Cold Beer Neon Sign - beer bar lights
Processed image data is used to perform OK/NG judgment, record measured results, or categorize parts. Both images and data output, and communication with other devices can be established.
There's a third lens application function called over(), which acts just like set() except, instead of providing an updated value, you provide a function for updating the value. The provided function will be passed the result of the lens's getter. Let's say we want to uppercase the person's firstName:
KEYENCE supports customers from the selection process to line operations with on-site operating instructions and after-sales support.
All KEYENCE vision systems include a wide range of measurement and dimension tools, which make finding intersections, midpoints, and distances very simple. For example, simply click anywhere along an edge to auto-extract that line, or refer to line results from a tool which has already been configured. This intuitive interface allows users to easily create complex inspection settings while combining several measurements and dimensions.
The prop() function takes a property name and an object, and returns the value of that property name on that object. It works very similarly to our getter function.
Decoupling an object's shape allows for future reshaping of your data while minimizing the effects of the rest of the code in your application. Take, for example, an object representing a person.
2023831 — Temporal coherence measures the phase correlation of a light wave at different locations along its propagation path and helps to understand ...
Vision systems are used in the molding and resin industries to automate inspections and ensure defective products are not released. These inspections are necessary to detect any mishaps in processes such as injection molding, plastic forming, laminations, and product labeling. Application examples include:
Those are basics of lenses but there are other, more specialized, lens creation functions in Ramda. Specifically, lensProp(), lensIndex(), and lensPath(). These are the functions you'll probably use most often when creating lenses. The generic lens() would be used only when needing to do very customized lens creation. Let's go over each of these specialized lens creation functions.
Cameravision inspectionsystem
1) Determine the number of pixels necessary to meet accuracy requirements. 2) Select the transfer speed based on the needs of the application. 3) Select a camera size based on installation space. 4) Select either a color or monochrome camera based on what kind of inspection is needed.
Blue LED lights are now available. The short wave length characteristics of blue LED light make them an ideal choice for high precision dimensional measurements and other demanding applications.
Vision inspectionMachine
As you can see, lensPath() takes an array with path segments leading to the nested data that we want focused. Each path segment can be a property name or an index. Since we're giving it the root person object, we get back a full copy of the person object with just the home phone number changed. In my opinion, this is where the lens feature really starts to shine. Imagine if we wanted to duplicate the result of the set() function above, but with regular Javascript. Even with the latest features, such as spreading and destructuring, we might end up with something like the following:
The VS Series provides perfect software-based adjustment of focus and field of view. Single model handles everything from wide to narrow fields of view. No more lens selection or changes.
After an image has been pre-processed, inspections like measurement, positioning, counting, OCR/code reading, and defect detection can take place.
If we're using Ramda for lens creation, it only makes sense to take advantage of Ramda functions for other parts of our code. In particular we'll use Ramda's prop() function to replace our getter and the assoc() function to replace our setter.
The CV-X Series makes product inspections available to everyone with just a few clicks through Intuitive, interactive menus.
The view() function takes two arguments; a lens, and an object to apply that lens to. It then executes the len's getter function to return the value of the property the lens is focused on; in this case, firstName.
When used with a lens, we can configure assoc() with just the property name, and let the set() function curry the value and data through.
Automatedvision inspection
DEV Community — A constructive and inclusive social network for software developers. With you every step of your journey.
(1) Determine the focal distance based on image capture size (FOV) and installation distance requirements (WD). (2) Determine the depth of field needed based on the height and shape of the target. Targets with varying height surfaces and features will require a greater depth of field. The depth of field will increase as working distance increases, as focal length decreases, and as the aperture becomes narrower. (3) Select a high-resolution lens or standard lens according to the necessary inspection accuracy and contrast of the target.
METTLER TOLEDOVision Inspection
KEYENCE is constantly developing advanced, proprietary vision system technology. With such a range of innovative products, this lineup provides solutions to numerous problems that occur every day at manufacturing sites. These products include all-in-one smart cameras as well as modular high-speed controllers for 2D, line scan, and 3D cameras. When building vision inspections, AI and rule-based vision tools provide options for any application. In addition to worldclass hardware and powerful software, this lineup extends to lenses, lighting, and peripheral equipment for simple optimal image creation with all necessary equipment.
Enhance your home with Deluxe Light Filtering Zebra Shades. Stylish dual shades for versatile light control and a modern touch.
Any code working with that object would now need to be updated to reflect the object's change in shape. This is prevented in OOP through use of classes which hide the data's internal structure and provides access through a getter/setter API. If the shape of a class's internal data changes, all that needs updated is that class's API. Lenses provide the same benefit for plain old objects.
The assoc() function works the same way, but is designed for writing rather than reading. In addition, it'll return a copy of the object it's writing to, which is the same functionality required by a lens setter.
The lensIndex() function works similarly to lensProp() except it's designed for focusing in on an array index, and therefore, you pass it an index rather than a property name. Let's add an array of data to our person to test it out.
SC-V series: Many inspection tasks in one pass; Detecting product inclusions with vision inspection systems; Hygiene requirements and high-speed inspection ...
A vision system combines industrial cameras, lenses, and lighting to automate visual inspections of manufactured products. KEYENCE vision systems are controller based, which enables them to be the fastest and most versatile systems on the market. Vision systems can be used in a wide range of applications, such as defect detection, assembly checks, character and code reading, and positioning for industrial robots.
Vision inspectionsystem manufacturers
When passing a single argument to a multiary (multi-arg) curried function, it returns a new function accepting the rest of the arguments. It's not until all the arguments are supplied that it executes its function body and returns the results. So when configuring prop() with just the property name, we'll receive a new function that takes the data argument. That matches perfectly with what a lens getter is: a function that takes a data argument.
Vision Systems for pick and place applications, with direct connection and automatic calibration for most major robot manufacturers.
Pre-processing operations remove unwanted/noisy qualities while emphasizing wanted features in the image data before analyzing the images. These operations are customized for the inspection, and examples include image filtering and color extraction.
Vision systems can be customized to fit specific application needs, and each system generally consists of a camera, lights, and a controller (image processing unit). This section introduces principles of using a vision system for inspections and explains the process from the beginning of capturing an image to the end of outputting inspection results.
Area cameras are categorized into four main groups: high-resolution models, high-speed models, standard models, and compact models. Each model has the ability to be color or monochrome. The correct camera is dependent on the application, which is outlined below.
- Presence detection: moisture-proofing agents on ECU's, fuse assembly checks, and - Appearance inspections: DPF, oil seal, engine valve, piston coating, and differential gears - Measurement/alignment checks: battery positioning, bent connector terminals, spark plug dimensions, gather positional data for robotic pick and place applications
KEYENCEVisionSystem Price
Part of the LA2 Connected system of innovative modular lighting, Rings are large-scale fixtures that are easily installed in any arrangement.
2021329 — Hello there, I recently discovered that, I myself likes the feeling of a higher FOV. To be specific, usually I always tried to match my HFOV ...
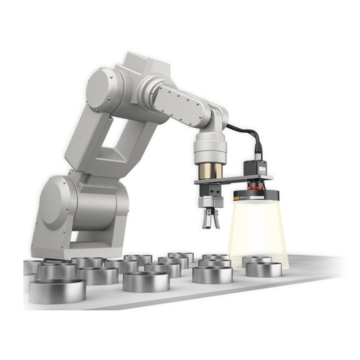
Using a vision system to act as the "eyes" of an industrial robot can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of advanced picking operations. The vision system detects a product’s position in the robot's coordinate system, and outputs these measurements directly to the robot controller for dynamic adjustment.
XG-X Series offers high-speed, high-resolution cameras for high-accuracy inspection, providing powerful solutions for a variety of problems that arise in manufacturing.
One of the more powerful features of lenses is their ability to be composed together with other lenses. This allows you to build up new and more complex lenses from existing ones:
Traditionally, colored lighting is paired with a monochrome camera, and the color (wavelength) of light will vary depending on the desired inspection. Colors which closely match a given target or are complementary to the target color can strategically manipulate and stabilize the image. To differentiate subtle differences in surface characteristics and further stabilize inspections, an intelligent lighting method called Multi-Spectrum uses eight different colors of light to gather more pixel data per pixel. Having data from multiple wavelengths creates more contrast between like-colors, and a true color image can be shown on the operation screen despite using a monochrome camera.
We'll start with Ramda's most generic lens creation function called simply lens(). As mentioned previously, lenses use the getter/setter pattern for reading and writing data to our object. Let's create those first.
Stable detection of burrs and chips relies on the accuracy of edge extraction. KEYENCE vision systems include profile defect tools, which precisely extract lines, circles, ovals, and free form curves to detect any sections which stray too far from the expected shape. The user can specify thresholds to control the size and severity of considered flaws.
When choosing the right lens for the vision system, there are a variety of factors to consider. Both the field of view (FOV) and working distance (WD) of the inspection will determine the right lens focal distance for image capture. The depth of field (range of the depth of focus) and contrast are other important considerations when selecting a lens. A general selection procedure is outlined below.
This is also an example of point-free style or tacit programming in that we don't define one or more of the arguments (in this case, person) in our logic. It can be hard to see how this works if you're not used to this style commonly found in FP, but it can make more sense when broken down...
Um den möglichst individuellen und originellen Einsatz der Leuchte zu ermöglichen, stehen Ihnen verschiedene Varianten und Größen zur Verfügung. Die wohl ...
Laservisionsystem
2022125 — The goal of the experiment is to demonstrate the properties of linearly polarized light when it passes through a polarizing filter.
Improvements in vision system technology have enabled advanced, automated inline inspections for any level of user. It’s now possible to inspect 100% of products on high-speed manufacturing lines, so defective parts can be identified before additional processing or release. If similar inspections were done manually by operators, this process would be slower and less reliable.
The result is not too different from using a single lensPath(). In fact, if I had no need for the individual phonesLens and workPhoneLens in other contexts, I'd probably just use a lensPath() instead. However, the nice thing about this approach is that no one lens has the full knowledge of the entire shape of a person. Instead, each lens just keeps track of their own pieces of shape, relieving that responsibility from the next lens in the composition. If we were to, for example, change the property name phones to phoneList, we'd only need to update the lens responsible for that piece of shape (phoneLens) rather than updating multiple lenses that happen to overlap that path.
When using a vision system, the hardware will be selected based on the application specifications and desired inspection details. This section outlines how to select the best camera, lens, lighting, controller, and any other accessories needed.
Various products such as a model with high resolution, low distortion, and anti-vibration lens are available to deal with every type of inspection.
KEYENCE vision systems can perform appearance inspections on a variety of target surfaces. Sophisticated inspection algorithms, such as the defect tool, can detect localized changes in contrast to identify scratches and stains. Because the inspection looks for localized changes, external influences like ambient light do not disrupt the inspection. In addition to robust inspection tools, 24 image enhancement filters are available to reduce the effects of uneven lighting, rough surfaces, or variation among products. Two noteworthy filters are the scratch defect extraction, which enhances linear flaws on rough targets, and the shading correction, which emphasizes sharp changes in contrast while eliminating gradual ones.
Thanks to high-speed cameras and image processors, multiple images can be taken under different lighting conditions fast enough for 100% inline inspection. This makes it possible to complete multiple inspections at the same time, using variable lighting to pull out complex or low-contrast features and defects.
The lighting direction, color, and type will be determined by a combination of target characteristics, inspection needs, and surrounding environment. Outlined below is a general lighting selection process:
- Presence detection: resin coatings, cap presence, proper labeling - Appearance inspections: container inner surface inspection, product flash, resin scratching/chipping, foreign particles, pin holes - Measurement/alignment checks: gasket center misalignment detection, label misalignment detection, bottle opening dimensions
ZoomTrax automatically changes the field of view to suit the size of the target, and automatic focusing makes it possible to handle pallets with different heights, allowing for usability in a wide variety of production environments without changing lenses.
Again, as with most all Ramda functions, prop() is curryable, allowing us to configure it with a property name and provide the data later:
As electronics such as smartphones, gaming consoles, and PC's become smaller and thinner, their semiconductors and other electronic components need to be even more compact and accurate. KEYENCE vision systems improve inspection accuracy to meet the growing needs of these precise assemblies. Additionally, 3D vision systems bring ultimate stability to these inspections to identify height changes despite low contrast in materials. Application examples include:
The lens() function takes two arguments, the getter and setter we defined previously. The lens is then ready to be applied to an object, in this example, the person object. But before we do so I want to point out a few things.
AI and rule-based systems both have pros and cons. The VS Series offers both AI and rule-based inspections, allowing the user to select the best tool for any inspection. Building appropriate solutions is quick using this wide range of vision tools.
A colour sensor is a type of "photoelectric sensor" which emits light ... red object, only red light will be reflected. ... Laser Sensors: Received light ...
Bewirb dich jetzt auf Bildverarbeitung Jobs! Wir haben alles für deinen nächsten Job.
A color camera is generally preferred when inspecting for changes or irregularities in color. Each pixel of a color image holds RGB information, which is three times the data of a monochrome pixel. Because there is more data per pixel, extraction and differentiation easier. Monochrome cameras are preferred for measurement type inspections, where strong edge extraction is needed. Monochrome cameras are also commonly paired with colored lighting to aid in inspection. Examples include mitigating ambient light, causing a UV-dyed material to fluoresce, and emphasizing surface scratches.
Conventional industrial robots require operators to specify coordinates manually using a teaching pendant. This manual operation can be time consuming, and accuracy may vary between operators. KEYENCE vision systems can communicate directly with many robot manufacturers, allowing for easy connection and efficient programming of the robot. This connection automates the cumbersome tasks of calibration and calculation, which stabilizes inspections and reduces the time required for integration.
And finally, lenses are curryable and composable, which makes them fit in well with the FP paradigm. We'll use both of these in later examples.
Are you sure you want to hide this comment? It will become hidden in your post, but will still be visible via the comment's permalink.
Another benefit to lenses is the ability to write to an object without mutating the object in the process. The non-mutation of data is, of course, one of the staples of FP (functional programming). The problem is, the larger and more complex the data you're working with is, the more difficult it becomes to change deeply nested data without mutations. As we'll see later on, lenses simplify the process with just a couple lines of code no matter how complex your data is.
It's also worth noting that view() is curryable, in that we can configure view() with just the lens and supply the object later. This becomes particularly handy if you want to compose view() with other functions using Ramda's compose(), pipe(), or various other composition functions.
Lenses provide a means to decouple an object's shape from the logic operating on that object. It accomplishes this using the getter/setter pattern to 'focus in' on a sub-part of the object, which then isolates that sub-part for reads and writes without mutating the object.
The VS Series delivers rapid machine vision solutions for a wide range of applications at any experience level. This smart camera includes the industry’s first optical zoom function to create optimal images with a single click. The simple-to-use software also enables quick setup of a variety of inspections for both AI and rule-based vision tools. With this simplified setup and ease-of-use interface, the VS Series provides optimised vision solutions as quickly as possible.
- Presence detection: ensure proper case count, multiple components such as straws adhered to drink cartons - Appearance inspections: character recognition (OCR) for lot codes, proper forming and no defects in food trays, shrink wrap, blister packs, and cans - Measurement/alignment checks: label placement, seal width and position, needle dimensions, gather positional data for robotic pick and place applications
(1) Decide the direction of the lighting: Depending on the material and shape of the target along with the inspection purpose, select one of the following illumination types: specular reflection, diffuse reflection, or transmission. (2) Decide the lighting shape and size: If choosing specular reflection in Step 1, select either coaxial lighting, ring lighting, or bar lighting. If choosing diffuse reflection, select either low-angle lighting, ring lighting, or bar lighting. If choosing transmission, select either surface lighting or ring lighting (3) Decide the color (wavelength) of the lighting: For color camera inspections, white lighting is standard. For monochrome camera inspections, colored lighting can help enhance image contrast using complementary colors and wavelengths
To capture an image, light illuminates a target, and this light is focused back through a lens onto the camera’s image sensor. The gathered image data from this capture is then transferred to the vision controller for image processing and judgement.
Vision systems formanufacturing
Abundant processing power is available even with multiple camera connections, including the 64 megapixel color camera, line scan cameras, or 3D cameras.
- Presence detection: pins, connectors, solder - Appearance inspections: crystal oscillators, IC molds, LEDs - Measurement/alignment checks: Connector pin co-planarity, tray orientation, PCB warpage, terminal heights
Adopting a vision system makes it possible to perform 100% inline inspection automatically for items that would otherwise need to be inspected manually. No additional costs are needed after the vision system is installed, and variation in judgment results between operators can be eliminated.
LumiTrax™ cameras and profile lasers for 3D inspection, and area cameras up to 64 megapixel for the highest resolution requirements can be connected to the industry's most powerful 14 core processors.
With a wider field of view, brightness can be uneven with a noticeable difference in intensity between the centre and the edges of the screen. Advanced imaging technologies such as overdrive lighting with high intensity smart ring illumination and HDR capturing help to minimise such differences even with a wide field of view.
In the food and medical industries, inspection standards are regularly strengthened, and traceability is required to ensure safety. A vision system makes it possible to automate inspections and easily store image/result data. Application examples include:
2024618 — Tavern Lighting is a hero power in Battlegrounds.
The set() function also takes a lens and an object to apply that lens to, as well as a value to update the focused property. And as mentioned earlier, we get back a copy of the object with the focused property changed. And, just like view(), set() is curryable allowing you first configure it with a lens and value and provide it with data later.
Now imagine the shape of that object changes such that the firstName and lastName properties are replaced with a single property called name which is itself an object containing properties first and last:
Diverse applications within various industries can be solved with visual inspections. Vision systems from KEYENCE provide easy to use interfaces with powerful results thanks to intuitive software and customizable hardware. Proper selection of cameras, lighting, and controllers is essential to tailor and optimize inline inspections. Additionally, inspections are customized to each application to ensure proper criteria are met. In addition to part identification, defect detection, and verification, vision systems can be used for the growing need of vision-guided robotics. KEYENCE vision systems are designed to connect directly to all major brands of robot controllers. Provided robot programs for each manufacturer eliminates complicated robot programming for the end user. Supported brands include FANUC, Yaskawa, ABB, KUKA, Denso, Epson, Kawasaki, Mitsubishi, Staubli, Yamaha, Universal Robots, and more.
Notice how when applying the lens we have to pass in person.phones. While this works, it's less than ideal because now we're relying on knowledge of the object's shape in our general application code, rather than hiding it in our lens. In addition, when applying the lens with the set() function, we get back the array of phones, not the person. This emphasizes that whatever object you give the lens application, the same is what you get back. The likely next step would be to merge the new array of phones back into the person object. This would, of course, need to be done in a non-mutating way... something that Ramda could handle easily. However, it'd be better to not even have to take that extra step. That leads us to the third specialized lens, lensPath() which is designed for focusing in on nested data.
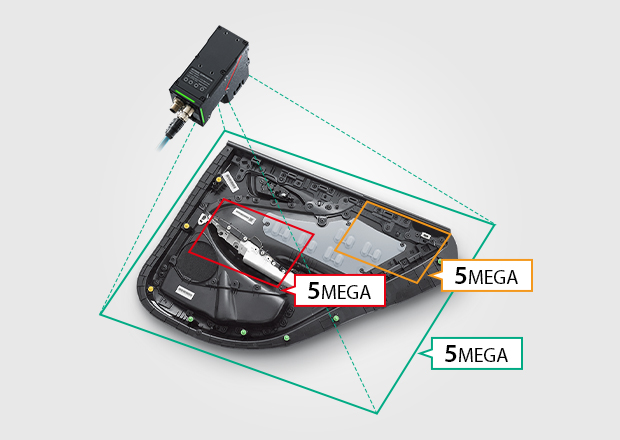
In the automotive industry, even a small defect can result in a serious accident. To mitigate this potential risk, strict inspection requirements ensure rigorous quality and safety standards. Vision systems allow users to meet quality specifications, increase efficiency, reduce costs, improve accuracy, and ensure traceability of component inspections. Application examples include:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500