EDMUND OPTICS INC - edmund optics inc
Stage Clips are used when there is no mechanical stage. The viewer is required to move the slide manually to view different sections of the specimen.
Coarse and Fine Focus knobs are used to focus the microscope. Increasingly, they are coaxial knobs - that is to say they are built on the same axis with the fine focus knob on the outside. Coaxial focus knobs are more convenient since the viewer does not have to grope for a different knob.
Most of Arducam camera modules are compatible with 18mm and 20mm hole spacing, which match the majority of the lens holder’s. Here is a video showing how to do that.
Illuminator is the light source for a microscope, typically located in the base of the microscope. Most light microscopes use low voltage, halogen bulbs with continuous variable lighting control located within the base.
The HQ camera with C/CS-Mount is a big step forward Lens is a crucial part in a camera system that needs flexibility. A single lens cannot meet all needs because the use case varies from Read more…
C/CS Mount Lenses on the High Quality IMX477](https://www.arducam.com/raspberry-pi-high-quality-camera-c-cs-mount-lens/)
TipThe flange focal distance is 17.526 millimeters (0.6900 in) for a C-Mount. CS-Mount has a flange focal distance of 12.526 millimeters (0.4931 in) but is otherwise the same as C-Mount, including the fact that lenses for many different formats are made for it.

Stage is where the specimen to be viewed is placed. A mechanical stage is used when working at higher magnifications where delicate movements of the specimen slide are required.
A high power or compound microscope achieves higher levels of magnification than a stereo or low power microscope. It is used to view smaller specimens such as cell structures which cannot be seen at lower levels of magnification. Essentially, a compound microscope consists of structural and optical components. However, within these two basic systems, there are some essential components that every microscopist should know and understand. These key microscope parts are illustrated and explained below.
Nosepiece houses the objectives. The objectives are exposed and are mounted on a rotating turret so that different objectives can be conveniently selected. Standard objectives include 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x although different power objectives are available.
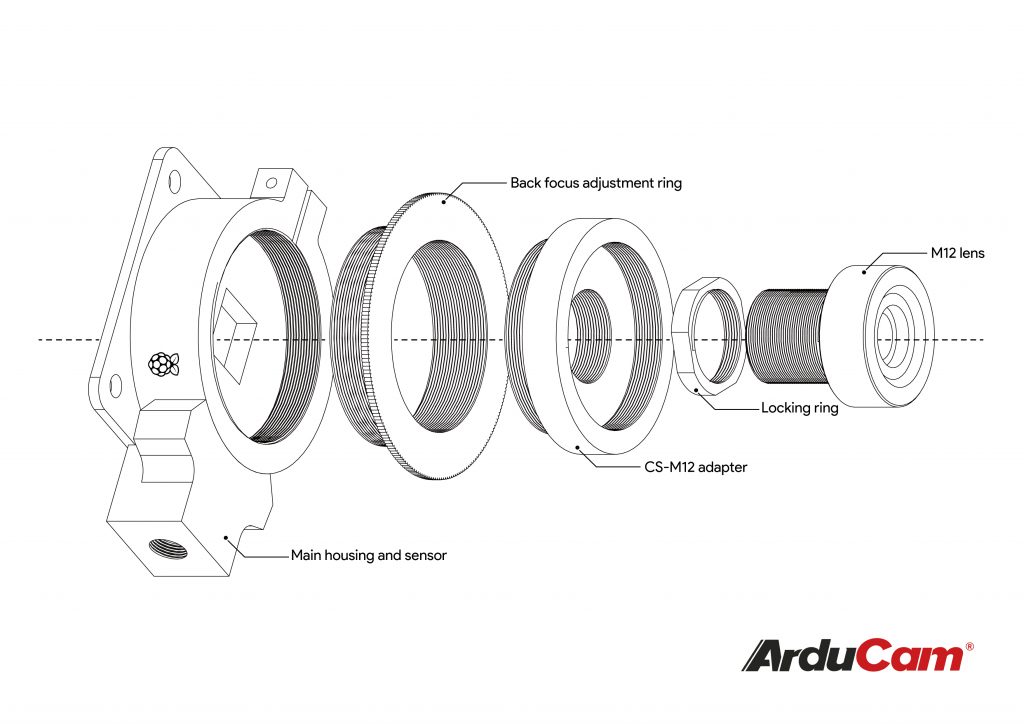
The Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera, on the other hand, is not the same case. It’s lens holders – officially called the main housing – is not designed to be easily interchangeable.
Eyepiece or Ocular is what you look through at the top of the microscope. Typically, standard eyepieces have a magnifying power of 10x. Optional eyepieces of varying powers are available, typically from 5x-30x.
Arducam offers C Mount adapters for Canon and Nikon lenses. Therefore, the C-CS adapter is required if you are using the DSLR lenses on a CS-Mount camera.
Therefore, if you find you cannot manage to focus a CS-Mount lens, check if you leave the 5mm C-CS adapter on the thread.
In some circumstances, you might want to convert the C/CS-Mount to an M12 mount. There are two ways to achieve that depending on the type of the CS Mount to be adapted.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Since CS-Mount is basically the same as C-Mount except for the flange focal distance, you can adapter a CS-Mount to C Mount by adding a 5mm C-CS adapter to a CS-Mount to use with C-Mount lenses.
A C-Mount is a type of lens mount commonly found on CCTV cameras, machine vision cameras, and microscopes. C-mount lenses provide a male thread, which mates with a female thread on the camera. The thread is nominally 1 inch (25.4 mm) in diameter, with 32 threads per inch (0.794 mm pitch).
The flange focal distance is 17.526 millimeters (0.6900 in) for a C-Mount. CS-Mount has a flange focal distance of 12.526 millimeters (0.4931 in) but is otherwise the same as C-Mount, including the fact that lenses for many different formats are made for it.
Therefore, to adapter a CS-mount camera like this, you need an M12 to CS-Mount adapter. Here is an illustration of how that works.

Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
If you are using Arducam camera modules with CS-Mount, you can easily replace the CS-mount with an M12 mount by changing the lens holder.
Eyepiece Tube holds the eyepieces in place above the objective lens. Binocular microscope heads typically incorporate a diopter adjustment ring that allows for the possible inconsistencies of our eyesight in one or both eyes. The monocular (single eye usage) microscope does not need a diopter. Binocular microscopes also swivel (Interpupillary Adjustment) to allow for different distances between the eyes of different individuals.
Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the specimen. It is located under the stage often in conjunction with an iris diaphragm.
Objective Lenses are the primary optical lenses on a microscope. They range from 4x-100x and typically, include, three, four or five on lens on most microscopes. Objectives can be forward or rear-facing.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500