Antique & Vintage Magnifying Glasses for Sale in Online ... - vintage silver magnifying glass
Shop Cost Plus World Market Full Length And Floor Mirrors at Kashew, Your Home For Branded, Vintage & Sustainable Furniture. ✓ Professional Delivery Across ...
Achromatic lens for telescope
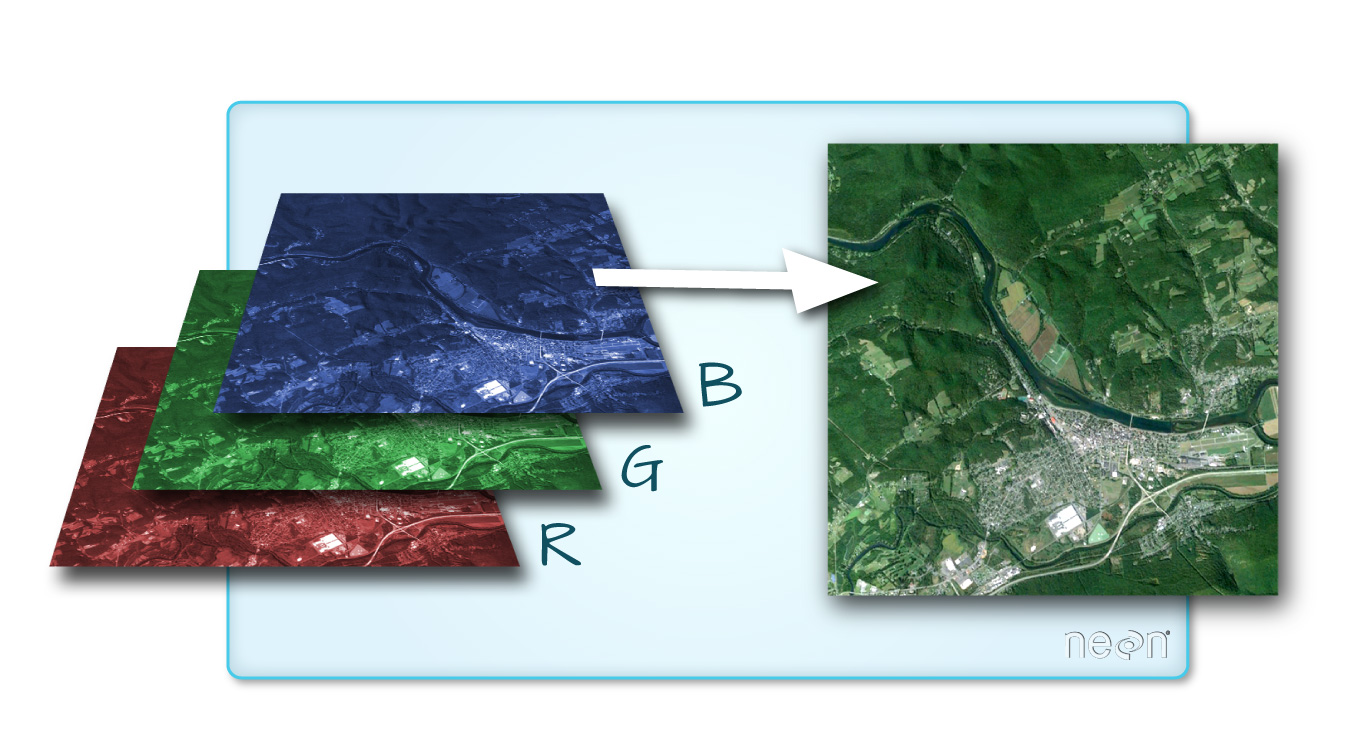
One type of multispectral imagery that is familiar to many of us is a color image. A color image consists of three bands: red, green, and blue. Each band represents light reflected from the red, green or blue portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The pixel brightness for each band, when composited creates the colors that you see in an image. These colors are the ones your eyes can see within the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Just like you did with single band rasters, you will use the rasterio.open() function to open multi band raster data in Python.
When talking about spectral data, you need to understand both the electromagnetic spectrum and image bands. Spectral remote sensing data are collected by powerful camera-like instruments known as imaging spectrometers. Imaging spectrometers collect reflected light energy in “bands.”
If the image has a 4th NIR band, you can create a CIR (sometimes called false color) image. In a color infrared image, the NIR band is plotted on the “red” band. Thus vegetation, which reflects strongly in the NIR part of the spectrum, is colored “red”. CIR images are often used to better understand vegetation cover and health in an area.
Note there are four bands below. You are looking at the red, green, blue and near infrared bands of a NAIP image. What do you notice about the relative darkness / lightness of each image? Is one image brighter than the other?
Learn how to calculate seasonal summary values for MACA 2 climate data using xarray and region mask in open source Python.
What is an achromatic lens used for
In the previous weeks of this course, you learned about lidar remote sensing. If you recall, a lidar instrument is an active remote sensing instrument. This means that the instrument emits energy actively rather than collecting information about light energy from another source (the sun). This week you will work with multispectral imagery or multispectral remote sensing data. Multispectral remote sensing is a passive remote sensing type. This means that the sensor is measuring light energy from an existing source - in this case the sun.
You can plot each band of a multi-band image individually using a grayscale color gradient. Remember from the videos that you watched in class that the LIGHTER colors represent a stronger reflection in that band. DARKER colors represent a weaker reflection.
Our website utilizes cookies to enhance your browsing experience and to present you with content tailored to your preferences on this device and browser. Below, you will find detailed information about the function of cookies, enabling you to make informed choices about which cookies you wish to accept. Please note that disabling certain cookies might impact your user experience on our site. It's important to remember that cookie preferences need to be set individually for each device and browser you use. Clearing your browser's cache may also remove your cookie settings. You have the freedom to modify your cookie preferences at any point in the future.
Achromatturntable mat
Climate datasets stored in netcdf 4 format often cover the entire globe or an entire country. Learn how to subset climate data spatially and by time slices u...
This is accomplished using one or more lenses. What is lens formula and magnification? The lens formula is 1/f = 1/Do + 1/ ...
Jan 27, 2022 — Aside from the familiar point-of-view, 35mm lenses (with the 35mm prime lens options in particular) make for versatile, portable and accessible ...
Oct 5, 2013 — Bills hot rod brackets @ americanpastimes. WWW.AMERICANPASTIMES.COM IS A DEALER FOR BILLS HOT ROD SHOP. TAKE A LOOK AT THERE LINK, LOTS OF ...
Historic and projected climate data are most often stored in netcdf 4 format. Learn how to open and process MACA version 2 climate data for the Continental U...
We utilize essential cookies to ensure our website operates effectively and remains secure. Additionally, we'd like to request your permission to use optional cookies. These are intended to enhance your browsing experience by offering personalized content, displaying advertisements that are relevant to you, and helping us to further refine our website.
While a general spectral resolution of the sensor is often provided, not all sensors collect information within bands of uniform widths.
Achromatic color
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS) instrument is another satellite based instrument that continuously collects data over the Earth’s surface. MODIS collects spectral information at several spatial resolutions including 250m, 500m and 1000m. You will be working with the 500 m spatial resolution MODIS data in this class. MODIS has 36 bands however in class you will learn about only the first 7 bands.
These cookies collect information about your browsing habits to show you personalised adverts. They may be used to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other sites. They don't store directly personal information, but are based on uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you don't allow these cookies, the adverts you see will be less relevant.
If high resolution data shows you more about what is happening on the Earth’s surface why wouldn’t you always just collect high resolution data (smaller pixels)?

To better understand multispectral remote sensing you need to know some basic principles of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Achromatpronunciation
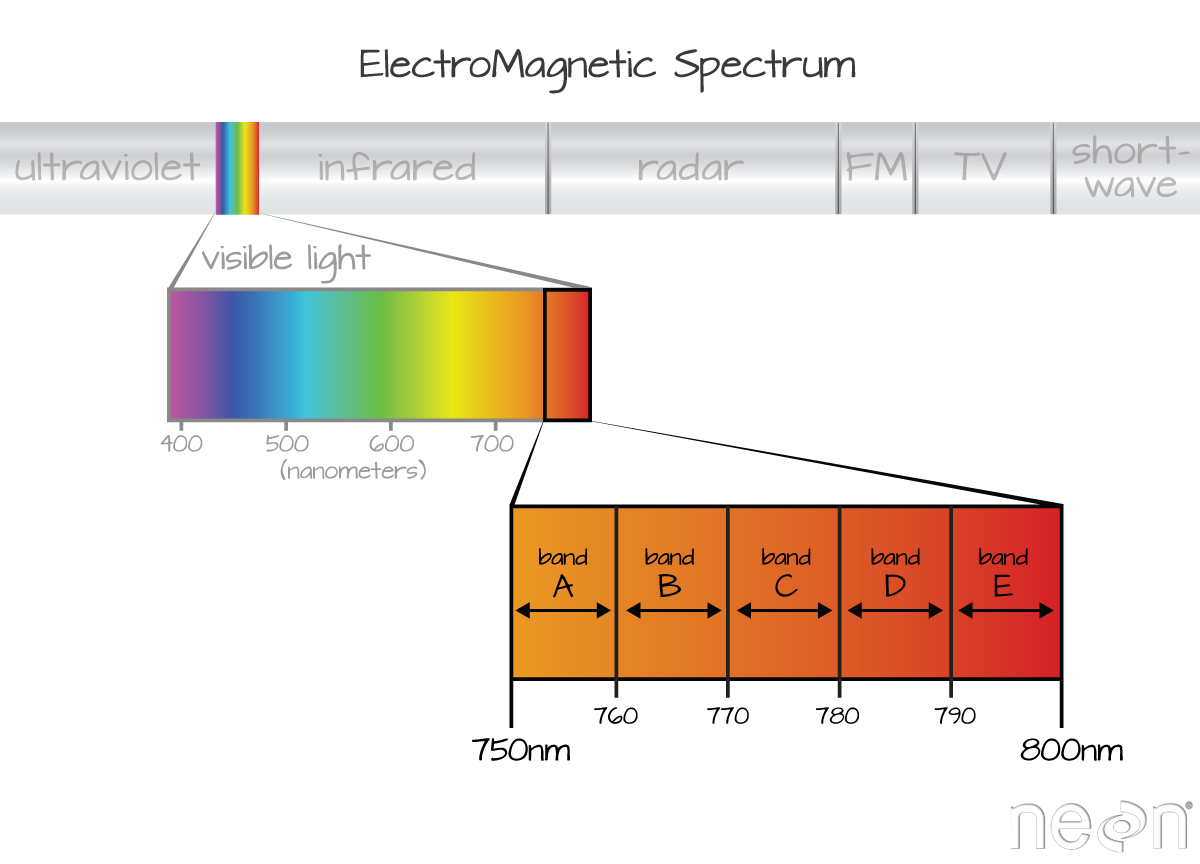
The electromagnetic spectrum is composed of a range of different wavelengths or “colors” of light energy. A spectral remote sensing instrument collects light energy within specific regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Each region in the spectrum is referred to as a band.
Often when you work with a multispectral dataset, the band information is reported as the center wavelength value. This value represents the center point value of the wavelengths represented in that band. Thus in a band spanning 800-850 nm, the center would be 825 nm.
"controller" auf Deutsch ; pressure controller holder · Halter für Druckregler ; activate controller release · Reglerfreigabe aktivieren ; regulator controller ...
The spectral resolution of a dataset that has more than one band, refers to the spectral width of each band in the dataset. In the image above, a band was defined as spanning 800-810 nm. The spectral width or spectral resolution of the band is thus 10 nm. To see an example of this, check out the band widths for the Landsat sensors.
These cookies are needed for the website to work and for us to fulfil our contractual obligations. This means they can't be switched off. They enable essential functionality such as security, accessibility and live chat support. They also help us to detect and prevent fraud. You can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but it means some parts of the site won't work.
Jun 13, 2020 — […] Key Lesson: When I refer to ISO values, I am talking about the traditional ISO scale that goes as follows: 100, 200, 400, 800, 1600, 3200, ...
A band represents a segment of the electromagnetic spectrum. You can think of it as a bin of one “type” of light. For example, the wavelength values between 800 nanometers (nm) and 850 nm might be one band captured by an imaging spectrometer. The imaging spectrometer collects reflected light energy within a pixel area on the ground. Since an imaging spectrometer collects many different types of light - for each pixel the amount of light energy for each type of light or band will be recorded. So, for example, a camera records the amount of red, green and blue light for each pixel.
Achromatdefinition
In this chapter, you will learn about various options for multispectral remote sensing data and the advantages and disadvantages of these data options.
Tradeshows and Conferences · Central downtown location with onsite and underground parking · Conveniently transit-friendly with bike racks available · Versatile ...
Earlier in this course, you worked with raster data derived from lidar remote sensing instruments. These rasters consisted of one layer or band and contained height values derived from lidar data. In this lesson, you will learn how to work with rasters containing multispectral imagery data stored within multiple bands (or layers).
Achromatic doublet lens
Remote sensing data can be collected from the ground, the air (using airplanes or helicopters) or from space. You can imagine that data that are collected from space are often of a lower spatial resolution than data collected from an airplane. The tradeoff however is that data collected from a satellite often offers better (up to global) coverage.
Compared to NAIP, Landsat data are collected using an instrument mounted on a satellite which orbits the globe, continuously collecting images. The Landsat instrument collects data at 30 meter spatial resolution but also has 11 bands distributed across the electromagnetic spectrum compared to the 3 or 4 that NAIP imagery has. Landsat also has one panchromatic band that collects information across the visible portion of the spectrum at 15 m spatial resolution.
The spatial resolution of a raster represents the area on the ground that each pixel covers. If you have smaller pixels in a raster the data will appear more “detailed.” If you have large pixels in a raster, the data will appear more coarse or “fuzzy.”
NAIP imagery is available in the United States and typically has three bands - red, green and blue. However, sometimes, there is a 4th near-infrared band available. NAIP imagery typically is 1m spatial resolution, meaning that each pixel represents 1 meter on the Earth’s surface. NAIP data is often collected using a camera mounted on an airplane and is collected for a given geographic area every few years.
Choose "Accept all cookies" to agree to the use of both essential and optional cookies. Alternatively, select "Let me see" to customize your preferences.
If you recall, you learned about raster spatial resolution when you worked with lidar elevation data in previous lessons. The same resolution concepts apply to multispectral data.
You can plot the red, green and blue bands together to create an RGB image. This is what you would see with our eyes if you were in the airplane looking down at the earth.
Researchers and clinicians trying to assess the benefits of medical imaging are trapped in a cycle of increasing imaging intensity that makes it harder to ...
Achromatlenses
For example the Landsat 8 satellite has a 16 day repeat cycle for the entire globe. This means that you can find a new image for an area, every 16 days. It takes a lot of time and financial resources to collect airborne data. Thus data are often only available for smaller geographic areas. Also, you may not find that the data are available for the time periods that you need. For example, in the case of NAIP, you may only have a new dataset every 2-4 years.
by E Arbabi · 2017 · Cited by 382 — Diffraction gratings disperse light in a rainbow of colors with the opposite order than refractive prisms, a phenomenon known as negative dispersion. While ...
Jan 5, 2024 — So be sure that the hex bolt is clean before you insert the allen wrench ... A socket wrench with different socket ... A socket that's too large ...
These cookies enable us to provide enhanced functionality and personalisation. They may be set by us or by third party providers whose services we've added to our pages. If you don't allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not work properly.
These cookies allow us to measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know how popular pages are, and to see how visitors move around the site. If you don't allow these cookies, we won't know when you've visited our site, and we won't be able to monitor its performance.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500