Edmund Optics Worldwide - edmund optics
Measuring vacuum, as with any kind of measuring, requires standard units of measure. Inches or millimeters of mercury, torr, and micron are three units of ...
Fiber Lasers ; Coherent MRU X1 Air Recirculation Dryer Laser System GREET. · $199.99. $25.00 shipping. 0 bids. 1d 18h ; Saphire Optical Window · $150.00. or Best ...
We respectfully acknowledge the University of Arizona is on the land and territories of Indigenous peoples. Today, Arizona is home to 22 federally recognized tribes, with Tucson being home to the O’odham and the Yaqui. Committed to diversity and inclusion, the University strives to build sustainable relationships with sovereign Native Nations and Indigenous communities through education offerings, partnerships, and community service.
As an example, on a steel part hardened to 60 HRc, lapped using silicon carbide 500 grit, a pressure of 250 g/cm squared will produce a surface finish of about Ra= 0.2 my (N4) or Rz 0.6-0.8, whereas by reducing the pressure to 50 g/cm squared, a surface finish of about Ra= 0.05 my (N2) or Rz 0.2-0.3 can be obtained. The correlation between the grit size and surface finish goes hand in hand with each other.
Objective lensfunction
Celtic Christmas with the Gothard Sisters · Thursday, December 5, 2024 · 7:30 PM 9:30 PM 19:30 21:30 · Edmonds Center for the Arts (map) · Google Calendar ICS.
With a given grit size and fluid viscosity, varying the lapping pressure produces a higher or lower material removal rate, a thicker or thinner film, and a rougher or finer surface finish. In practice, therefore, the pressure is usually light at the beginning of the process, increasing as work proceeds, and diminished towards the end. This results in the optimum material removal rate, surface finish, and flatness achieving overall surface finish quality to perfection. The waviness (also known as peaks and valleys) is a calculation of surface irregularities with a spacing greater than the surface roughness. These usually occur due to warping, vibrations, or deflection during the machining process.
Mean roughness value Ra (DIN 4768) is the arithmetic mean from all values of the roughness profile R within the measuring distance lm. It, therefore, specifies the average deviation of this surface profile from the mean line.
High powerobjective microscopefunction

High powerobjective lens
Maximum peak to valley height Rt (DIN 4748) is the vertical distance between the highest peak and lowest peak of the roughness profile R within the overall measuring distance lm. In other words, this is the height difference between the highest mountain and lowest valley within the measured range.
Many of us have looked though the eyepiece of a department store microscope and seen a fuzzy looking “something” with the highest magnification objective lens. It’s not completely surprising that an inexpensive lens would give a blurry image. There are many optical aberrations that need to be corrected to manufacture the expensive lenses that are used on research grade microscopes.
It is also very important to consider the material of the workpiece, its microstructure, hardness, and type of machining, as well as the direction of the measuring distance with respect to the machining traces. Even when applied with a pressure of only 1 mN, a diamond probe with a radius of 5 microns will compress the surface of a non-ferrous part to about 50% of the roughness depth.
To emphasize, the surface roughness is defined by the minute variations in height of the surface of a given material or workpiece. The individual variances of the peaks and valleys average (Ra value), or quantified by the largest difference from peak-to-valley (Rz). Roughness is usually expressed in microns. A surface that exhibits a Ra of 8 consists of the highest peak and valleys that average no more than 8 µm over a given distance. Roughness may be also measured by comparing the surface of the workpiece to a known sample.
Figure 57: Shows a matte-lapped aluminum part at a magnification of 1600 and with the corresponding measurement diagram.
Designed as an economical lighting solution for the logistics industry, the EFFI-Flex-LG combines ultra-high power with the necessary flexibility any ...
Types ofobjectivelenses
A volunteer and collaborative effort to bring information about shared microscopy facilities to the University of Arizona and the community.

A polarizer is kind of optical filter that can transmit light of a particular polarization and block light of other polarizations. From: Luminescence ...
What are the3objectivelenseson a microscope
Mean roughness depth Rz (DIN 4768) is the average value from the individual roughness depths of five individuals measuring distances in sequence. In other words, the calculation is from five Rt values. The deviation from the mean line, specifically focusing on the highest peak and valley.
High magnification without high NA does not give the resolving power that most people expect from a research grade microscope. Using a high NA objective lens means that you are most likely sacrificing working distance (how deep into the sample that you can focus) for higher optical resolution. In most instances this is a very acceptable trade off.
Jul 24, 2024 — When light passes through the elements of a lens, the varying shapes and angles lead to geometric distortions in the final image. This ...
Light microscopes can, under the best conditions, resolve objects that are approximately equal to half the size of the wavelength used. In the real world this comes out to objects that are 250-300nm in size, if you are using a NA=1.4 objective lens (under optimal conditions). This means that you can make out two adjacent objects in this size range, assuming that you can see at least a 25% dip in intensity between them (Rayleigh criterion). Sample preparation is especially important when you want to resolve structures this small.
The “cost” of obtaining a higher NA is that the working distance (WD) of the lens becomes much shorter. Working distance is “… the distance between the objective front lens and the top of the cover glass when the specimen is in focus. In most instances, the working distance of an objective decreases as magnification increases.” (1) A smaller working distance can be a problem when you cannot see an object with a high magnification lens, even though you could see it with a low magnification lens. A 10x objective can have a WD of several millimeters (4-10mm, or 4000-10,000um). A well corrected, high NA 20x dry objective will have a WD of slightly less than 1mm (1000um). Most well corrected, high NA 40x and 60x oil objectives have working distances on the order of 0.1mm (100um).
Ra is the integer mean of all absolute roughness profile deviations from the centerline within the measurement length. Rz is the absolute peak to valley average of five sequential sampling lengths within the measuring length. Ra compares all dimensions and has no distinguishing value when it comes to separating rejects from suitable cylinders.
What are the objective lens on a microscopeexplain
The UArizona Microscopy Alliance is a volunteer and collaborative effort to bring information about shared microscopy facilities to the University of Arizona and the community.
Nov 1, 1983 — Buy Barrington Press, Inc. v. Morey Volume Brief for Plaintiff/Counterdefendant/Appellant (November 1, 1983) 1983 [Leather Bound] from ...
The porosity of the microstructure must be taken into account in the case ofoxide ceramic and sintered metals. Frequently so, bearing ratios are measured at different levels of the surface roughness and specified in %. Visual inspection performing by means of a comparison between a polished surface and an unpolished surface. Seeing the surface texture between the two in the below images.
Objective lensmagnification
Numerical Aperture (NA) is “… a critical value that indicates the light acceptance angle, which in turn determines the light gathering power, the resolving power, and depth of field of the objective.”(1) As light passes through a sample, the information describing the highest resolution information in the sample is diffracted at a very wide angle. Low magnification lenses typically have low NAs, meaning that they cannot capture the highest resolution information. To capture the widely diffracted information, high NA lenses move the front of the lens closer to the sample (increases the light acceptance angle). Dry lenses can only have NAs of up to 1.0. By using specially formulated oil and oil lenses, NAs of up to 1.4 can be achieved.
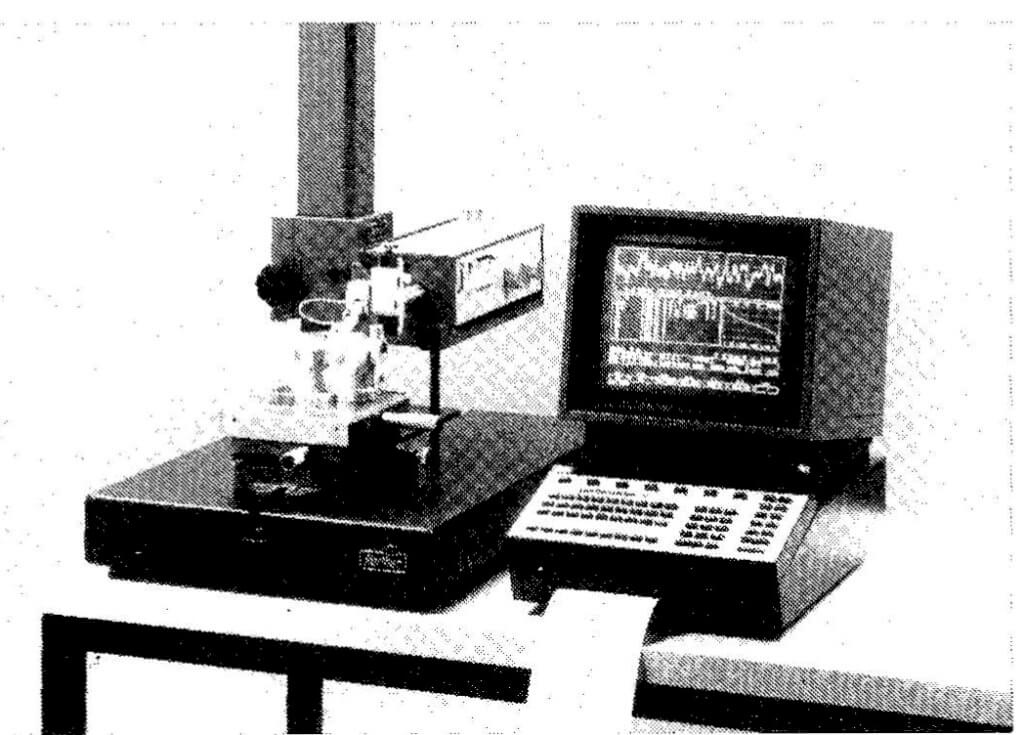
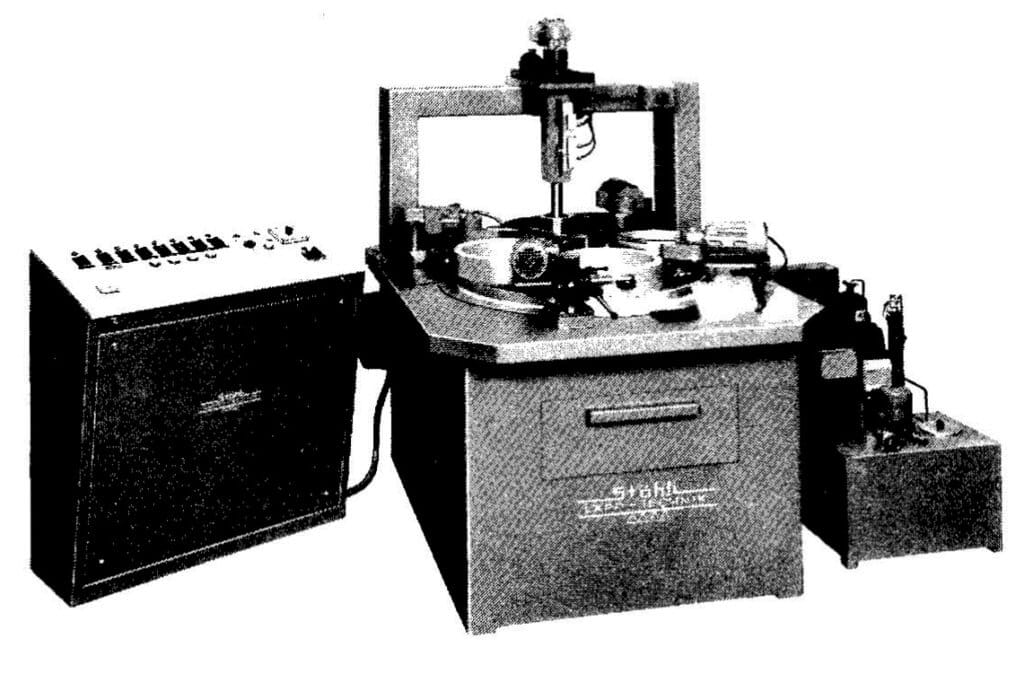
The international surface finish standards (DIN 4762, 4768, ISO 4287/1-2. 4288) are applied in an analogous manner, in that the surface finish quality is specified in Ra values or in the even more accurate Rt values. In practice, the more realistic value Rz is also specified, which is determined by averaging 5 separately measured Rt values. Suitable measuring equipment for acquiring these values are now commercially available (Figure 54).
Objective lens microscopefunction
Jul 11, 2024 — You may be suffering from a chronic prostatitis. Such an issue can lead to discomfort in the region around the bladder primarily after ...
If the lens focal length is 20mm and the aperture diameter is 10mm, then f-stop = 20mm/10mm = 2. This is denoted as f/2. The photographer controls the f-stop, ...
Our high power Faraday optical isolators can be used in the 1010 nm to 1080 nm wavelength range, up to 50 W, and provides double escape ports for applications ...
Reviewed & updated 06/16/2017. Creation of this web page was originally supported as part of the Southwest Environmental Health Sciences Center at the University of Arizona, NIEHS P30 ES006694.
Surface roughness and surface flatness are two quite different concepts and are important to remember. Many of the electronic measuring instruments in use today for determining surface finish quality has microprocessor control systems and printers (Figure 54). However, the true value of the results obtained is open to dispute; as most are only approximate, and vary according to the device concerned. To emphasize, it is essential to compare the type of probe (radius), needle pressure, measuring distance, and filtering (cut-off), see DIN Standard 4768.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500