Catalog Unsubscribe Request - catalog stop
Hi Tuan Anh, I’m glad you found the article helpful. If you imagine the rule of thirds grid over your composition, then usually I’m focusing on the bottom third line. That usually works for landscapes and cityscapes. However, in this frame, the walking bridge (and the train bridge) were about one-third the distance away from me – in relation to the objects furthest from my camera, which would be the trees at the very back. And since my focus point (the person on the bridge) was very far away from me, then I get a greater depth of field too. I’m not sure if that makes sense. It’s much easier to explain with a video or images than in words.
Antireflectivecoatingmaterial
You can still get sharp images with a deep depth of field using a low f-stop though. F/2.8 isn’t just for creating beautiful bokeh. Before I explain why, let’s get clear on a few important terms.
The mistake some photographers make is thinking the only way to control depth of field is to change the aperture. Actually, there are three ways you can control depth of field in camera: by aperture, focal distance, and focal length. Let’s take a look at each method and this great cheat sheet by Digital Camera World.
Antireflectivecoatingdisadvantages
If you’ve spent any time around photographers, especially landscape photographers, you’ve probably heard that f/8-f/11 is the holy grail of f-stops. It’s where most lenses are sharpest while offering a sufficient depth of field. That’s true.
Ar coating
Lower/faster f-stops (f/2.8 for instance) use larger/wider/open apertures that let in more light and produce a shallower depth of field. Higher/slower f-stops (f/22 for example) use smaller/narrow/closed apertures that let in less light and give a deep depth of field. Confusing, right?
EKSMA Optics uses cookies to give you the best shopping experience. If you continue to use our services, we will assume that you agree to the use of such cookies.
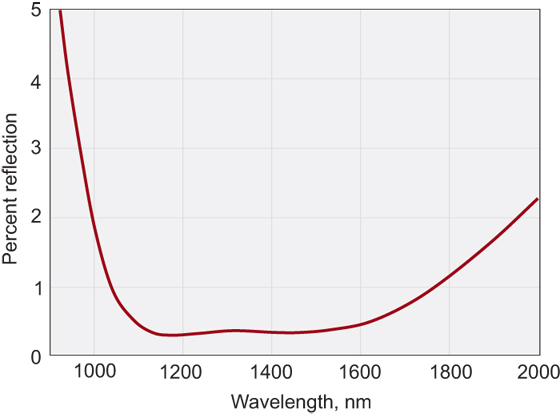
Broad band anti-reflection BBAR coatings are designed for reducing the reflectivity of a component to near-zero for specific range of the wavelength. Therefore light is efficiently transferred through complex optical systems rather than being lost to glare and scatter. Our AR coatings are intended for use at normal incidence, and when used in this way will achieve maximum efficiency transmission.
These multilayer anti-reflective coatings are designed to reduce the reflectivity of a component to near-zero for one very specific wavelength.
Ar anti reflection coatingfor glasses
If everything is in focus from the front of your photo to the back, then you have a large depth of field. And if only your subject is in focus and everything in front of our behind it is blurry, then you have a shallow depth of field, like in the photo above.
AntiReflectivecoatingPhysics
Hi, I am interested in obtaining Max DOF in Macro Photography. Focus stacking seems to be the best method I have experienced. I use a 100mm macro lens in full manual mode. What f stop do you suggest for each in focus shot taken from front to back when the focus point is managed either with a rail or manually focusing each point with the lens focus ring. Here the camera is remaining at a fixed distance compared to using a rail. Your reply is appreciated.(I photograph Fungi in rainforest conditions where sometimes the light is filtered but generally shoot at ISO 100.) I seem to get best results with f11-f22 I don’ t think the focus distance is long enough to use f4. Your reply is appreciated.
Whether you’re a landscape, portrait or street photographer, understanding depth of field opens a world of creative possibilities. It’s true that f/8 – f/11 makes for a great starting point. In some situations though, you’ll need to move outside the box to nail your shot. Use aperture, focus distance, and focal length, to make your photo sharp by increasing your depth of field. Make it one of your photography goals to master DoF!
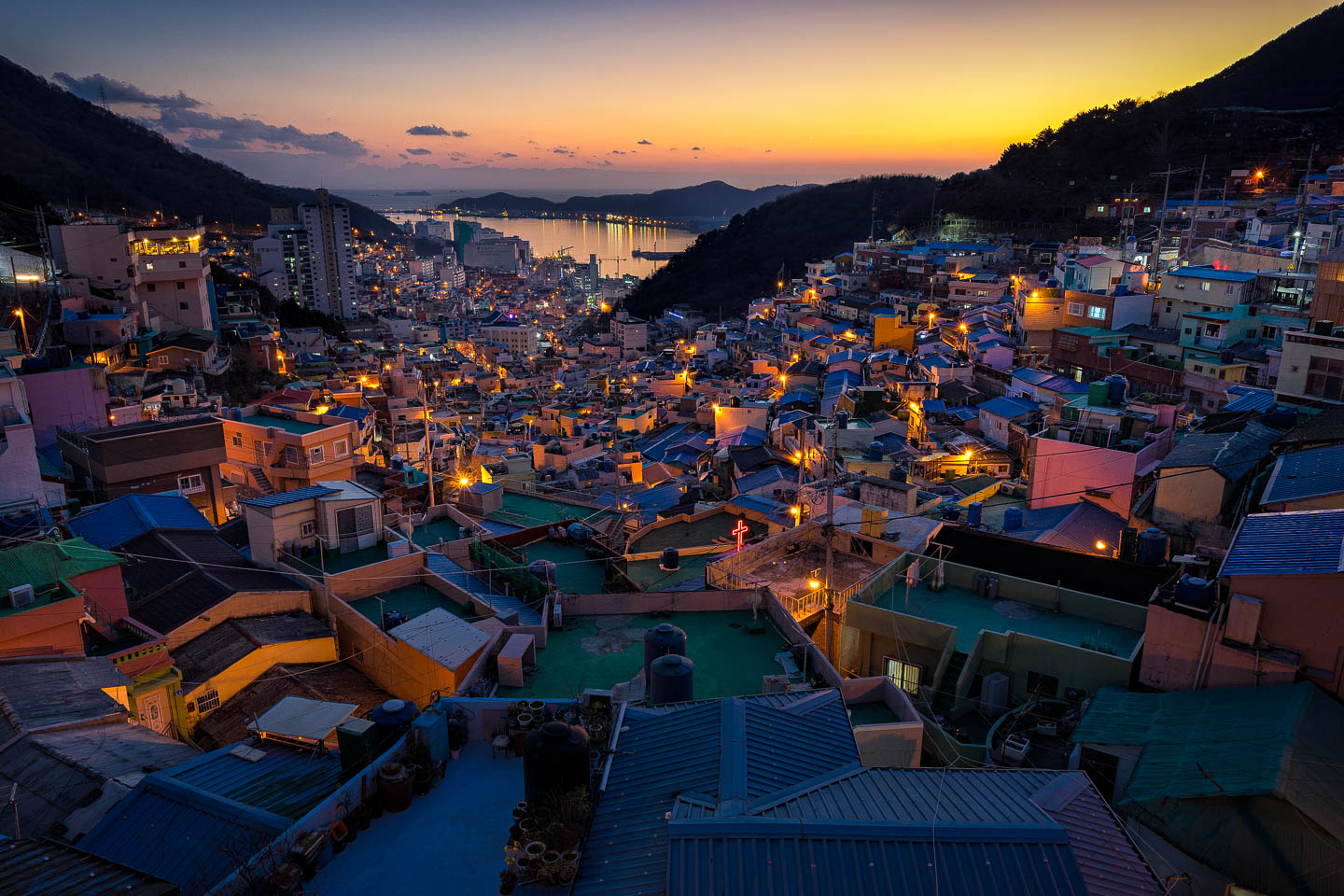
As a result, I shot wide (16mm) and made sure I was far away from the thing I was focusing on (about 100m/328ft ). In this case, I focused on the bridge just in front of the rain vortex.
Depth of Field (DoF) is an extremely important concept every photographer should know. Whether you want to blur the background in your photos or have everything in focus, it’s one of the keys to creating stunning images, and is often misunderstood by both beginner and more advanced photographers alike.
Pro Tip: Keep it simple. I never check my depth of field with an app or calculate the hyperfocal distance. I just focus on whatever is one-third of the distance away from me into my scene.
Anti reflection coatingprinciple PDF
Antireflectivecoatingspray
Hi Pete, Thanks for such a great informative post. One thing i’m not really clear of though, you mentioned near the end that you “just focus on whatever is one-third of the distance away from me into my scene”. What do you mean by “one third of the distance away to the scene”? Is it the bridge that you’re focusing on one third of the distance between you and the vortex? And why is the number 1/3? Thanks again and looking forward to your reply.
Hi Ian, I’m not a macro photographer, but I’ll try to help out. As I mentioned in the article, most lenses have a sweet spot where they perform best. It’s usually 2 or 3 stops from the widest f-stop of your lens. For instance, if your widest aperture on your lens in f/4, then your lens will most likely be sharpest at f/8 or f/11. So in your case, I’d stick with f/11. Also, you’re depth of field would be much lower at f/4, meaning you’d have to shoot and stack many more images than at f/11.
If you took a string and stretched it out to the bridge I focused on, then dropped the end of the string to the floor a few stories below me, I bet it would be a similar distance. That means what was below me should be in focus as well because it was within my depth of field.
Another thing, if you’re using a zoom lens, it can also be sharper at different focal lengths. My 16-35mm is said to be sharper at 16mm than 35mm, although I’ve never really checked. The best thing to do is to research the ideal focal length and f-stop of the lens you’re using. You can find that with a quick search on Google.

Anti reflection coatingformula
When I photographed the Rain Vortex at Singapore’s Jewel Changi Aiport, I had to use a low f-stop for two reasons. I wanted a faster shutter speed to freeze the motion of the water, train, and people. Also, I couldn’t use my tripod – it was too crowded where I took the photo – to shoot at a slow shutter speed.
What should you do if you’re shooting in low light and you don’t have a tripod? Or maybe you do have a tripod but you want to increase your shutter speed to freeze the movement in your scene.
EKSMA Optics uses cookies to give you the best shopping experience. If you continue to use our services, we will assume that you agree to the use of such cookies.
These multilayer anti-reflective coatings are designed to reduce the reflectivity of a component to near-zero for one very specific wavelength. Therefore valuable laser energy is efficiently transferred through complex optical systems rather than being lost to glare and scatter. Our anti-reflective (AR) coatings are intended for use at normal incidence, and when used in this way will achieve maximum efficiency transmission.
Depth of field (DoF) is defined as the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects giving a focused image. In other words, it’s a flexible zone that includes everything that’s in focus – from in front of to behind your subject.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500