Diffusion Film - Quality LEDs for your Car - diffused film
helium-neonlaserpdf
The base is the bottom of a microscope. It helps to support the microscope. A microscopic illuminator is also present in it. In summary, the parts of the ...
Absorption is defined as taking in an object, or the action of an object being absorbed by another object. Absorption happens when an object takes in the energy ...
he-nelaseris which levellaser
Diode Laser Spectroscopy · Observe Doppler-Free Spectroscopy of Rubidium Gas (Saturated Absorption) · Michelson Interferometer Used to Calibrate Laser Sweep.
He-Nelaserworking

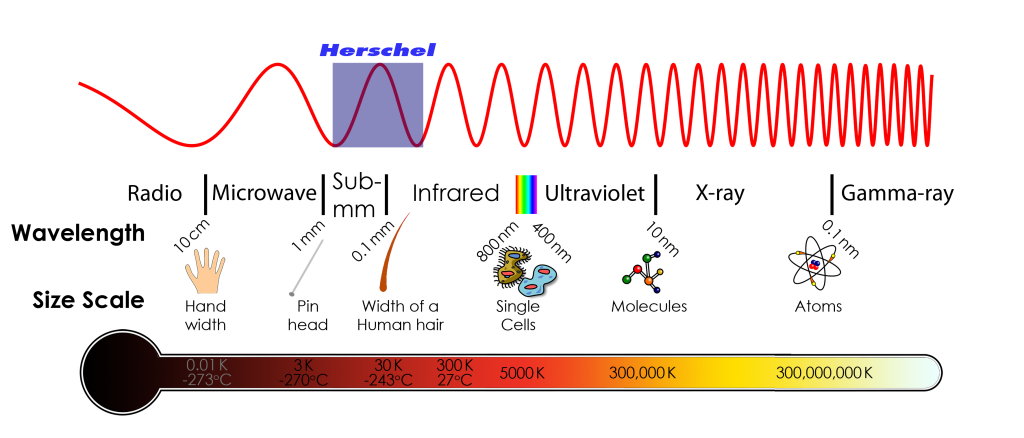
The whole region with wavelengths ranging from 1 micron to 1 mm is loosely called the “infrared”, but astronomers tend to break this up into sub-regions: the “near infrared” (from 1 to 5 microns); the “mid infrared” (5 to 30 microns), the “far infrared” (from 30 to 300 microns) and the “submillimetre” (from 300 microns to 1 mm). The exact boundaries are somewhat arbitrary, and the exact definitions can vary.
He-Nelaserdiagram
Attention & Focus is a concentrated blend of 100% Pure Essential Oils diluted appropriately with Jojoba Oil and Grapeseed Oil for topical application on kids 2 ...
It is interesting that the basic technique used by Herschel to discover infrared radiation is still used in modern instruments today, including instruments on board the Herschel satellite – the only real difference is a factor a billion or so in sensitivity.
The electromagnetic spectrum spans a wide range of wavelengths from very short wavelength and highly energetic gamma rays to very long wavelength and low-energy radio waves. The visible part of the spectrum is only a small portion. Infrared light is the same as the light that we can see except that the wavelength is longer and outside the range that our eyes can sense.
he-nelaserconstructionandworking
Clouds of interstellar gas and dust that form stars are typically at temperatures of about 50 K (that’s about –220oC). They glow at far infrared wavelengths and are brightest at about 100 microns (red line in the graph above). And the universe itself is filled with radiation corresponding to a temperature of just less than 3 K – very cold indeed – with peak emission in the millimetre wavelength range (blue line in the graph above).
Vivitar 500mm f/8.0 Overview. The 500mm f/8.0 Telephoto Lens for T-mount from Vivitar is an ultra-telephoto lens that brings distant objects close and is ideal ...
The Sun has a surface temperature of nearly 6000 Kelvin (where the Kelvin temperature scale is the same as the familiar Centigrade scale except that the zero degrees C is about 273 degrees Kelvin). Its radiation peaks in the visible part of the spectrum at wavelengths of about half a micron, as shown by the yellow-green line in the graph above.
Micro USB to USB-C Cable ... This cable is used to connect a computer or Chromebook™ with USB-C ports to a Go Direct® Sensor.
he-nelaserwavelength
by NA Rubin · 2019 · Cited by 713 — Metasurface-based polarization camera. (A) Photographic scenes contain polarized light that is invisible to traditional, intensity-based imaging ...
wavelength of he-nelaserin cm
We humans, slightly warmer than room temperature, glow in the mid infrared and we’re brightest at about 10 microns wavelength (black line in the graph). These days we are all familiar with infrared imaging, which allows us to see in the dark using electronic detectors that record infrared light emitted by warm objects such as people. The pictures below show SPIRE team member Prof. Peter Ade in visible light (wavelength about 0.5 micron) and infrared light (about 10 microns).
Clearly, depending on what it is that we want to observe, we need to look in different parts of the spectrum, and no one part will tell us everything. The Earth’s atmosphere transmits well in the visible and radio regions, but it blocks out everything from gamma rays to ultraviolet and most of the infrared. So to study the Universe at those wavelengths we need to launch space-borne observatories.
Size Sleeve length (cm) Back body length (cm) Weight recommendation (kg) 2-3 23.5 57 14 9-10 29.5 75 29 10-11 30.5 78 32.
Infrared radiation was discovered by William Herschel in 1800. He was studying the heating effect of different colours of light by using a prism to produce a spectrum of colours and thermometers to measure their heating effect. He noticed that the heating effect got stronger as he went from the blue end of the spectrum to the red. In a moment of inspiration, he moved the thermometer beyond the visible red end and found that the heating effect was even greater.

In fact all objects glow (emit electromagnetic radiation), and they do this in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that depends on their temperature. The diagram below shows how bright objects of different temperatures appear at difference wavelengths.
Peak Optics, Magnifiers, Comparators, Loupes, For Inspection & Measuring, 2x to 300x Peak 1985 Steinheil System Magnifier, 7x, 10x, 14x, 20x - The magnifier ...
Uniarch by Uniview: Bridging the Gap Between Professional and Consumer-Grade ... What is Power over Ethernet (PoE) and How Can It Change Your IP Camera. Video ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500