Disposable Gloves - lab gloves
How doesadaptive opticswork
In 1957, the American physician Robert B. Leighton of the California Institute of Technology succeeded in reducing atmosphere-induced image distortions using the 1.5-metre telescope at the Mount Wilson Observatory in California. His technique consisted of inclining the telescope’s secondary mirror several times per second. In so doing, he managed to obtain the best images ever recorded of Jupiter and Saturn.
Get free, unlimited access to our video asset library! Download royalty-free music, color grade presets, webinar bumpers and overlays, script templates, and more — curated for marketers, created by us!
In 1970, the American engineer W. Thomas Cathey and his collaborators were the first to experimentally demonstrate an adaptive optics system that operated in real time.

Adaptive opticsOphthalmology
A telephoto lens generally has a focal length of 60mm or longer. This goes for both prime and zoom lenses. You can have a telephoto prime lens, and a telephoto zoom lens.
In that same year, the Soviet physicist Vladimir Pavlovich Linnik published an article in which he proposed that an artificial “guide star” could be created by pointing a laser at the sky and targeting its focal point in the upper atmosphere to agitate gas molecules.
When you use a camera with a crop sensor, it affects how the lens works on the camera, measured by its multiplier. For example, a crop sensor could have a 1.5x multiplier. When you attach a 50mm lens, the focal length is multiplied by 1.5x. So, this means a 50mm lens acts like a 75mm lens on a crop sensor DSLR. This essentially crops out the edges of the frame, which increases the focal length.
The first research into resolving the problem of image distortion related to atmospheric turbulence was conducted in 1902 by the German physician Karl Strehl, who proposed a method of evaluating the image quality produced by optical systems.
Another partial solution is to make improvements to the observatories themselves. More ventilation traps can be added along the observatory walls so the air around the telescope is the same temperature as the outside air. Laminar air currents can also be blown across the surface of the mirror to minimize turbulence.
Adaptive Opticsmirror
A single number, like 24mm, on a lens represents a prime or fixed lens. This means the lens isn’t capable of zooming. A 24mm prime lens is made for only a 24mm focal length. If you want a range of focal lengths, you could use a different lens, like a 24–70mm zoom lens, which gives you the ability to change your focal length in the range of 24mm to 70mm.
When you compare a crop sensor to a full-frame sensor, the most noticeable difference is how much of what you’re seeing is being captured by the sensor.
A. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION. Authority: Office of Management Budget (OMB) Memorandum (M) 03-22, OMB Guidance for Implementing the Privacy.
A simple means to minimize the effects of this inconvenient phenomenon is to build astronomical observatories at high elevations so that the telescopes only peer through the upper levels of the terrestrial atmosphere. The images obtained in this manner will be up to ten times better than those obtained at sea level.
In 1981, the American physicist Robert Q. Fugate and his team began to work on a system that would use a laser to generate a guide star – the idea originally proposed by Linnik in 1957. The first tests were performed in 1983 and 1984. Since then, several adaptive optics systems have been equipped with a laser that operates on this principle.
The main difference is that a zoom lens has a variable focal length while a prime lens has a fixed focal length. Here’s more on the differences:
The Earth’s atmosphere consists of layers of air at different temperatures that interact and cause large-scale movements of air masses (referred to as turbulence by scientists). For astronomers, turbulence is detrimental to their work as it disrupts the trajectory of light rays. This causes stars in the sky to twinkle and telescope images to be distorted.
Newlight Photonics Inc. Cart: 0 item(s) - US$0.00. Tel: (416)536-8368 (9AM-5PM, EST).
Adaptive opticstelescope
In 1953, the American astronomer Horace Welcome Babcock invented adaptive optics, a process that corrects image distortions caused by the terrestrial atmosphere. The technique consists of taking a sample of the light received by the telescope and calculating its degree of distortion. Deformable mirrors are then used to redirect the light rays and produce a corrected image. The proposal was promising, but Babcock was not able to construct his system for technical reasons.
Another method, albeit much more radical, is to install telescopes in space where the atmosphere no longer has any effect on astronomical observations. It is for this reason that today’s astronomers are launching space telescopes – like Hubble, FUSE and MOST – into orbit.
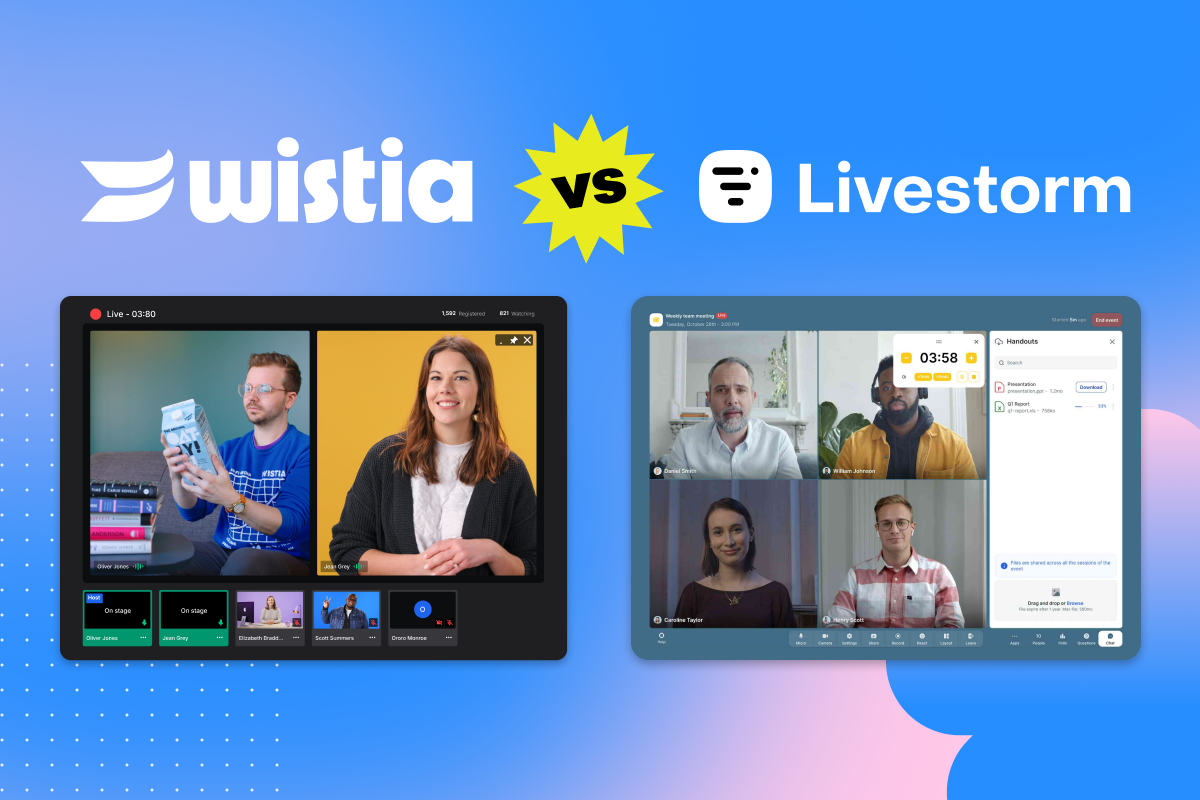
Here's a quick recap of our live event where our co-founders shared how we're making Wistia an all-in-one video marketing ...
Dec 10, 2018 — CCD sensors, as mentioned above, create high-quality, low-noise images. · Because each pixel on a CMOS sensor has several transistors located ...
A prime lens has a fixed focal length (e.g., 35mm). This means you only have a 35mm focal length on one lens. Like a zoom lens, a prime lens has its own pros and cons:
Note that the image is not inverted. A compound microscope uses an objective lens close to the object being viewed to collect light, which focuses a real image ...
WHO grading of astrocytomas · grading · neoplasia. The WHO grading system is currently most widely used for grading of astrocytomas. The last revision was ...
In 1941, the Soviet mathematician Andrei Nikolaevich Kolmogorov made several breakthroughs into the study of turbulence. His work would later be integrated into atmospheric models used to correct distortions affecting astronomical images.
Definition of Magnification ... Magnification refers to the act of visually enlarging an object, meaning that the object itself doesn't become physically larger ...
Crop sensor refers to a DSLR sensor that mimics a full-frame 35mm format, but is not a true 35mm format. If you’re using a crop sensor camera, it basically is a “cropped” view of a full-frame 35mm camera.
Full-frame refers to a DSLR camera with an image sensor that is the same size as 35mm format film, measuring 36 x 24mm. For comparison, the more popular APS-C sensor size found in most DSLRs measures 22 x 15mm. Full-frame sensors have more than 2.5 times the surface area of an APS-C sensor. When you compare a crop sensor and a full-frame sensor, the most noticeable difference between full frame and crop sensor is their field of view. If you put a 35mm lens that’s designed for a full-frame camera on a crop sensor the field of view will be cropped in. Speaking of crop sensors, let’s jump into what a crop sensor is and how it affect your images.
As of 2005, 18 observatories and 26 large telescopes are equipped with image correction systems. These systems are now considered as standard equipment for big observatories.

May 31, 2024 — By minimizing reflections on your lenses, AR coatings provide clearer and more comfortable vision in bright conditions like sunny days, during ...
Focal length is the main optical property of a camera lens. It’s displayed in millimeters and by a number that looks like this: 35mm, 50mm, or 100mm. Lenses are named by these numbers and used when refferencing different types of lenses.
Adaptive opticsastronomy
A macro lens is used for taking photo or video extremely close to a subject. With a macro lens, you can fill the entire frame and have everything be in focus. Most zoom lenses and prime lenses wouldn’t be able to focus this closely on a subject, blurring the image. Macro lenses are generally telephoto, typically with focal lengths from about 100 to 200 mm.
Learn how this multi-product SaaS company used the power of video, analytics, and Wistia to increase their engagement by 60% ...
Adaptive opticsexamples
In 1991, the American army been declassifying their confidential work on adaptive optics. Upon accessing the documents, the astronomy community realized that they had already designed and constructed more powerful and less costly systems than those of the military.
Three years later, in 1973, another American engineer, John W. Hardy, built the first adaptive optics system intended for astronomy. Originally designed to detect Soviet military satellites, the system used a deformable mirror. Astronomers took advantage of the technique and new adaptive optics systems began to appear.
Essentially, focal length is the angle of view, or how much of the scene will be captured and the magnification of the image. The longer the focal length, or the higher the mm of the lens, the narrower the angle of view is and the higher the magnification of the image. The shorter the focal length, or the lower the mm of the lens, the wider the angle of view and the lower the magnification of the image.
A zoom lens has a variable focal length (e.g., 16–35mm). This gives you a wide variety of focal lengths in one lens. There are pros and cons to having a zoom lens:
Adaptive opticsreviews
A wide angle lens is any lens that has a short focal length: shorter than 24mm. So, lenses from 14mm-24mm are considered wide angle lenses.
In 1977, the American physicist Andrew Buffington developed the first system to use a segmented mirror. Each of the six segments is controlled by a piston that could adjust the inclination.
If you have a 35mm lens for a full-frame camera, and put it on a crop sensor camera, it’s effectively a 50mm lens. This is because crop-sensor cameras offer a cropped view of a 35mm format. If you’re shooting with a cropped APSC sensor, then you could purchase lenses that are compatible with your camera and account for the cropped sensor.There are a few common cropped sizes for digital sensors. APSC, Super 35, Micro Four Thirds, Super 16.
The commonly accepted focal length of our eyes is around 22mm-24mm. Our visual attention is about 55 degrees wide. So, on a 35mm full frame DSLR, this gives you a 43mm lens. This focal length provides exactly the same viewing angle as a human eye.This is why many photographers and cinematorgraphers find a 50 mm lens pleasing for quality video production, because it is very close to our own eyes.
Adaptive opticslaser
If an adaptive optics system uses a natural “guide star”, it must be bright enough compared to the celestial object of interest to provide adequate light for the telescope’s detector. The guide star and the study object must also appear sufficiently close in the sky. It is not always easy to find a star that fulfills these criteria, hence the idea of creating an artificial guide star. Linnik’s proposal was revolutionary, but unfortunately remained unknown to the international scientific community until 1992 when his article was finally translated into English.
The main difference is that a wide angle lens has a short focal length and a telephoto lens has a long focal length. Here’s more on that:
0.3937 x cm = inches example 0.3937 inches x 6 cm = 2.362 inches. Inches to Millimeters Multiply number of inches by 25.4 to get length in millimeters. 25.4 x ...
Download scientific diagram | a. Beam clipping, short-wavelength case. from publication: Modeling the affect of multiple beam clipping in FIR and ...
Discover the importance of infrared light for understanding the universe, and how NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will show infrared in ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500