Brennweite von Objektiven - Teil 1 - brennweite objektiv
Helping research labs with tools and equipment like Mitutoyo M Plan APO 50x/0.55na Objective since 1977.
For example, in the medical field, lasers are used in medical tools such as laser scalpels, as well as in medical treatments. In communications, high-capacity, high-speed optical communications cannot be achieved without lasers. In the construction field, measuring instruments using lasers are used to make sure structures are level and to measure distances between features.
Ahmed, Usman. (2022, November 02). What is the Role of Lenses in Microscopy?. AZoOptics. Retrieved on November 25, 2024 from https://www.azooptics.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=2339.
Microscopic lenses result in higher magnification of the object under examination to the observer. At higher magnification, it becomes easy to analyze even minute details of the object. By using multiple lenses in a microscope, object image becomes clearer and easier to examine. With the help of multiple lenses, an object image can even be magnified more than 1000 times.
What are the 3types oflasers
Description Specifications Resources T-thread Extension, 30mm length. Outside Diameter: 1.84" (46.7mm) Overall Height: 1.38" (35mm) Clear Aperture: 1.5" ...
The blank is clamped into a vice and kept in place beneath a diamond-tipped, cylinder-shaped cutter that spins at high speed. The blank's surface is trimmed with this cutter in the desired curvature.
A microscope uses two smaller lenses, i.e., an objective lens near the sample and an ocular lens near the observer. The magnification of both these lenses can be the same or different from one another. Multiplying the magnification of each lens yields the overall magnification of the microscope. With a 10x ocular and a 30x objective, the microscope's total magnification is 300x.
A microscope is used to magnify the image of tiny objects. The objects are clearly seen with a microscope because at least one lens magnifies the image. This lens refracts the light so that it enters the eye and magnifies distant objects.
Usman holds a master's degree in Material Science and Engineering from Xian Jiaotong University, China. He worked on various research projects involving Aerospace Materials, Nanocomposite coatings, Solar Cells, and Nano-technology during his studies. He has been working as a freelance Material Engineering consultant since graduating. He has also published high-quality research papers in international journals with a high impact factor. He enjoys reading books, watching movies, and playing football in his spare time.
When atoms absorb energy from external sources, they transition from a low-energy state to a high-energy state. This is known as excitation.
・Monochromaticity (all of the light in a laser has the same wavelength)・High directivity (all of the light travels in the same direction)・High coherence (all of the light has the same wavelength and is in phase, i.e., the peaks and troughs are aligned)・High energy density (because laser light has high directionality, all of the light energy is concentrated in a single direction)
Fowler, S. A., & Allansmith, M. R. (1981). The Effect of Cleaning Soft Contact Lenses: A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study. Archives of Ophthalmology, 99(8), 1382–1386. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/633879
Types of laser lightand their uses
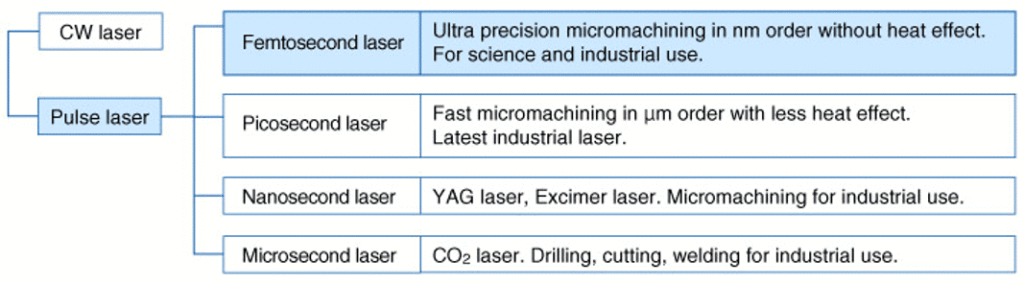
Lasers can also be classified according to the laser oscillation method. There are two types of lasers: continuous wave lasers that emit laser light continuously, and pulsed lasers that emit light in pulses. Pulsed lasers are further classified into microsecond, nanosecond, picosecond, and femtosecond lasers according to the pulse length. Machining performance varies with each pulse length. For example, a femtosecond laser with a pulse length of approximately 100 fs (femtoseconds) can perform nanometer-order ultrafine processing without thermal effects.
To return to a lower energy state, the electrons release some energy as light. This release of energy is known as spontaneous emission.


Lasers can be broadly categorized as continuous-wave lasers, which emit light continuously, and pulse lasers, which emit pulses of energy. Very short pulses of light can be emitted.
Quarter Ball ¼-Turn Ball Valve Frost Proof Sillcock; 12" Wall Thickness; ½ m.p.t. x ½ Copper Inlet Connection QB-112MC : Amazon.ca: Patio, Lawn & Garden.
Normal visible light is made up of a mixture of light with different wavelengths travelling in all directions. In contrast, laser light is made of a single wavelength of light and travels unidirectionally. Because laser light travels so straight, it is possible to focus all of the light and its energy into a very small area and increase the density of the transmitted energy.
Shop Solar Eclipse Glasses - Solar Filters Glasses with Solar Safe Filter Technology - CE and ISO Certified 2024 - 10-Pack MedicalKingUsa at Target.
The laser light produced by stimulated emission is amplified by an optical resonator (resonant optical cavity). The resonator consists of two mirrors. A laser beam whose half wavelength is a whole fraction of the distance between the mirrors (a harmonic) is repeatedly reflected between the mirrors. As a result, stimulated emission of light occurs in a chain reaction, generating a large amount of light with the same wavelength and phase, thereby creating powerful laser light.
The raw materials and specific optical glass are combined in the correct ratios. This cullet (i.e., optical glass) serves as a flux. A flux helps lower the temperature at which raw materials normally react. A glass furnace is typically used for melting this mixture around 1400 °C. The temperature may fluctuate depending on the type of lens being manufactured.
The lens the observer looks through when using a microscope is called an ocular lens. It takes light from the objective lens and re-magnifies it to show a large image. In most cases, the ocular lens magnifies 10x or 15x.
When an electron in an excited state is struck by light of the same energy, it emits light of the same energy, phase, and direction. This phenomenon, in which one unit of light produces two units of the same light, is called stimulated emission. This is the fundamental basis for laser light.
Most compound microscopes use four objective lenses, including a low-power lens, a high-power lens, a scanning lens, and an oil-immersion lens.
After cutting, a lens inspection is carried out, and if the required curvature is not achieved, cutting is done again. This process requires a few minutes to well over an hour.
How manytypes of laser
The optical properties of optical glass depend highly upon its composition, which includes a mixture of boron oxide, sodium oxide, barium oxide, zinc oxide, potassium oxide, or lead oxide.
The word laser is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Lasers are created by exciting the electrons in gasses, liquids, or solids to a high energy state and emitting that energy as light. Lasers have the following properties:
YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) lasers that use YAG crystals as the laser medium, and ruby lasers that use sapphire crystals doped with chromium are examples of solid-state lasers. Solid-state lasers are powerful and able to achieve high outputs compared to their size.
Ahmed, Usman. "What is the Role of Lenses in Microscopy?". AZoOptics. https://www.azooptics.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=2339. (accessed November 25, 2024).
While examining a slide or an object in a microscope, the lens closest to it is called the objective lens, which collects light and increases the magnification of the object being examined.
Types oflasers for skin
Registered members can chat with Azthena, request quotations, download pdf's, brochures and subscribe to our related newsletter content.
The VINCI series of ultrafast fiber lasers has a central emission wavelength of 1064 nm and features a unique combination of short pulse durations.
Laser processing is especially ideal for microfabrication of extremely hard materials such as diamond, sapphire, quartz glass, and ceramics, as well as materials that are prone to cracking and chipping.
When atoms are exposed to light, their electrons absorb the light energy and transition from the lowest energy state (the ground state) to a higher energy state. As they absorb energy, the electrons move from their normal orbitals to outer orbitals.
Magnesium fluoride is commonly used as an anti-reflective coating on lenses. If a microscope contains a mirror, it is often made up of Pyrex glass. Silica (SiO2) is often used as a protective coating for mirrors, whereas aluminum is used for reflective coatings.
Types of laserin Physics
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Semiconductor lasers use semiconductors such as GaAsP (gallium arsenide phosphide), InGaAsP (indium gallium arsenide phosphide), and GaN (gallium nitride) as lasing media. Although semiconductors are solids, they are categorized as a separate laser type. They are widely used in applications such as optical communications light sources, printer light sources, audio player light sources, and laser pointers.
Optical glass is often used to create microscopic lenses. It is considerably more uniform and has higher purity than conventional glass.
While we only use edited and approved content for Azthena answers, it may on occasions provide incorrect responses. Please confirm any data provided with the related suppliers or authors. We do not provide medical advice, if you search for medical information you must always consult a medical professional before acting on any information provided.
There are various kinds of microscopes used for magnification. An optical microscope is the most common type, creating an image from visible light using lenses. Another commonly used type of microscope is an electron microscope which uses an electron beam to form images.
Normal light is made up of different wavelengths of light that are not in phase with each other, i.e., the peaks and troughs of each wave are unrelated to the others. Laser light, in contrast, is completely synchronized, with the peaks and troughs of the light waves always being in phase. This is known as coherence.
Your questions, but not your email details will be shared with OpenAI and retained for 30 days in accordance with their privacy principles.
Types of laserwith example
CO2 lasers have a long wavelength (10.6 μm) and are used for a range of applications such as drilling, cutting, and marking of paper, cloth, plastic, rubber, and wood. By increasing the energy output, they can also be used for welding and cutting metals.
YAG lasers with a wavelength of 1064 nm are common solid-state lasers. They are frequently used in industrial applications such as metal cutting, welding, drilling, fine hole processing, and marking. However, transparent objects such as glass, diamond, and sapphire cannot be processed with this laser, because their transparency renders them unaffected by this particular frequency of light.
Thickness; Surface; Milled Thickness; Length; Width; FSC® Certification. White Oak Prime Lumber. 13 Products. Configure: Thickness; Surface; Milled Thickness ...
A conventional microscope employs numerous lenses and a light source to significantly enhance the image of the object under examination.
Gas lasers include CO2 lasers that use carbon dioxide gas as the lasing medium, and excimer lasers that use a mixture of gases such as rare gases and halogens.
These lenses provide magnification of 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x, respectively. Generally, shorter lenses have less magnification power than longer ones.
Below is a typical structure of a resonator for producing laser light. A laser medium, the substance that is the source of the stimulated emission, is placed between optical resonators with mirrors facing each other. The excitation source excites the electrons to a higher energy state (called pumping). There are various excitation sources, such as light, electric current, and chemical reactions, depending on the type of laser.
Lasers can be used in instruments that make very exact measurements of length, detect the presence or absence of flaws, and discern missing parts while performing very precise measurements quickly. Lasers are also used for various processes such as cutting, marking, drilling, and welding.
These F-theta lenses by Avantier are designed for consistent spot size and uniform field curvature correction, ideal for high-resolution imaging applications.
Furthermore, if a femtosecond laser with a pulse length of 100 fs is used, the laser irradiation ends before any heat is transferred to the material. As a result, nanometer-order ultra-fine processing is possible without cracks or debris (substances that are melted and vaporized by the laser and redeposited on the processed surface) caused by heat. A hole diameter as small as 0.5 μm can be achieved with aspect ratios up to 100. Surface roughness of Ra ~ 0.01μm with no work-affected layer can be achieved.
The compound microscope uses a series of lenses to magnify the image. These lenses are made of optical glass, which is significantly purer and clearer than regular glass.
In order to generate laser light by stimulated emission, a state in which there are more electrons in high energy states than in low energy states is required. This state is called “population inversion.” This allows more light to be stimulated and emitted than is absorbed, producing laser light.
Reuven Silverman of Ophir discusses the critical role of M2 measurements in laser technology for optimization and quality control in various industries.
Now! Shop Bi-Mart & Cascade Farm & Outdoor Online, Pick Up at Your Local Bi-Mart Store Learn More · Logo for Bi-Mart Employee owned. Real Value. Every Day.
27/64. 10.7156. 59/64. 23.4156. 7/16. 11.1125. 15/16. 23.8125. 29/64. 11.5094. 61/64 ... Convert 2-51/64 inches into millimeters. From Table II. 2-25/32 inches = ...
The shape of the lens has a considerable effect on the refraction of light. In microscopes, convex lenses are usually employed because of their ability to concentrate light on a specific spot.
LIS Technologies is on the road to transforming nuclear fuel enrichment through advanced laser techniques, ensuring a sustainable and cost-effective approach to energy production.
Types of laserPDF
The human eye's biological lens is also convex because it focuses light onto the retina, where rod and cone cells are located to enable vision.
A condenser lens is located between the light source and the slide platform. It focuses the beam of light on the object and further passes it to the objective lens. The diaphragm controls the quantity of light entering the condenser lens. Anytime a different objective lens can be used to view the item, the amount of light entering the lens can be changed. With magnifications of 400x or more, condenser lenses are very useful.
A representative liquid laser is the dye laser. Dye lasers use an organic dye as the medium, in which dye molecules are dissolved in an organic solvent such as ethylene glycol, ethyl, or methyl. They are mainly used for scientific and medical purposes.
Learned B-spline parametrization of lattice focal coding for monocular RGBD imaging. We employ B-spline parameterization for the DOE surface geometry ...
Types of laserppt
Light is a type of electromagnetic wave. There are many types of electromagnetic waves, such as microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, x-rays, gamma rays, etc. Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths between 360 nm to 830 nm can be detected with our eyes. These are called the visible light spectrum. Electromagnetic waves in this range reflect off of objects and enter our eyes, where we process them into the colors and images we see.
For example, pulse oscillation UV lasers with a wavelength of 355 nm can be used to create micro-holes in transparent materials with high hardness such as diamond and sapphire. For sapphire, holes with a diameter of 60 μm and an aspect ratio of 30 can be drilled. With a pulsed laser, the material is irradiated for a very short time. This makes it possible to obtain a smooth processing surface while minimizing the process deterioration layer that can be caused by thermal effects.
The mixture becomes a very thick liquid and is poured into lens molds at this stage. The annealing is carried out at 500 °C after cooling the mixture to approximately 300 °C. Annealing helps eliminate the internal stresses developed during the early cooling phase and weakens the glass. The glass is then gradually cooled to room temperature, and pieces are removed from the molds. These pieces are called blanks.
Lorenz, K. O., Kakkassery, J., Boree, D., & Pinto, D. (2014). Atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy analysis of daily disposable limbal ring contact lenses. Clinical and Experimental Optometry, 97(5), 411–417. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cxo
Electrons in their excited states are unstable and continually try to stabilize by returning to a lower energy state. This is called transition.
A microscope is an additional lens placed in front of your eye. The microscope lens functions like a magnifying glass, bending light to make the object appear wider to get the desired magnification effect. However, a single large lens provides blurry and dark images.
Scanning Electron Microscopy is used to examine morphology (physical features) of size ranging from many microns to a few nanometers. The advantages over an ...
Ahmed, Usman. 2022. What is the Role of Lenses in Microscopy?. AZoOptics, viewed 25 November 2024, https://www.azooptics.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=2339.
Zhang, Y., & Gross, H. (2017). Systematic Design of Microscopic Lenses. Optical Design and Fabrication 2017 (Freeform, IODC, OFT) (2017), Paper IW4A.1, IW4A.1. https://opg.optica.org/abstract.cfm?uri=IODC-2017-IW4A.1
Lasers are categorized based on the laser medium. There are solid-state lasers, gas lasers, liquid lasers, and semiconductor lasers.
Furthermore, the surface morphology of materials can be observed with the help of a tunneling microscope. Such microscopes use a beam of electrons that can tunnel through the surface of objects at incredibly small distances and form an image of the surface.
To drive air bubbles to the surface, the temperature is raised to 1550 °C. The mixture is then steadily cooled to 1000 °C with continuous agitation.
Ahmed, Usman. "What is the Role of Lenses in Microscopy?". AZoOptics. 25 November 2024. .
The second harmonic of the YAG wavelength is 532 nm. YAG lasers of this wavelength are known as “green lasers” and are used for fine hole processing and silicon wafer marking. The third harmonic (355 nm) and fourth harmonic (266 nm) YAG lasers are called “UV lasers” and are used in ultra-fine drilling, cutting, stereolithography, and similar applications. UV lasers have very high energy, which can be amplified by focusing the laser with a lens to create very high energy densities. UV lasers can therefore be used for very fine processing of transparent materials such as diamond and sapphire.
The Klein LL5 Long-Arm Hex Key is made from top-grade alloy steel that is heat-treated and tempered for added strength and durability. The long side allows ...
Lasers are different from ordinary visible light. Because of their special properties, they are used in a wide variety of applications, from industry to medicine and communications to entertainment.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500