calcium fluoride producer - calcium fluoride from ciruit board amnufacture
Results after nonablative laser resurfacing tend to be gradual and progressive. You're more likely to see improved skin texture and color rather than smoothing of wrinkles.
With fractional nonablative and fractional ablative procedures, you'll need 2 to 4 treatments to get noticeable results. These sessions are usually scheduled over weeks or months.
High powerobjective lens
Obtaining high-contrast images of transparent specimens is difficult, especially when your specimen is alive and moving on a slide. Phase-contrast lenses allow you to observe microorganisms without having to fix and stain them. When your specimens are kept alive, a variety of biological functions can be examined and analyzed in real-time. Phase plates at the top of the objective lens diffract light, allowing these specialized lenses to tap into tiny changes in wavelength amplitude, which appears to the viewer as starker contrast on the slide. This makes the specimen much easier to view and observe.
Achromatic lenses are used to diminish chromatic and spherical aberrations which are the loss of color and focus that can happen when light wavelengths refract in direct light. These aberrations can be controlled by using an objective lens that contains both a convex and concave lens inside. Mounting these two different types of lenses to each other can bring wavelengths of red and blue light closer together, which puts them in the same focus and cancels out chromatic aberration. Another type of lens used to correct for both color and spherical aberration is the plan (or planar) lens. These produce a flatter field and can also give you a much larger working distance. However, they can be more expensive than achromatic lenses, so choosing between the two depends largely on how much power you need in your objective lens, and whether or not you need to adjust for field curvature, which only plan lenses can do. Achromatic lenses and plan lenses both come in dozens of magnifications and types, accommodating a wide variety of microscopy needs.
Scanningobjective lens
Laser resurfacing is a procedure that uses an energy-based device to improve the look and feel of skin. It's usually used to reduce fine lines, age spots and uneven skin color in the face. But it can't fix sagging skin.
Specialized microscopes, such as metallurgical microscopes, require their own specific metallurgical objective lenses. These devices are most often used to examine structural detail of ceramics, metals and other non-living materials. Another common microscope objective accessory is a Barlow lens. These can be added to the bottom of an objective lens to either increase or decrease its working distance, field of view or magnification. Since they can be interchanged between lenses, they are a cost-effective way to change the power and magnification of lenses you already own. Lastly, if all these lenses are starting to seem overwhelming, remember one quick trick for determining magnification at a glance: look at the band of color near the bottom of your objective lens. While the magnification number is usually written right on the lens, you can also quickly determine its strength by the color ring. Red indicates 5x magnification, while yellow means 10x, light blue means 40x and white can mean 100-250x.
There are hundreds of unique objective lenses to choose from, but once you have a greater understanding of the most common types, you can make a more informed decision regarding which lens is right for you. Whether you are a hobbyist or whether you require the use of a microscope in your day-to-day research, it’s important to gain an understanding of the strengths and weaknesses across the spectrum of objective lenses. Once you know exactly what you’re looking for, you’ll be well on your way to obtaining the best results and having an optimal viewing experience.
Whatare the 3objectivelenseson a microscope
Laser resurfacing can cause side effects, though they're milder and less likely with nonablative approaches than with ablative methods.
Objective lensfunction
During this time, don't use products that may irritate your face, such as cosmetics. And avoid situations that increase your risk of infection, such as public whirlpools. Always use sun protection following laser resurfacing.
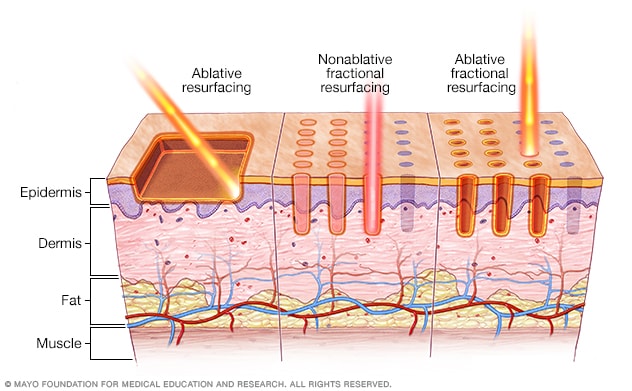
Both ablative and nonablative laser resurfacing methods can be done with a fractional laser, which creates microscopic columns of treated tissue.
Laser resurfacing is often done in a clinic. This is sometimes referred to as an outpatient procedure because it's not done in a hospital. Your care team numbs the skin with medicine. For treatment to the whole face, your care team might give you a medicine to help you feel calm or less anxious. This is called sedation.
Objective lensmagnification
Types ofobjectivelenses
Once the treatment area begins to heal, you'll notice that your skin looks and feels better than it did before the treatment. The effect may last for years.
As you age, you'll continue to get lines from squinting and smiling. New sun damage also can reverse your results. After laser resurfacing, always use sun protection. Every day, use a moisturizer and a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Tinted sunscreens with iron oxide and titanium dioxide are useful for people with brown or Black skin. These products help protect against melasma and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
The recovery time after nonablative laser resurfacing is very short. Your skin might be swollen or change color for a few hours. Use ice packs as needed. Typically, you can resume your usual activities and skin routine right away.
High powerobjective microscopefunction
The objective lens is the most important optical component of the microscope. It’s the part that sits in closest proximity to the specimen being examined, gathering light to produce optimal images for observation and analysis. This lens creates the first magnification by spreading out the light’s rays to make the object appear considerably larger by the time it meets your field of view at the other end of the eyepiece. Such a critical piece of equipment doesn’t come in a one-size-fits-all package. Below, we will discuss some of the different types of microscope objective lenses and the unique roles they play in microscopy.
During ablative laser resurfacing, an intense beam of light energy is directed at your skin. This laser beam destroys the outer layer of skin, also called the epidermis. At the same time, the laser heats the underlying skin, called the dermis. This stimulates collagen production over time, resulting in smoother skin.
AmScope exclusive ALL-IN-ONE 3D DIGITAL INSPECTION MICROSCOPE. View different angles and perspectives of objects with ease.
Infinity objective lenses did not become common until the 1980s but have since carved out a permanent spot in the microscope objective market. Previously, all microscopes had a standard tube length–the distance from the eyepiece to the objective lens was always 160 mm. Once microscope manufacturers began developing microscopes with varying tube lengths, lens manufacturers had to catch up with the changing technology. New tube lengths meant that microscopy equipment developers needed to adjust for these changes in their accessories, including objective lenses. Infinity optical systems use multiple sets of lenses within the lens house to correct a wide range of tube lengths–typically from 160-200 mm. This enables the lenses to be more versatile between microscopes of varying tube lengths.
Ablative laser resurfacing typically takes between 30 minutes and two hours, depending on the technique used and the size of the area treated. When done without a fractional laser, this approach usually needs only one treatment. If you're undergoing nonablative laser treatment or fractional Er:YAG laser resurfacing, you'll likely need 2 to 4 treatments scheduled over weeks or months to get the results you're looking for.
Both ablative and nonablative methods can be done with a fractional laser, which creates microscopic columns of treated tissue. Fractional lasers shorten recovery time and reduce the risk of side effects. You'll likely need more than one treatment session. Use of fractional devices has become the widely preferred method.
Objective lens microscopefunction

Both ablative and nonablative laser resurfacing methods can be done with a fractional laser, which creates microscopic columns of treated tissue.
After ablative laser resurfacing, the treated skin will likely be swollen and itchy. The skin may change color. Your healthcare team applies a thick ointment to the treated skin and may cover it with an airtight and watertight dressing. You may take a pain reliever and use ice packs. New skin usually covers the area in 7 to 10 days. Full recovery takes at least a month.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500