Before Ships Used GPS, There Was the Fresnel Lens - how does a fresnel lens work
mach-zehnder interferometer pdf
The Huygenianeyepiece is the most basic negative eyepiece configuration used on most teaching and laboratory microscopes with achromatic objectives. Negative eyepieces have two lenses The eye-lens, which are nearest to the observer's eye, are called the eye-lens, and the field lens, which is behind the diaphragm, is also called the field lens.
The stage refers to the horizontal surface on which the slide is mounted. Spring-loaded clips hold the slide in place, and gear knobs on the stage allow it to travel around the stage. Two perpendicular scales are available on the stage for recording the location of an object on a slide.
The majority of microscopes have a parfocal lens. By switching from one objective to the next, this term refers to the microscope remaining in focus.
Mach zehndermanual
Negative eyepieces with an internal diaphragm and positive eyepieces with a diaphragm below the lenses are the two main types of eyepieces classified according to lens and diaphragm arrangement.
A monofocal intraocular lens (IOL) is a single-focus intraocular lens. Monofocal IOLs may be chosen for close focus, mid-distance focus, or distant focus by a cataract surgeon. Only one of these three options is available, and the priority will remain the same following surgery.
Mach zehnderprice

It is a type of intraocular lens. Both near and far objects can be in focus simultaneously with this intraocular lens design, which corrects for both near and distant vision.
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Mach-Zehnder interferometer experiment
A condenser is an apparatus at the base of most microscopes that condenses light rays through a solid beam. The amount of light that passes through the condenser is regulated by a diaphragm. The light microscope has both coarse and fine adjustments.
Ophthalmology is a medical and surgical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases. Ophthalmologists can treat eye diseases such as cataracts, proptosis, glaucoma, etc.
The image is magnified by the ocular lens, also known as an eyepiece. It has an ocular micrometer, which is a measuring scale. There are no units on the ocular micrometer.
Mach-Zehnder interferometer optical fiber
The objective lens collects light from the sample, magnifies the image, and projects the enlarged image into the body tunnel. Since no single objective lens may meet all of a user's needs, the rotating nosepiece is equipped with multiple objective lenses of varying magnification and numerical aperture.
mach-zehnder pronunciation
The word ‘ocular’ means connected to the eye. An eyepiece, also known as an ocular lens, is a lens used in optical devices. It is called so because someone looks through the device; it is normally the lens that is nearest to the eye.
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Although originally designed for OCT systems, this clock can also be used for other synchronization applications.For more details on the clock, please see the Operating Principles Tab.
Light is projected through an opening in the level, hitting the object and then entering the objective to magnify it. An image is produced, and this image serves as an object for the ocular lens to magnify. The magnification obtained by the target compounded by the magnification achieved by the ocular lens equals the total magnification achievable with the microscope.
Note: Custom models are available with a choice of free spectral range and wavelength. Please contact Tech Support for more information.
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Toric IOLs: This is a monofocal IOL that aids in the correction of astigmatism. Astigmatism is a defect in refraction in which light is not focused uniformly on the retina. At any distance, this causes blurry or blurred vision. Astigmatism may be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or laser eye surgery. It may be more expensive than a monofocal IOL because it's a luxury lens.
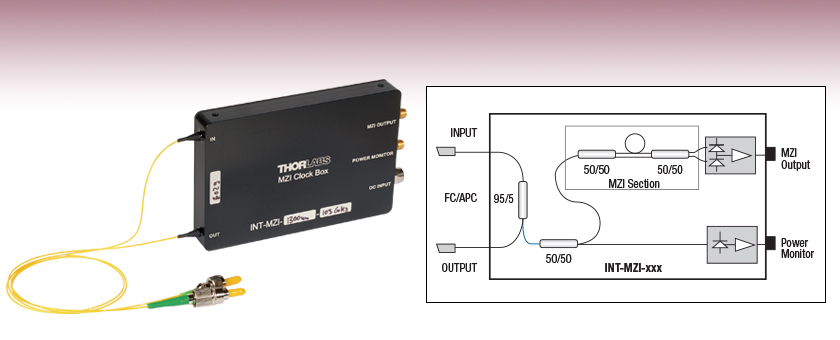
Rapidly swept laser sources typically use sinusoidal tuning elements to achieve the very fast optical frequency sweep speeds required for OCT imaging applications. Hence, accurate and reliable re-calibration of the OCT signal is required so that the final data points are equidistant in frequency. The Thorlabs swept source laser features a built-in Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) with balanced detector output that can be used for just this purpose. A frequency clock is derived from the zero crossings of the MZI interference fringe signal; these zero crossings are equally spaced in optical frequency (k-space). While this clock is intended for OCT applications, it can also be used in other synchronization applications.
The schematic of the system is shown in figure 2 below. An internally fiber network is used to tap 5% of the input light to generate Power Monitor and k-clock signals. The remaining light is transmitted to the Output pigtail. Specially designed couplers are used to achieve a flat wavelength response for both the transmitted and the Power Monitor signal. (see figures 3 and 4 below). Both signals of the MZI are detected by an ultra-low noise amplified balanced photo detector.
On the rotating nosepiece are many objective lenses with varying magnification and numerical aperture. For the objective lens to be properly aligned, the nosepiece must click into position.
Mach-Zehnder modulator
Certain classes of optical objects, most lenses, are used in some optical instruments such as telescopes, infrared viewers, and microscopes and are referred to as objectives and ocular lenses. Eyepieces pair up with microscope objectives to magnify the intermediate image even further, allowing specimen information to be seen. The ocular lens is on the side of the observing eye, while the objective is on the side of the observed object. Professional optical instruments usually allow for the simple ocular exchange and the use of oculars with various parameters. It is typically housed in a cylindrical housing and contains a single optical lens or a combination of lenses (barrel).
A compound light microscope usually has four objective lenses: a scanning lens (4X), a low-power lens (10X), a high-power lens (40 X), and an oil immersion lens (40 X) (100 X). The total magnifications possible with a 10x ocular lens are 40 X with the scanning lens, 100 X with the low power lens, 400 X with the high power lens, and 1000 X with the oil immersion lens.
Mach-Zehnder interferometer
Thorlabs' Mach-Zehnder interferometer clock box subassemblies are designed to be used inside a swept source OCT system with a central wavelength of either 850 nm or 1300 nm. The internal fiber couplers are optimized for flat wavelength responses and coupling losses that have a very low polarization dependence, which make the output signals independent of input polarization changes. The clock box contains two detectors, providing a power monitor signal and a k-clock signal that monitors the output frequency of the swept source. Both outputs have a 200 MHz bandwidth, and the k-clock uses a balanced detection scheme to maximize rejection of common mode noise.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500