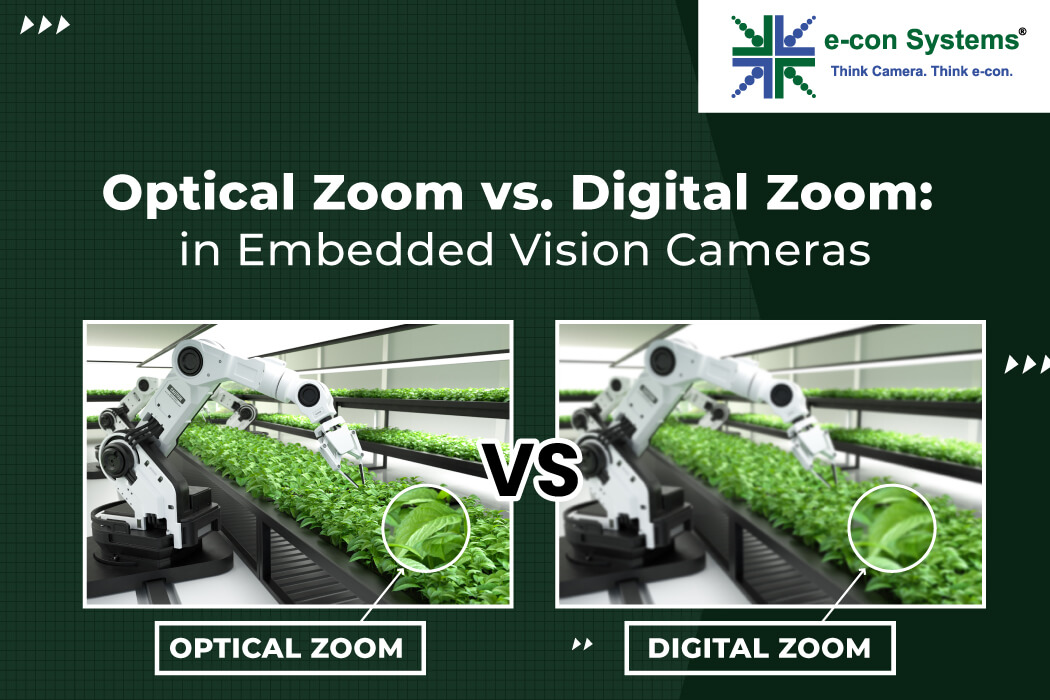
Optical zoom in embedded cameras is characterized by the physical alteration of the camera lens’s focal length. This is achieved through the movement of glass elements within the lens assembly. By changing the distance between these elements, it becomes possible for the camera to easily zoom in or out on a subject. This mechanical adjustment allows for a variable field of view while maintaining the integrity of the image sensor’s resolution.
ZoomOptics as seen on TV
Digital zoom employs a software-centric approach rather than mechanical lens adjustments. Leveraging the Image Signal Processor (ISP) or camera software, digital zooming involves selecting and cropping a specific region from the camera’s source frame and then resizing this cropped area to match the desired resolution. This process is completely managed by the camera’s computational capabilities and doesn’t involve any physical alteration of the camera’s optics.
Firstly, the 20MP camera captures far more detail initially, providing a richer source image from which to crop and zoom. Digital zoom also involves software algorithms that can apply sharpening and noise reduction to the cropped image, potentially enhancing clarity. Finally, there is more flexibility in post-production to refine the image, adjust the crop, apply corrections, etc.
Zoomoptics Amazon
BuyZoomOptics
Despite significant advancements in digital imaging technologies, optical zoom maintains its significance in many embedded camera applications. One of the primary reasons is its ability to preserve image quality at various levels of magnification.

ZoomOptics near me
Prabu is the Chief Technology Officer and Head of Camera Products at e-con Systems, and comes with a rich experience of more than 15 years in the embedded vision space. He brings to the table a deep knowledge in USB cameras, embedded vision cameras, vision algorithms and FPGAs. He has built 50+ camera solutions spanning various domains such as medical, industrial, agriculture, retail, biometrics, and more. He also comes with expertise in device driver development and BSP development. Currently, Prabu’s focus is to build smart camera solutions that power new age AI based applications.
These zoom technologies, each with distinct advantages and limitations, play a crucial role in the functionality and application of modern camera systems across various sectors. So, let’s start exploring these topics in detail.
e-con Systems has 20+ years of experience in designing, developing, and manufacturing OEM cameras. Over the years, we have provided varied customization services like form factor changes, zooming capabilities, lens mount modifications, enclosure design, etc. Our aim is to ensure that our camera solutions are tailored to perfectly suit the demands of your embedded vision applications.
Optical zoom, unlike digital zoom, involves the physical adjustment of lens elements, changing the focal length without altering the original pixel count of the image. It means the image retains its original resolution and clarity, even when zoomed in. Other reasons include better performance in low light conditions compared to digital zoom and more suitable for applications requiring zooming from a distance.
If you require any help integrating a world-class camera into your product, please write to camerasolutions@e-consystems.com.
ZoomOptics Binoculars
ZoomOptics reviews
The 20MP camera utilizing digital zoom to achieve a 2MP output typically produces a clearer image than a 2MP camera using optical zoom.
Let’s compare two cameras—one equipped with a 2MP resolution featuring optical zoom and the other a 20MP resolution with digital zoom capabilities.
Optical zoom and digital zoom represent two different approaches to magnification in camera technology. Optical zoom, relying on the physical adjustment of lens elements, offers a tangible alteration in the image’s focal length, preserving image quality at various magnifications. In contrast, digital zoom, which employs software algorithms to crop and enlarge the image, presents a more flexible yet resolution-dependent method.
This method of zoom is critical in applications where image detail plays a major role, especially when paired with lower resolution sensors. In such cases, optical zoom enables closer views without the pixelation or image degradation that can accompany digital enlargement. It’s advantageous in embedded systems where capturing detailed imagery from a fixed position is vital, such as in certain types of industrial inspection, medical imaging, or remote monitoring.
Basically, the cropping resolution is determined by dividing the source resolution by the zoom factor, and then this cropped region is resized to the final output resolution. This resizing is important for maintaining the frame size, but it invariably leads to a decrease in image quality.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500