Buy Linear Polarizer Film, Polarized Film with Adhesive - polarization film sheet
Nov 21, 2017 — This reference induces a known amount of spherical aberration that is equal to the difference between the aspheric surface and a standard lens.
What is a microscopemade of
Scheme of coma/astigmatism - light rays do not point parallel to the optical axis, thus creating an asymmetric image (yellow ellipse) in the projection plane (blue circle).
Microscopeparts and functions
Köhler's lighting principle is the principle of setting the light apparatus in such a way as to achieve the best possible results in the contrast of the specimen. Applying Köhler's principle, the condenser projects a field diaphragm into the object plane, and the condenser diaphragm allows light to flow only into the field of view of the objective [4].
Similar to lenses, a larger number of lenses will provide better correction of optical defects; so-called plan eyepieces provide the best correction of optical defects.
... camera. There ... Show more ▾. Related articles. How to Switch Between Different Camera Modes on Snapchat · What is Dual Camera on Snapchat and how do I use it?
In the preparation of specimens, dyes are often used , which cover the true color of the sample; however, different shades and depths of color are still preserved in places with different chemical and physical properties.
Oct 17, 2020 — Just checking over comparative specs between the MA2,MM and M2P and noticed that DJI state the gimbal on the MA2 is motorised whereas the ...
What is a Microscope Objective Lens? Microscope objective lenses, vital optical elements in microscopy, enable precise observation of specimens. Objective lens ...
Types ofmicroscope
The width of the airy disk is used to define the theoretical maximum resolution for an optical system (defined as the diameter of the first dark circle). airk ...
There are other types of compound microscopes in common use too. A phase contrast microscope uses a special lens, called a "phase contrast objective lens," together with a phase slider (or phase turret condenser). This combination intensifies the contrast of the object being observed, without the need to stain it with dye. These "phase contrast" microscopes are often used in university and medical research settings, to look at bacteria, blood cells, and other tiny structures in living creatures. We’ll go into them in more detail below.
Scheme of chromatic aberration - a) simple lens: rays of different wavelengths create three different foci, b) diplet lens: rays of different wavelengths meet at a common focus.
Light starts its journey at the base of the microscope from the source of illumination. This light travels upwards through the condenser and aperture where it then passes through the contents of the stage. The image of the slide or specimen on the stage is picked up by the powerful magnification of the objective lens above it (4x, 10x, or 100x). The light then moves up the head of the microscope where it reaches the eyepiece and is again magnified by the ocular lenses (5x-30x, 10x eyepiece is by far the most common).
Feb 26, 2013 — ... dovetail (what these stores call English dovetails), and a less-impressive sliding dovetail. I can only assume that furniture stores did so ...
Diagram of light flow through a light microscope: 1) light source, 2) collector lens, 3) mirror, 4) field diaphragm, 5) condenser and condenser diaphragm, 6) stage with specimen, 7) objective
A compound microscope is an instrument that is used to view magnified images of small specimens on a glass slide. It can achieve higher levels of magnification than stereo or other low power microscopes and reduce chromatic aberration. It achieves this through the use of two or more lenses in the objective and the eyepiece. The objective lens or objectives located on the nosepiece have a short focal length and are close to the target specimen where it collects light and focuses the image of the object into the microscope. The second lens, in the eyepiece, has a longer focal length and further enlarges the image.
The objective is the most important part of the microscope - the quality of the objective determines the resulting magnification of the microscope and the resulting image quality. It is also the most difficult to construct. It usually contains a large number of lenses of different shapes and in different groups (in triplets, doublets or individually) fixed in the lens barrel. The layout, number and shape of the lenses is individual for each type of lens and significantly affects all lens parameters. The entire lens system of the objective functions together as a connecting lens.
Neutral density filters reduce or modify the intensity of all wavelengths or colors equally without changing hue of the color rendition.
The light microscope is mainly used for its relatively easy production and the ability to observe preparations dynamically, without damaging them (unlike microscopes using other types of electromagnetic radiation) and with preservation of color (unlike electron microscopes).
In addition to lenses, eyepieces also have an eyepiece diaphragm. According to the position of the eyepiece diaphragm in relation to the lenses, we distinguish two basic design types of eyepieces: the positive eyepiece, in which the diaphragm is located in front of the lenses (closest to the object plane), and the negative eyepiece, where the diaphragm is usually located behind the first lens. The simplest type of positive eyepiece with two lenses is called a Ramsden piece; the simplest type of negative eyepiece is called a Huygens eyepiece.
Most of us remember using a microscope at some point in school, usually in biology class (or a science class that included a section on biology), and for most of us it was the same kind of microscope. A biological microscope is one kind of a compound microscope. Sometimes other names are used for biological microscopes too. If you hear either of the terms "brightfield microscope" or "transmitted light microscope," it is referring to the same thing.
Diagram of the appearance of the cone of light when the condenser diaphragm is open (a) and closed (b) - the condenser is located at the bottom, the light is directed into the lens.
What is a microscopein biology
After being directed by the lighting apparatus, the light first passes through the observed specimen and then through the objective and eyepiece. Angled mirrors can be placed between the individual components of the lighting apparatus, which direct the light rays in the desired direction, but do not adjust the shape of the light cylinder/cone.
Add your own personal touch to envelopes, stationery and gifts with this address stamp. Featuring a pair of glasses at the top of the stamp above your ...
Another type of compound microscope is the polarizing microscope. These use an analyzer and a polarizer to cross-polarize and pick out even subtle differences in colors in the optical path of whatever it is being examined. These microscopes are especially useful in science and industries that examine chemicals. Pharmaceutical companies, petrologists and geologists often use polarizing microscopes for the examination of chemicals, minerals, and thin slices of rock sample.
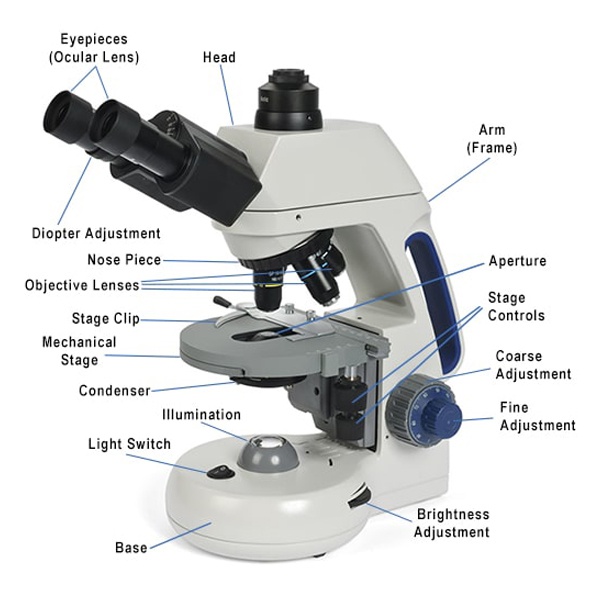
These parts are supplemented by a mechanical system into one functional unit. In developmentally older microscopes, it was common to use only one biconvex connecting lens and a kahan or candle light [1].
Who inventedmicroscope
What is a microscopein science
Finally, fluorescence microscopes and differential interference contrast microscopes (DICs) are other types of compound microscope. They are both used most commonly in biology-related fields and use different light wavelengths to fluoresce an object under observation, highlighting particular features of the sample.
A metallurgical microscope is another of the compound microscopes and, as the name indicates, is often used in metallurgy and related endeavors. These microscopes may have transmitted and reflected light working together, or only reflected light. The reflected light enters through the objective lens. These microscopes are most useful when it comes to viewing materials that are opaque, that don’t allow any light to pass through them. Another technique used to observe opaque substances using metallurgical microscopes is called "darkfield microscopy." This technique backlights the observed object to help highlight specific features of the metal, including flaws in precious stones or hairline cracks in metals.
What is a microscopecalled
These parameters fundamentally depend on the construction of the lens. In practice, the values for a specific lens are usually written on the side of the body (mount) of the lens itself.
When choosing an eyepiece, it is essential to choose an eyepiece that best matches the given lens - the main factors are the brightness , focal length and numerical aperture of the lens.
Bill's Pipes MX2 Works Pipe. Performance tested and race proven, the Bill's Pipes 2-stroke line has been the choice of champions and serious riders all over ...
Schematic of the appearance of almost completely open (a) and half-closed (b) field diaphragms when viewed through the eyepiece.
A light microscope is a complex optical device that, with the help of several optical systems, enlarges the eye of vision and thereby improving its Resolution up to a thousand times.
In total, we distinguish three basic construction types of lenses: achromatic lens, fluorite lens and the most complex apochromatic lens. Achromatic and fluorite lenses have a smaller number of lenses at the same magnification value and thus a significantly worse correction of optical defects [5].
What is a microscopeused for
In practice, the mechanical system is the system with which the user comes into contact the most. A properly designed mechanical system is a necessary condition for a high-quality microscope: it ensures firm anchoring of the lenses and apertures, the correct angle of the light rays and the object plane, and a very fine mutual displacement of the optical systems and the object plane ("focusing").
The Eyepieces are the last part of the microscope through which the light rays from the light source pass. They participate in the final adjustments of the image. Similar to lenses, they consist of several lenses that work together as a connecting lens; but the number of lenses in the eyepiece is significantly smaller. The eyepiece lenses collectively produce an apparent, magnified, non-inverted image; the overall image produced by the microscope is therefore apparent, magnified and inverted.
The lighting apparatus is used to illuminate the object plane as perfectly as possible (that is, the plane of the table on which the specimen is located). The main function is to ensure the correct direction and intensity of the light rays to adequately illuminate the preparation (without unwanted reflections, so that the features and structures of the preparation are as clear as possible). This function is best fulfilled when applying the so-called Köhler lighting principle, which will be described below.
Current and developing technologies in 3D Sensing rely on a controlled field of light with customized shape, irradiance and intensity. Light shaping optics ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500