Convert 38.1 millimeters to inches | InchPro.com - 38.1 mm in inches
In this section, we will explain the features, advantages / disadvantages, and manufacturing methods of aspheric lenses.
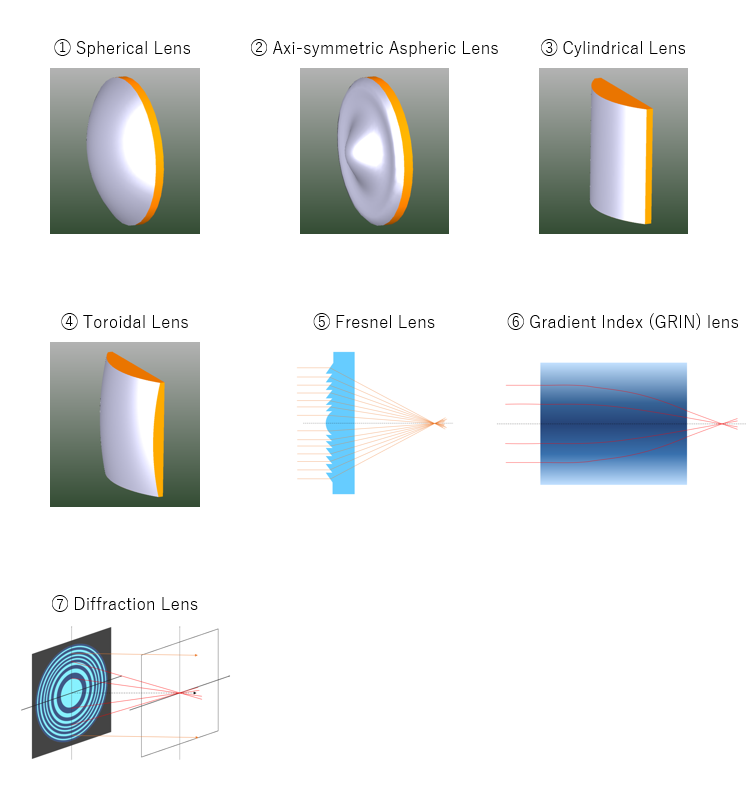
Lenses ② to ④ are lenses with continuous, smooth, non-spherical lens surfaces and are called aspherical lenses in a broad sense. ② is a lens with an aspheric surface that is axi-symmetric (rotationally symmetric) with respect to the optical axis of the lens, and is often used in imaging optical systems. Lenses ③ to ④ are aspheric lenses that do not have axisymmetry (rotational symmetry) with respect to the optical axis of the lens, and are mainly used in lighting and focusing optical systems.
If you are thinking about something like, “If only there was a product like this…”, or, “Is it possible to do these kind of things with lenses?”, Optical Design Technology Navigator, a website operated by a group of optical design professionals, is the place to go. If you have any questions about optical design, please feel free to contact us at Optical Design Technology Navigator.
Disadvantagesofaspheric lenses
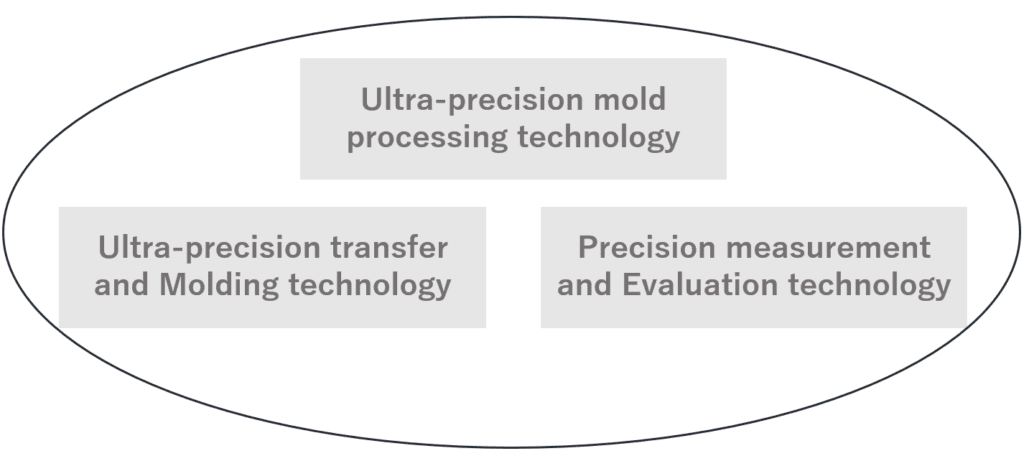
The method of manufacturing aspherical lenses by transferring and molding the aspherical shape of the mold onto the lens requires three technologies: ultra-precision mold processing technology, ultra-precision transfer and molding technology, and precision measurement and evaluation technology for these surface shapes.
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that uses special light beams instead of instruments for surgical procedures. LASER stands for "Light Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of Radiation." Lasers were first developed in 1960.
In addition, when axi-symmetric aspheres are used in illumination and focusing optics, it is possible to achieve uniform illumination distribution and increase the degree of freedom in ray control.
Aspheric Lensesprice
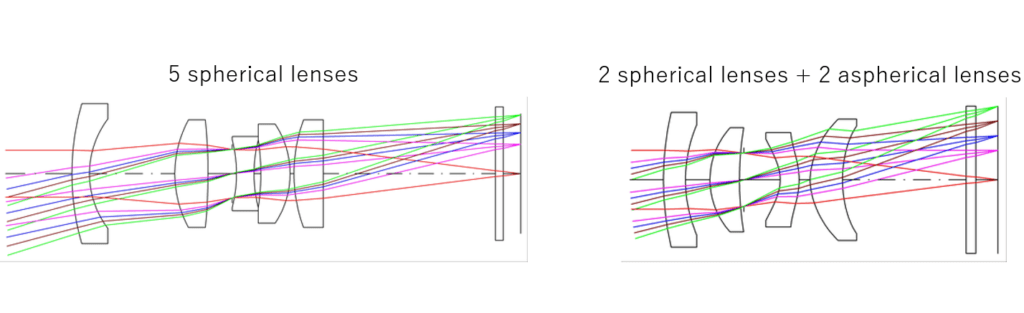
In imaging optics, multiple spherical lenses are used in combination to reduce aberrations such as image blur and distortion. By using aspherical lenses, it is possible to reduce the number of lenses while maintaining the same performance. For example, you can achieve the same performance of an 5-spherical-lens optical system with a total of 4 lenses using 2 spherical lenses and 2 aspherical lenses.
Aspheric lensesvs spherical
Axi-symmetric aspheres include rotational parabolas, rotational hyperbolic surfaces, rotational elliptic surfaces, and rotational quadric surfaces. In imaging optics, the use of such axisymmetric aspheres increases the degree of freedom in shape and makes it possible to suppress aberrations that would be difficult with spherical lenses alone.
Argon lasers: Argon lasers pass only through superficial layers of tissue such as skin. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses argon laser light to activate chemicals in the cancer cells.
Spherical surfaces are characterized by the fact that the radius of curvature is the same at all positions on the sphere, and this leads to the fact that they are easy to polish and high precision can be obtained. On the other hand, aspheric lenses require the radius of curvature to be made different depending on the position, which requires precision mold processing and technology to precisely transfer and mold the aspheric shape.
Asphericcontactlenses
On the other hand, in the case of ⑥, the refractive index inside the lens is not homogeneous but distributed, and in the case of ⑦, light is focused and diverged by using the diffraction effect on the surface instead of refraction.
Newer laser modifications continue to have a large impact on medical and surgical practices. A large part of their impact has been seen in the treatment of various skin lesion and diseases.
Access your health information from any device with MyHealth. You can message your clinic, view lab results, schedule an appointment, and pay your bill.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers: Carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers can remove a very thin layer of tissue from the surface of the skin without removing deeper layers. The CO2 laser may be used to remove skin cancers and some precancerous cells.
A spherical glass lens is processed by grinding one surface at a time, but grinding and polishing an aspherical lens one surface at a time would be very expensive. For this reason, aspheric shapes are generally processed into molds, which are then transferred and molded onto glass or plastic.
Lenses ① to ⑤ are lenses that have a focusing and diverging effect solely due to refraction on the lens surface. Of these, lenses ① to ④ have a continuous smooth surface, while lens ⑤ has a lens surface that is divided into discontinuous zones.
Aspheric lenses advantages disadvantageswikipedia
The Stanford Medicine Online Second Opinion program offers you easy access to our world-class doctors. It’s all done remotely, and you don’t have to visit our hospital or one of our clinics for this service. You don’t even need to leave home!
Aspheres that are not axi-symmetrical (rotationally symmetrical) can be used to change the magnification of vertical and horizontal images in imaging optics. Also, in illumination and focusing optics, light emitted from a point light source can be projected in the form of a line. In this way, aspheres that are not axisymmetric (rotationally symmetric) can achieve new functions that cannot be achieved with spherical lenses alone.
We are a comprehensive manufacturer of Opto-mechatronic systems that conceptualize customer needs from design to development.
Aspheric lensesmeaning
Nonaspheric lenses advantages disadvantages
With fewer lenses, it is possible to reduce lens materials, processing costs, and assembly man-hours, leading to overall cost reductions.
Although the time required for transfer and molding is shorter than for the spherical polishing process, manufacturing of precision aspheric molds (which incurs cost) in advance are necessary. For this reason, consideration of whether or not to use aspheric lens prior to production, based on the estimated total cost of the production volume is necessary.
Aspherical surfaces are classified into two categories: axi-symmetric aspherical surfaces, which have axial symmetry (rotational symmetry) with respect to the lens optical axis, and aspherical surfaces, which do not have axial symmetry. Each type of aspheric surface has its own characteristics.
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that uses special light beams instead of instruments, such as scapels, to perform surgical procedures. There are several different types of lasers, each with characteristics that perform specific functions during surgery. Laser light can be delivered either continuously or intermittently and can be used with fiber optics to treat areas of the body that are often difficult to access. The following are some of the different types of laser used for cancer treatment:
An aspherical lens is a lens whose lens surface is not spherical. By using lenses with aspherical surfaces, which offer a high degree of freedom in design, it becomes possible to reduce aberrations that could not be fully corrected with spherical lenses alone.
Aspheric lensesglasses
At Optical Design Technology Navigator, we use state-of -the-art ultra-precision processing machines to process aspheric surfaces on a sub-micron order, transfer these aspheric surfaces using molding technology that incorporates a high level of know-how, and then transfer these aspheric surfaces into an ultra-precision 3D mold.
In this way, aspherical lenses make it possible to reduce the size and weight of products, and even to cut costs. However, the production of aspherical lenses requires a very high level of manufacturing technology.
Laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT): Laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT) uses lasers to heat certain areas of the body. The lasers are directed to areas between organs (interstitial areas) that are near a tumor. The heat from the laser increases the temperature of the tumor, thereby shrinking, damaging, or destroying the cancer cells.
In this section, we will introduce the advantages and disadvantages of axi-symmetric (rotationally symmetric) aspheres in imaging optics. There are three major advantages.
TOYOTEC, operator of the Optical Design Technology Navigator, is an all-around optical manufacturer with proficiency in optical, mechanical, and electronical technology. We can design and develop products from scratch based on our customers’ needs, and provides integrated support from design to productization. In addition to manufacturing aspheric lenses, we offer one-stop manufacturing services from ultra-precision machining of lens cores to the design and assembly of lens units, including systems and peripheral components.
There are many different types of lenses. They can be broadly classified as the following according to the principle of light focusing and divergence and the type of surface.
Neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Nd:YAG) lasers: Neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Nd:YAG) lasers can penetrate deeper into tissue and can cause blood to clot quickly. The laser light can be carried through optical fibers to reach less accessible internal parts of the body. For example, the Nd:YAG laser can be used to treat throat cancer.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500