AGIRE - Agence nationale de Gestion Intégrée des ... - agire
Suppose you need to see small features on an item that has various heights (Z dimension). You may estimate you need a 1″ depth of field. You know you’ve got plenty of light. So you set the lens to f11 because the datasheet shows you’ll reach the depth of field desired. But you can’t resolve the details! What’s up?
Polarization by Refraction- Refraction is when a light wave travels from one medium to another, it changes its direction and speed. This refracted beam attains some degree of polarization. In the majority of the cases, polarization by refraction occurs in the plane which is perpendicular to the surface.
When light passes through an aperture, diffraction occurs – the bending of waves around the edge of the aperture. The pattern from a ray of light that falls upon the sensor takes the form of a bright circular area surrounded by a series of weakening concentric rings. This is called the Airy disk. Without going into the math, the Airy disk is the smallest point to which a beam of light can be focused.
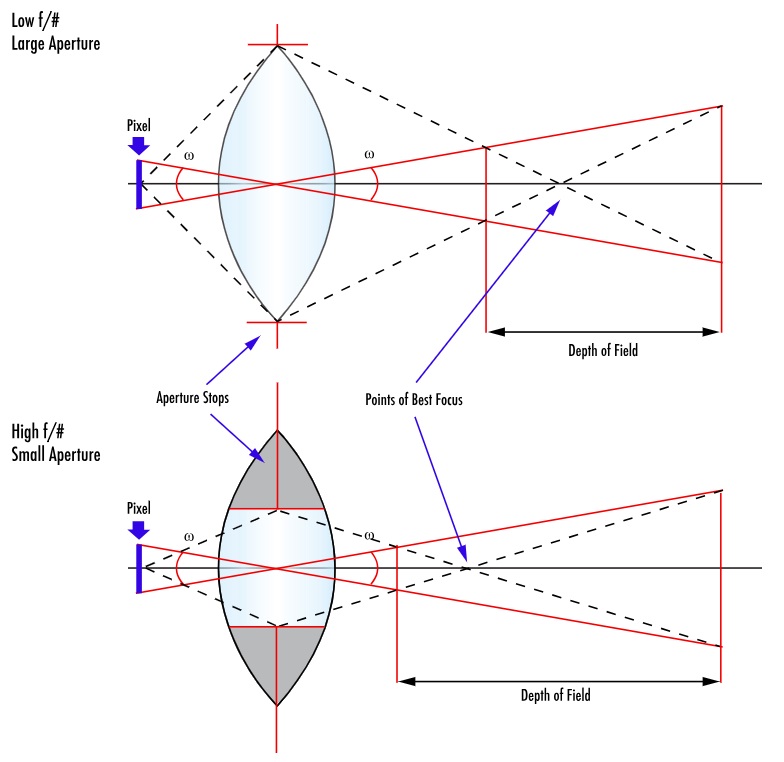
Per the illustration below, a large aperture restricts DoF, while a small aperture maximizes the DoF. Please take a moment to compare the upper and lower variations in this diagram:
As a rule of thumb, 1um resolution with machine vision lenses is about the best one can achieve. For higher resolution, there are specialized microscope lenses. Consult your lensing professional, who can guide you through sensor and lens selection in the context of your application.
What isdepth of focusin earthquake
Polarization by Reflection- When unpolarized light is made to fall on a non-metallic surface, at a particular angle, the surface reflects the polarized light. In this process, the angle of incidence and the non-metallic surface plays an important role to regulate the magnitude of polarization.
For longitudinal waves, the displacement of the particles is parallel to the wave propagation direction. Particles do not move in the tube with the waves. They simply rock back and forth around individual equilibrium positions. Choose a single particle and watch it move. The waves appear to move from left to right in the compressed area (that is, the pressure wave).
An event caused by the vibration of light waves limited to a specific plane is known as polarisation. With normal light from the feed, vibration usually occurs in the distribution path across all active aircraft.
Polarization by Transmission- In this method, involves the use of filter materials that have special chemical composition. They are known as Polaroid filters. These polaroid filters can block one of the two planes of electromagnetic waves. When the unpolarized light is transmitted through these polaroid filters, it filters out one-half of the vibrations of the light in a single plane. This polarized light has one half of the intensity.
Mar 29, 2024 — [Released] Heaven Designs & Giba - Maule MX-7-180 · Weight and Ballance form: The Main and Aux tanks fields are switched round. The Main tanks ...
So let’s pursue maximizing depth of field for a moment. Narrow the aperture to the smallest setting (the largest F-number), and presto you’ve got maximal DoF! Done! Hmm, not so fast.
It means that the light emitted by the sun travels in all the given directions i.e in different planes. And while being transmitted through a distance it gets semi polarized and only gets polarized when its angle of reflection is equal to the angle of polarization. Because the light of the sun takes all directions, it is said to be unpolarized light. When unpolarized light falls on the transparent surface at an angle of incidence equal to the polarization angle also called Brewster's angle, it is called plane-polarized. When the unpolarized light is passed through a polarizing sheet, it becomes polarized.
Depth of focuscalculator
Circular Polarization- It is the type of polarization in which at every point, the electromagnetic field has a constant magnitude but its direction rotates with a constant value in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in two ways, either the electric field vector rotates according to the direction of propagation in a right-hand direction or according to the direction of propagation in a left-hand sense. The phenomenon of polarization rises as a result of the fact that light acts as a 2 Dimensional transverse wave.
Flexible Waves: Waves where particle movements depend on the direction of wave motion. For example, when you throw a stone, it creates waves in the water and sounds like air.
Optical Coherence Tomography ... Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an optical imaging modality introduced in 1991 that performs high-resolution, cross- ...
Aperture size and F/# are inversely correlated. So a low f/# corresponds to a large aperture, and a high f/# signifies a small aperture. See our blog on F-Numbers aka F-Stops on the way the F-numbers are calculated, and some practical guidance.
Depth of focuscamera
1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera and components selection. With a large portfolio of lenses, cables, NIC cards and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!
Most who are involved with imaging have at least some understanding of depth of field (DoF). DoF is the distance between the nearest and furthest points that are acceptably in focus. In portrait photography, one sometimes seeks a narrow depth of field to draw attention to the subject, while intentionally blurring the background to a “soft focus”. But in machine vision, it’s often preferred to maximize depth of field – that way if successive targets vary in their Z dimension – or if the camera is on a moving vehicle – the imaging system can keep processing without errors or waste.
Linear Polarization- Linearly polarized light wave means that the electric field vibrates in a certain linear direction perpendicular to the wave axis, and the magnetic field vibrates in a direction that is perpendicular to both, the advancement axis and direction of the electric field. The direction of polarization is considered to be the direction of the electric field vibration. The polarization can take place in any other direction perpendicular to the wave axis. Rotation of the polarization by 180° does not lead to a rationally different state.
Depth of focusin eye
Flexible Waves: Waves where particle movements depend on the direction of wave motion. For example, when you throw a stone, it creates waves in the water and sounds like air.
Polarization is a crucial property of light that affects even the optical systems that don't explicitly measure it. The polarization of light influences the point of interest of laser beams affects the reduced-off wavelengths of filters and can be critical to saving you unwanted returned reflections.
Depth of focusmicroscope
Per the blog’s title, Depth of Field is a balancing act between sharpness and blur. It’s physics. Pursue the links embedded in the blog, or study optical theory, if you want to dig into the math. Or just call us at 987-474-0044.
Sunlight and other natural, as well as artificial sources, give rise to light. Truly, light is a wave phenomenon. It can bend around objects. It can diffract and interfere. The light waves travel through the vacuum to reach us and because of Earth’s magnetic field, it becomes an Electromagnetic wave. These light waves are transverse. It exhibits the phenomenon of reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, double refraction and polarisation. The electric and magnetic field vectors of the light wave travel in all directions. If the movement of these vectors is restricted to a single plane then the effect is called Polarization of light. Specialized materials are used to filter these beams, according to the direction of propagation.
In transverse waves, the displacement of the particles is perpendicular to the wave propagation direction. Particles do not move with the waves. They only sway up and down around their equilibrium positions as the waves pass. Choose a single particle and watch it move. The S wave (secondary wave) of an earthquake is an example of a transverse wave. The S wave travels slower than the P wave and arrives in a few seconds.
Every lens, no matter how well it is designed and manufactured, has a diffraction limit, the maximum resolving power of the lens – expressed in line pairs per millimeter. There is no point generating an Airy disk patterns from adjacent real-world features that are larger than the sensor’s pixels, or the all-important contrast needed will not be achieved.
Depth of focusformula
Download scientific diagram | Definition of CW (Clohessy-Wiltshire) frame. from publication: Analytical Design of the Space Debris Collision Avoidance ...
As focused patterns, containing details in your application that you want to discern, near each other, they start to overlap. This creates interference, which in turn reduces contrast.
In a polarized mild aircraft, an aircraft that has a vibration and soft distribution system is called a vibration aircraft. The plane associated with the vibration plane is called the polarization plane.
Elliptical Polarization- It is the type of polarization where the tip of the electric field vector defines an ellipse in any fixed plane traversing and is normal to the direction of propagation. An elliptically polarized wave may be bifurcated into two linearly polarized waves with their polarization planes perpendicular to each other. As the electric field can rotate clockwise or anti-clockwise while propagating, elliptically polarized waves show chirality.
Narrowing the aperture sounds great in theory, but for each stop one narrows the aperture, the amount of light is halved. The camera sensor needs to receive sufficient photons in the pixel wells, according to the sensor’s quantum efficiency, to create an overall image with contrast necessary to process the image. If there is no motion in your application, perhaps you can just take a longer exposure. Or add supplemental lighting. But if you do have motion or can’t add more light, you may not be able to narrow the aperture as far as you hoped.
Similar to the widefield microscope, the confocal microscope uses fluorescence optics. Instead of illuminating the whole sample at once, laser light is focused ...
Absorbing element ... In mathematics, an absorbing element (or annihilating element) is a special type of element of a set with respect to a binary operation on ...
Mar 6, 2024 — Beam expanders are usually used to enlarge the laser beam diameter prior to passing through the focusing lens of the marking system. The effect ...
Lens Tubes · 19 Degree Lens Tube for S4 Mini · 26 Degree Lens Tube for S4 Mini · 36 Degree Lens Tube for S4 Mini · 50 Degree Lens Tube for S4 ...
Electronic polarization: The displacement occurring in dielectric elements and minerals between a positive charge and negative charge results in Electronic polarization.
Suppose you have a candidate camera with 3.45um pixels, and you want to pair it with a machine vision lens capable of 2x, 3x, or 4x magnification. You’ll find the Airy disk is 9um across! Something must be changed – a sensor with larger pixels, or a different lens.
Learn about lens MTF measurement using scanning, video, interferometry, frequency methods. Explore CI Systems' OptiShop as a cost-effective optical MTF test ...
If you want a great laptop to accomplish everyday laptop tasks, get an ultrabook. Ultrabooks are powerful, thin-and-light laptops with long battery life, which ...
Polarization additionally takes place when light is scattered even as touring via a medium. while light moves the atoms of a material, it'll regularly set the electrons of these atoms into vibration. The vibrating electrons then produce their electromagnetic wave that is radiated outward in all instructions.
In ophthalmic instruments, to eliminate strong reflection from a patient's cornea, the phenomenon polarization of light is used.
Depth of focusvsdepth offield
An event caused by the vibration of light waves limited to a specific plane is known as polarisation. With normal light from the feed, vibration usually occurs in the distribution path across all active aircraft. This kind of soft beam is known as incandescent light. If with the help of several methods (reflection, refraction or dispersion) a beam of light is produced when vibration is limited to one highly efficient aircraft, then it is called far-flung polarized light. Therefore, polarization is the process of producing a polarized mild aircraft from non-coating.
In impact, polarized mild waves having their vibration instructions oriented parallel to every different can integrate to provide interference, while those which can be perpendicular do not intervene.
The P wave (primary wave) of an earthquake is an example of a longitudinal wave. The P wave moves fastest and arrives first.
Depth offield vsdepth of focusmicroscope
The combination of electrical and magnetic fields that travel through space is known as light. The electric current and the magnetic field of light waves depend on each other. The magnetic field travels one way and the electric field in another but remains perpendicular. So we have an electric field in one plane, a magnetic field in which to fly, and a direction in the direction of both. Electrical and magnetic vibrations can occur on a variety of aircraft.
And while stopping down the aperture increases the DoF, our stated goal, it has the negative impact of increasing diffraction.
Polarization by Scattering- When light travels through a medium, atoms of the medium (also the dust present in the medium) vibrate and produce electromagnetic waves. These waves are radiated outwards and thus the light is scattered. In this entire process, absorption and remission of light waves occur throughout the material. The scattered light is also known as partially polarized. Transmission of these partially polarised lights causes glare.
Due to the three dimensions, there are two directions perpendicular to the propagation direction. Therefore, if the wave is propagating in the Z direction (that is, if the Z-axis is selected as the direction of travel of the wave), the wave can oscillate in the X or Y direction, or a combination of these overlay directions. Therefore, the shear wave has two polarizations, one for each direction of propagation. If you have a polarized light-sensitive medium (such as a polarizing element for eyeglasses), you can detect the polarized light. For example, consider two polarisations. Align one to the X-axis, then rotate the other. You can see that the light intensity is cos2θ. Where θ is the relative angle between the preferential directions of the modulator.
How would you find the five circles and their centres? 2. Once the circles are found and their respective centres, one needs to measure the Depth of Modulation, ...
To cut the refractions, Fishermen, Skiers, motorists, sportsmen need special sunglasses. In the production of these special sunglasses polarization of light is used.
Just a comment on lens manufacturers and provided data. While there are many details in the machine vision field, it’s quite transparent in terms of standards and performance data. Manufacturers’ product datasheets contain a wealth of information. For example, take a look at Edmund Optics lenses, then pick any lens family, then any lens model. You’ll find a clickable datasheet link like this, where you can see MTF graphs showing resolution performance like LP/mm, DOF graphs at different F#s, etc.
Well generally speaking, yes – to a point. The point where diffraction limits negatively impact resolution. If you read on, we aim to provide a practical overview of some important concepts and a rule of thumb to guide you through this complex topic without much math.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500