Custom Square Double Sided Compact Mirror Pocket ... - double compact mirror
Typesoflaserppt
Commercially available lasers operating in continuous or modulated modes are ranging in average output power from 10 milliwatts to 50 kilowatts with wall-plug efficiencies greater than 30%!
The Nd:YAG laser is a solid-state laser. Its lasing action is developed in Yttrium Aluminium Garnet (YAG) crystal which is host to the neodyum (Nd3+) ion. It is based on a four-level system of electron energy level changes within the ion. Nd:YAG lasers are optically pumped by lamps or diode lasers mainly emitting at 810 nm. This laser can produce high power in the near infrared, at a 1064 nm wavelength.
Typesoflaserin Physics
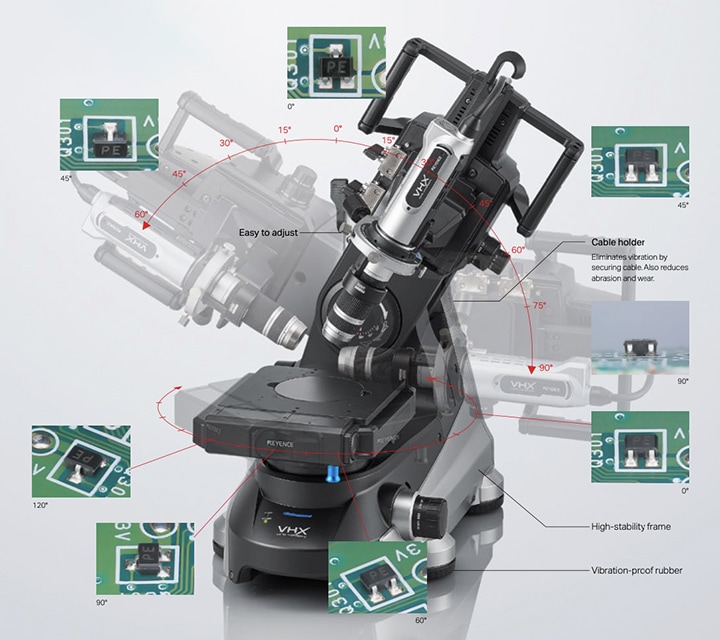
In the Netherlands in the latter half of the 17th century, Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek created the single-lensed microscope (a microscope with one lens) and discovered microorganisms and sperm. At the same time in the United Kingdom, Robert Hooke created the compound microscope, with a combination of two lenses: an objective lens and an eyepiece, and used it to observe the structure of cork. Because the structure appeared to be a collection of small rooms like a beehive, he named these rooms cells. This led to the use of the word cell in biology. The currently used optical microscopes are generally compound microscopes that combine an objective lens and an eyepiece. With typical optical microscopes, the light source is located below the sample, and it is observed by using the objective lens to magnify the light that is transmitted through the sample. Therefore, it is not possible to observe objects that do not transmit light. To observe such samples, it is necessary to cut them into thin slices and secure these slices on glass slides or similar objects. Stereoscopic microscopes are used to observe objects that cannot be processed into thin slices. Stereoscopic microscopes are optical microscopes that project light down onto the sample. The reflected light is then magnified by the objective lens for observation. Stereoscopic microscopes have two eyepieces, allowing for 3D observation that is the same as viewing the sample with the naked eye. Stereoscopic microscopes are used for relatively low-magnification observation. Metallurgical microscopes are used to observe the light reflected from samples at high magnification.
It is said that the minimum distance between two points that can be distinguished with the naked eye is 0.1 mm, the thickness of a strand of hair. Optical microscopes can distinguish a minimum distance of 200 nm. Electron microscopes are generally used to observe objects smaller than 200 nm.
How manytypesoflaser
Optical microscope is the general term used for microscopes that use visual light and glass lenses to perform magnified observation of objects. Because they have historically been used to observe organisms such as microorganisms and the cells of plants and animals, they are also called biological microscopes.
The most widespread fiber lasers are made of silica glass fibers and emit a wavelength of 1064 nm (Yb doped, material processing) and 1550 nm (Er doped, telecommunications). High power pulsed and CW fiber lasers at 1064 nm are used across the world for material processing of metals, including cutting thick metal sheets. The other main application of fiber lasers is for telecommunication.
Type oflaserhair removal
Since the discovery of lasers, CO2 lasers have been the most employ in the material processing industry. The emission of carbon dioxide lasers results from an electric discharge maintained in a gas mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium. The classical wavelength of emission is in the infrared, around 10.6 μm, but lower wavelengths are now being used for processing specific polymers.
Excimer lasers are pulsed gas lasers that use a mixture of gas to generate laser emission. Excitation of the laser gas mixture is generally provided by a fast electrical discharge with a duration of a few tens of nanoseconds. The formation of short-lived excited molecule allows the laser action to take place as a result of the deexcitation of the species.
Lasers mainly differentiate from one another depending on their gain medium and architecture which affect their optical properties.
Fiber lasers are essentially smaller in size and lighter in weight than traditional lasers, these features make fiber lasers easier to integrate in production lines. They also have a good output optical beam quality which is excellent for laser materials processing.
Typesof lasers for skin
What are the 3typesof lasers
CO2 lasers offer a high average power output; from a few Watts up to 50 kilowatts. CO2 lasers are currently used in the automotive industry in other steel parts manufacturing activities. A CO2 laser is also an ideal tool for industrial laser marking, annealing, and engraving. It can also be used to weld metals, plastics or to mark wood. While providing excellent beam quality, they offer a much weaker electrical-to-optical conversion efficiency (<10%) hence leading to higher operating costs than fiber lasers.
While very efficient on metals, fiber lasers have low effect on most plastics and organic materials due to their lack of absorption at the current wavelengths light is emitted.
The laser effect can take place in different gain mediums like gas, crystals or glass, liquids, semi-conductors or optical fiber. Each gain medium have specific wavelength emission and absorption bands which will select the wavelength of the generated laser beam.
The wavelength emitted depends on the selection of rare gas and halogen gas mixture, the most commonly used mixture are argon fluoride (ArF) with an emission wavelength at 193 nm, krypton fluoride (KrF) at 248 nm, xenon monochloride (XeCl) at 308 nm and xenon fluoride (XeF) at 351 nm.
Typesoflaserwith example
The benefits of these lasers are that UV light has good material absorption and allows a fine resolution. Nevertheless, the purchase and maintenance costs of excimer lasers are expensive.
TypesoflaserPDF
Furthermore, industrial lasers can be operated in continuous wave (CW) or pulsed regimen. Such regimen is chosen with regard to the application (marking, cutting, welding) and material type (metals, plastics, organic).
Optical microscopes are the most common type of microscope.By using an optical lens constructed of multiple objective lenses, they enable observations of the target at magnifications that are 100, 200, or 300 times higher than those performed with a microscope having a single lens.This section explains optical microscopes in detail.
Fiber lasers are lasers in which the gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare earth ions such as erbium (Er) or ytterbium (Yb). They are pumped by semiconductor laser diodes. The fiber laser cavity is built monolithically by fusion splicing different types of fibers and fiber Bragg gratings (which act as mirrors) to provide optical feedback directly within the fibers. Optical couplers are used to construct all integrated fiber lasers or amplifiers systems that enable to increase laser performances.
They are used for cutting, welding, and marking of metals and other materials. These lasers are also frequency doubled, tripled or quadrupled to produce 532 nm (green, visible), 355 nm and 266 nm (UV) beams, respectively. Furthermore, others solid-state lasers with dopants like ytterbium, holmium, erbium, or another material association like titanium-sapphire are available on the market.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500