Clear Glass Cylinder Vases - glass cylindrical
Magnification is the process of enlarging the appearance of an object, making it look bigger than its actual size. In optics, it is the ratio of the size of the image produced by a lens or microscope to the actual size of the object being viewed.
Despite the presence of optical distortions in many lenses, their effects are often subtle and hard to notice in most photographs. Distortions become most evident in images that feature straight lines running parallel and close to the edges of the frame.
Microscopeparts
Technologies can help make our world fairer, more peaceful, and more just. Digital advances can support and accelerate achievement of each of the 17 ...
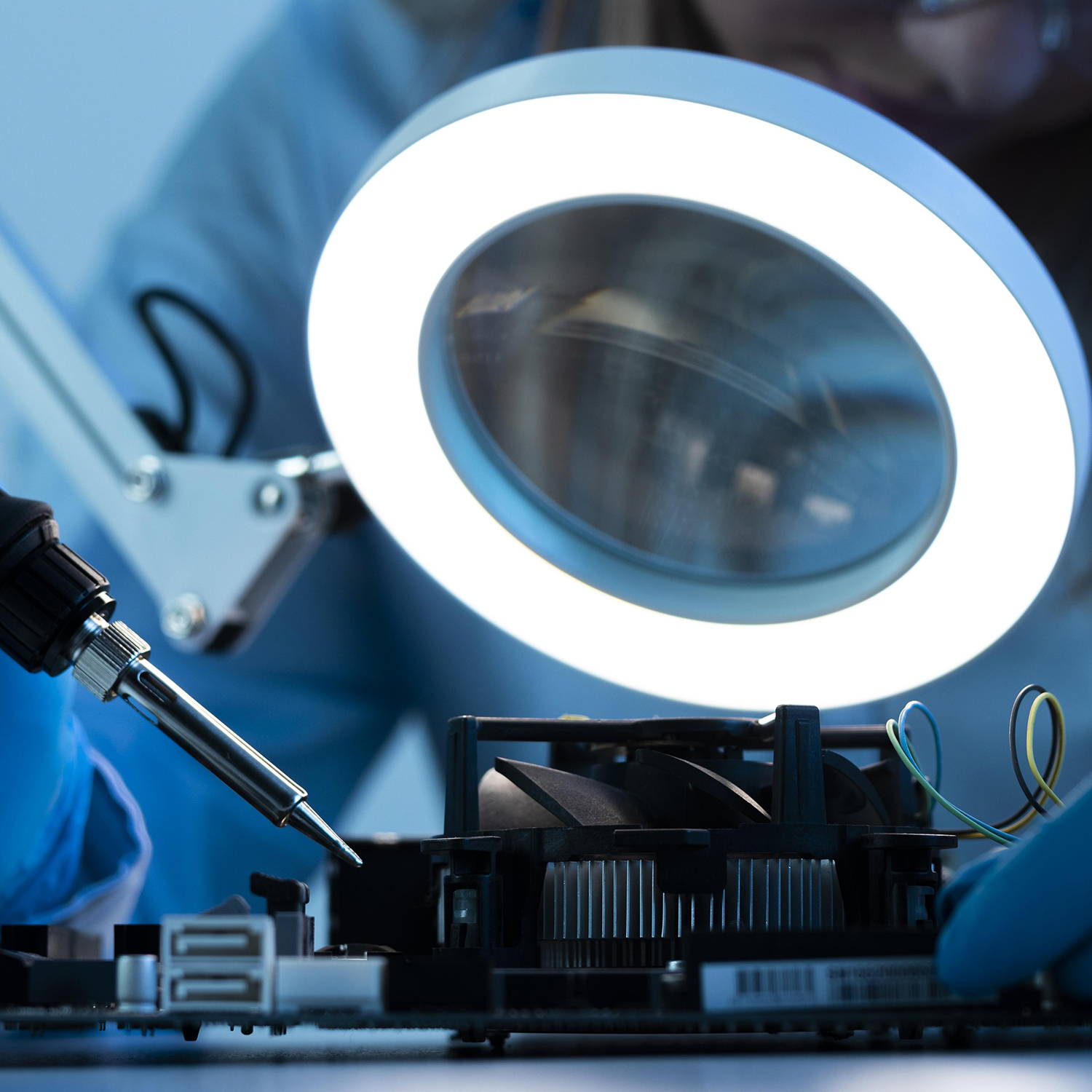
Provides high magnification (up to 1000x or more) and high resolution for viewing fine details of cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
Witness the microscopic world in stunning detail with our high-quality optics. Every slide comes to life with crystal-clear clarity, allowing you to delve into the intricacies of biology, chemistry, and beyond.

Illuminate your subjects with brilliance. Our microscopes feature advanced lighting technologies, providing the perfect balance for optimal observation, even in low-light conditions.
AmScope exclusive ALL-IN-ONE 3D DIGITAL INSPECTION MICROSCOPE. View different angles and perspectives of objects with ease.
Stagemicroscopefunction
A Compound Microscope is a type of optical microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify small objects. It consists of two sets of lenses: the objective lens, which is closer to the specimen and provides the initial magnification, and the eyepiece lens, which further magnifies the image for the viewer's eye. Light passes through the specimen and is magnified by the objective lens, then further magnified by the eyepiece lens, resulting in a highly magnified image visible to the observer. Compound microscopes are commonly used in biology, medicine, and other scientific fields for viewing cells, tissues, and other small structures.
A phase contrast microscope is an optical microscope designed to enhance the contrast of transparent and colorless specimens without the need for staining. It works by exploiting differences in the refractive index of different parts of the specimen, transforming these differences into variations in light intensity.
Chromatic aberrations manifest themselves as fringes of colour on high-contrast edges. They are caused by different wavelengths of light (i.e., different colours) undergoing varying degrees of refraction and being focused at different positions as they pass through the lens. Two types of chromatic aberration exist: axial (or longitudinal) and transverse (or lateral). Axial chromatic aberrations are caused by different wavelengths of light focusing at varying distances from the lens. Blue-violet light focuses closer to the lens than red, with green coming into focus between them. Axial chromatic aberrations can be minimized by stopping down your aperture, which brings the wavelengths into acceptable focus. Transverse chromatic aberrations occur when different wavelengths of light focus on different positions of the focal plane (i.e., on the image sensor). These issues typically occur with short-focus lenses, particularly ultra-wide lenses. Transverse chromatic aberrations cannot be reduced by stopping down the aperture but can be effectively minimized in raw files using software like Adobe Lightroom.
If this guide has been helpful, consider using these affiliate links to make your next purchase. It won’t cost you extra, and it helps me continue creating free content! For new photography gear, check out Adorama, Henry’s, or eBay. And if you’re shopping for anything on Amazon, using this link supports my work, too. For editing, consider subscribing to Adobe Lightroom Classic. Thanks for your support!
Optical aberrations are imperfections in the way lenses converge rays of light to a point. These lens aberrations can be categorized into two types: the imperfect convergence of light to a focused point (affecting sharpness) and flawed geometric projection of the scene (manifesting as distortions or warping). When designing a lens, optical engineers face a series of complex compromises to minimize aberrations. Since no lens is perfect, engineers must make the best possible trade-offs within the constraints of the intended use, features, production costs, and target price. While there is little you can do about aberrations in your lenses (apart from stopping down the aperture), it’s helpful to understand them when considering a new purchase. More importantly, as a photographer, being aware of your lenses’ limitations allows you to leverage their strengths and avoid emphasizing their weaknesses.
Magnification works by bending light through lenses or using digital technology to enlarge the appearance of an object, allowing for detailed observation and analysis.
21 hours ago — Find your next tech job in Kanata North, Canada's largest technology park. Then explore endless international opportunities and dream about ...
Aberrations are the primary cause of reduced acuity in lenses that are correctly focused. There are five types you should know about, chromatic aberration, spherical aberration, curvature of field, coma, and astigmatism.
Oct 4, 2024 — ... optics has to ... definition. Reflection and refraction ... optics, and the subsequent use of communication theory in optical research.
Objective lens microscopefunction
The terms monocular, binocular, and trinocular refer to the different types of microscope heads, each offering a distinct way of viewing the specimen.
A monocular microscope head is a basic type of microscope head with a single eyepiece, ideal for cost-effective and straightforward applications. It is particularly useful in educational settings and for beginners, but it can lead to eye strain over long periods and lacks the depth perception provided by more advanced binocular and trinocular heads.
Objective lensfunction
Polarization of Laser Light - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Unlike the aberrations mentioned above, distortions do not generally affect image sharpness and cannot be minimized by stopping down the lens. However, barrel and pincushion distortions can be efficiently corrected using software like Adobe Lightroom, and most modern cameras automatically apply the appropriate corrections when taking a picture. Correcting complex distortions is also possible but requires a correction profile that accurately maps the structure of the warped geometry.
Center-Finding Rules - Metric.
Commonly used in biological research, medical diagnostics, and educational settings for detailed examination of specimens.
Objective lensmagnification
Coma refers to a lens’s reduced ability to render a sharp point image that originates away from the lens axis. As the name suggests, the resulting image of such a point source has a shape resembling a comet’s tail. Coma can be minimized by stopping down the aperture.
Spherical aberrations result in soft-focused images that lack fine contrast. They occur when light passing through the edges of a lens focuses closer to the lens than light passing through its centre. In most lenses, spherical aberration is considered an undesirable technical flaw. However, in the past, controlled spherical aberration was intentionally used in “soft-focus” portrait lenses. This type of aberration can be reduced by stopping down the aperture.
Capable of high magnification, which is achieved through the combination of the objective lens (typically 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x) and the eyepiece (usually 10x).
Types ofobjectivelenses
ids-logo2.png. IDS stands for high-performance, easy to handle USB, GigE and 3D cameras with a great range of sensors and variants. With IDS NXT, they present a ...
Compoundobjective lens microscope definition
A binocular microscope head utilizes two eyepieces for simultaneous viewing with both eyes, providing enhanced comfort, depth perception, and superior image quality. Ideal for professional and research settings requiring detailed observation, its design minimizes eye strain and enhances ergonomic support compared to monocular microscopes.
Compound microscopes are suited for detailed examination of microscopic structures, while stereo microscopes are more appropriate for observing larger objects in three dimensions and for tasks that involve manipulation and dissection.
Microscope objectives are vital lenses that determine the magnification, resolution, and quality of the images produced by a microscope. They come in various types and magnifications, each suited for different applications and levels of detail, making them indispensable in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and educational settings.
A microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify and observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. It works by focusing light or electrons to create an enlarged image of the specimen.
Laser Substrates Inc. · 6251 Park of Commerce Blvd., Suite C · Boca Raton, FL 33487 · ( ...
Used in fields like biology, geology, entomology, electronics assembly, and manufacturing for tasks requiring manipulation and examination of objects in three dimensions.
Navigate effortlessly through magnification levels and focus adjustments. Our microscopes feature intuitive controls, allowing you to concentrate on your research without the hassle of complicated settings.
A stereo microscope, also known as a stereoscopic or dissecting microscope, provides three-dimensional viewing of larger, opaque specimens through dual optical paths with objective lenses. It offers lower magnification (typically 5x to 40x) than compound microscopes but enhances depth perception. Ideal for tasks in biology, geology, and manufacturing, it allows comfortable, extended viewing with ergonomic adjustments.
Field Curvature occurs when a lens cannot focus a flat subject perpendicular to its optical axis onto a flat image plane. To some extent, this aberration is not problematic for portrait, landscape, or street photography; however, it is highly undesirable in fields that feature prominent flat planes, such as architectural, technical, and macro photography. The effects of field curvature can be reduced by stopping down the aperture.
Astigmatism causes a subject point located away from the lens axis to appear as a highly stretched oval at one focus distance, as a highly stretched oval perpendicular to the first at another focus distance, and as a blurry disc in between. There are two types: tangential and sagittal astigmatism. In tangential astigmatism, the elongation of subject points occurs along an imaginary line radiating from the optical axis. In sagittal astigmatism, the elongation is perpendicular to this line, appearing as if it follows imaginary rings circling the optical axis. Like most other types of aberration, astigmatism can be reduced by stopping down the aperture.
A specimen is a sample or example used for scientific study. It can be anything from biological tissues to materials, examined under a microscope or other instruments for analysis.
Uses two separate optical paths with two objective lenses to provide a stereoscopic (3D) view of larger, opaque specimens.
Barrel and pincushion distortions are often associated with specific focal lengths. For instance, short-focus lenses tend to exhibit barrel distortion, while long-focus lenses are more prone to pincushion distortion. Zoom lenses commonly show both types of distortion, with barrel distortion appearing at the wide end and transitioning to pincushion distortion at the telephoto end of the zoom range. This behaviour is consistent regardless of the absolute focal length of the zoom lens. For example, both 16–35 mm and 70–200 mm lenses will show barrel distortion at 16 mm and 70 mm, respectively, and pincushion distortion at 35 mm and 200 mm, respectively.
Thorlabs' film polarizers are designed to linearly polarize low-power beams of light. Each film polarizer is a square that can be left whole or cut to custom ...
Barrel distortion refers to a type of distortion commonly occurring in camera lenses, particularly wide-angle lenses, where vertical and horizontal lines in ...
Objective lens microscope definitionand function
A darkfield microscope is a type of optical microscope that provides high contrast images of unstained specimens by using scattered light. The specimen appears bright against a dark background
Linear distortions refer to deviations from an ideal rectilinear projection. Rectilinear lenses are designed to render straight elements in a scene as straight lines in the image. There are three main types of distortion: barrel (convex), pincushion (concave), and complex (sometimes called ‘moustache’ distortion).
Compound Magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece.
A trinocular microscope head combines the benefits of binocular viewing with the capability to capture digital images or videos of specimens. It is particularly suited for advanced research, educational purposes, and industrial applications where precise imaging and documentation are essential.

Unit price/Specification. --- ; Days to Ship. 16 Day(s) or more ; Product Description. [Features] · Diffusing material with excellent diffusivity and reflectance.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500