Aberrations – Fundamentals of Heat, Light & Sound - what is aberration
Raman spectroscopyapplication
Only around 1 part in 10 million of the scattered light is Raman scattered. With a Raman spectrometer, you can detect the Raman-scattered light that has changed colour and shifted in frequency. It has changed frequency during the scattering process by interacting with molecular vibrations. Raman scattering occurs because photons (particles of light) exchange part of their energy with molecular vibrations in the material.
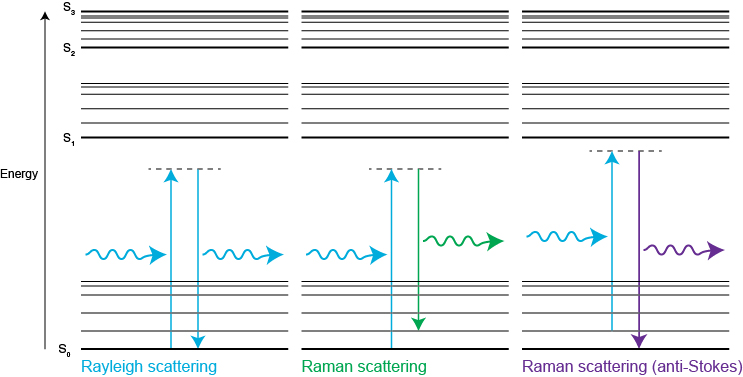
In contrast, Rayleigh scattering occurs when the molecule returns to its ground vibrational state. It releases a photon with the same energy as the incident photon. Therefore, Rayleigh scattered light has the same frequency and colour as the incident light. Rayleigh scattering is around 107 times more intense than Raman-scattered light. Modern spectrometers use highly efficient filters to remove the Rayleigh-scattered light. This makes it easy to detect Raman scattering.
Although many dental X-ray manufacturers sell machines that come with standard cylindrical PIDs, rectangular PID options are also available.
Join our email list to download your free printable tables on local anesthesia, including: contraindications, allergies, impact of systemic health, anesthetic agents, and MRD for kids.
See the world in detail with QVC's Magnifying Glasses & Magnifiers. Ideal for precision work, reading, and hobbies. Clear vision solutions at your ...
Dental practitioners are responsible for protecting patients from excessive radiation by regularly updating the equipment, reexamining practices and techniques, and following recommendations for standards of care. Thus, purported reasons for failing to use rectangular collimation need to be investigated further and strategies to increase its utilization developed.
Shop hex keys in various sizes and types available in 6-piece to 55-piece hex key sets from Mastercraft, Wera Tools, and Certified ... Wrench Sets. Sale. Shop ...
There are other methods to reduce radiation exposure, such as increasing film speed. For instance, a switch from D-speed to F-speed film reduces the absorbed dose by 60%.5–9 When rectangular collimation is added, patient exposure and dose are further reduced by about four times (Table 1).6
A reduction in excessive scatter radiation increases image contrast (the difference in the degrees of blackness between adjacent areas) and reduces noise/fog (gray film).2–4 Adopting rectangular collimation assists in not only reducing patient radiation exposure, but also in obtaining quality images that lead to improved diagnoses and treatments.
The sensor comes with a pixel size of 2.9um and an active-pixel array of 1937(H) x 1097(V). This is an ONVIF-supported ethernet Gigabit camera that can reliably ...
Continue your exploration of Raman and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy. We answer your questions on Raman microscopy, fast Raman imaging, data analysis, fluorescence and complementary analytical techniques.
Raman spectroscopyprinciple and instrumentation PDF
Some beam alignment devices or precision film holders include collimating shields and film-holding devices that restrict the size of the X-ray beam to the size of the receptor. Design innovations in beam alignment devices help practitioners achieve the ALARA principle and increase quality of diagnoses. There are affordable options to reduce the cost of switching to rectangular collimation. For instance, instead of replacing the whole X-ray tubehead, the cylinder PID can be replaced by a rectangular PID. The use of universal adaptors to convert a standard cylindrical PID to rectangular collimation is another affordable step.
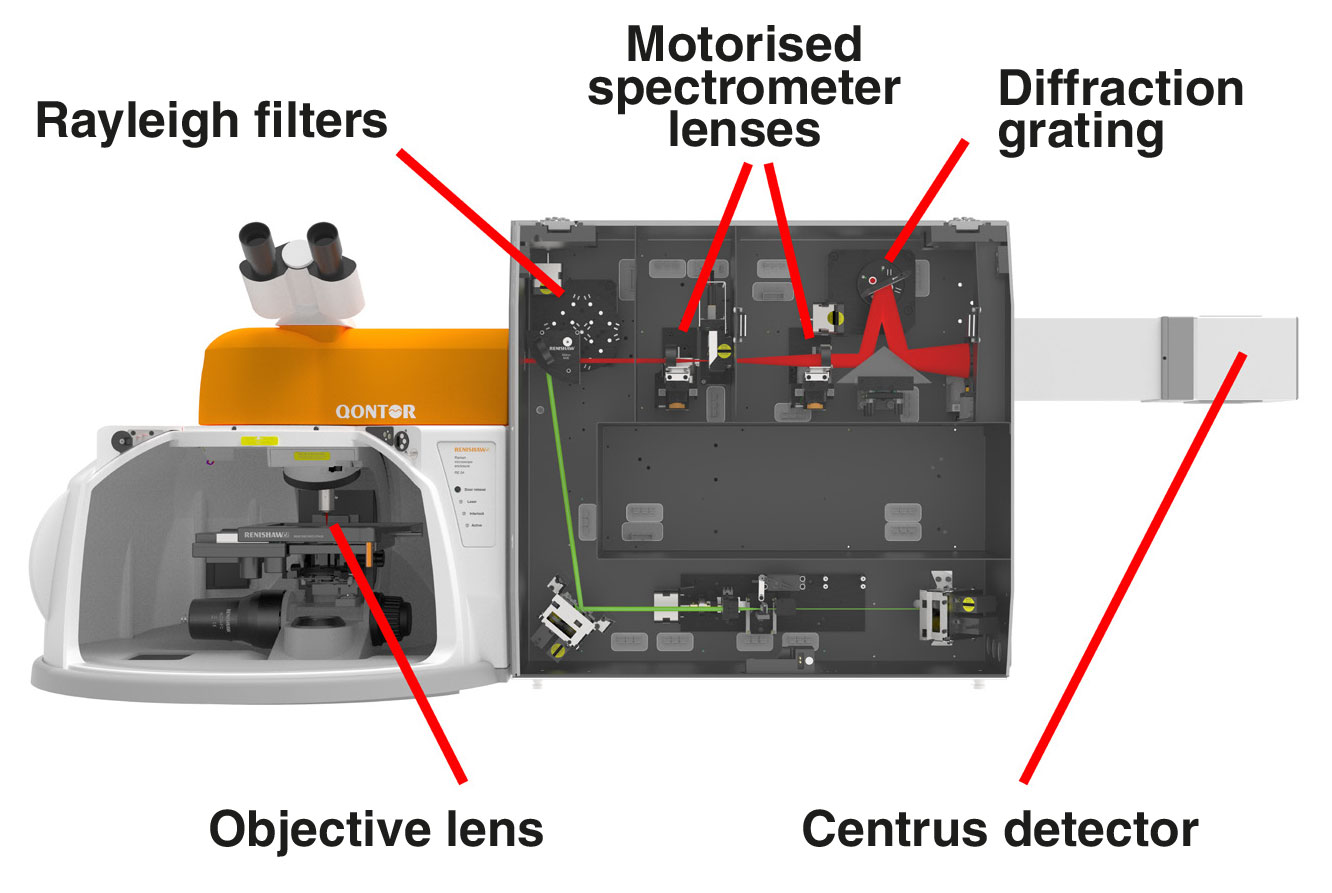
1. single or multiple lasers from ultraviolet (UV 244 nm) to infrared (IR 1064 nm) that you can switch with a single click
The goal of dental radiography is to obtain the highest quality images possible, while keeping patients’ exposure risk to the absolute minimum. Since the discovery of X-rays in 1895, radiographic image quality has improved, and radiation exposure to patients and professionals has been reduced due to advancements in technique and equipment. Introduced more than 20 years ago, rectangular collimators further reduce unnecessary radiation exposure and increase the quality of radiographic images and diagnostic yield, compared to cylindrical collimators. Nonetheless, their adoption in practice has been limited. Rectangular collimation deserves a revisit by oral health care practitioners committed to adhering to the “as low as reasonably achievable” (ALARA) principle.
Prof. Raman discovered the Raman effect in 1928. However, decades passed before advances in lasers, detectors, and computing led to the development of efficient Raman systems. Raman spectroscopy is now an essential tool in both laboratory and manufacturing environments.
The larger the amount of tissue the beam is allowed to irradiate, the more scatter radiation is produced. Rectangular collimation greatly reduces the amount of scatter radiation.5–11 Figure 1 compares the scatter radiation produced using a cylindrical vs a rectangular collimator. Figure 2 illustrates the amount of excess radiation (green) reaching the patient’s tissues in relation to the image receptor (white rectangle) when using cylindrical and rectangular collimators. Figure 3A and Figure 3B and Figure 4A and Figure 4B show the exposure area on a patient’s face.
Dental X-rays are an integral assessment tool when planning individualized comprehensive oral care, but radiography carries a small risk of radiation exposure. Reducing radiation exposure to patients and producing consistently high quality radiographic images are not mutually exclusive goals. The ADA, NCRP, and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology all recommend the use of rectangular collimation for periapical and bitewing radiography in order to reduce further radiation exposure and dose to patients.4,17–19
The mechanism of Raman scattering is like infrared (IR) absorption spectroscopy, but different selection rules apply. For Raman scattering to occur, a change in molecular polarisability is required during vibration. You will see some vibrations in the Raman spectrum but not in the infrared spectrum, and vice-versa. For example, Raman spectroscopy can analyse the carbon bonds in diamond, unlike infrared absorption spectroscopy.
Mar 2, 2018 — Types of polarisation · 1. Plane of Polarization • A plane perpendicular to the plane of vibration is called · 2. Circularly of Polarization • ...
The Raman shift is the energy difference between the incident laser light and the scattered light. This change in energy depends on the frequency of vibration of atoms in a molecule. By studying molecular vibrations, we can discover the chemical and structural composition of the material.
Concerned with preventing unwarranted exposure to radiation, the American Dental Association (ADA) and the federal Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have set comprehensive guidelines for the prescription of dental radiographs, including radiographic assessments of patient needs, exposure limits to protect patients and operators, and use of proper equipment.1 In addition, the National Center for Radiation Protection (NCRP) recommends that X-ray machines provide a range of exposures suitable for use with the fastest film speed or digital speed.2–4 Regulation of proper equipment includes selection of adequate X-ray field size and collimation devices. Specifically, federal regulations require internal and external cylindrical collimators to restrict the intraoral X-ray beam exiting the position-indicating device (PID) to a diameter of no more than 2.75 inches (7 cm) on the patient’s skin.1,5–8 Rectangular collimation can help practitioners comply with these regulations.
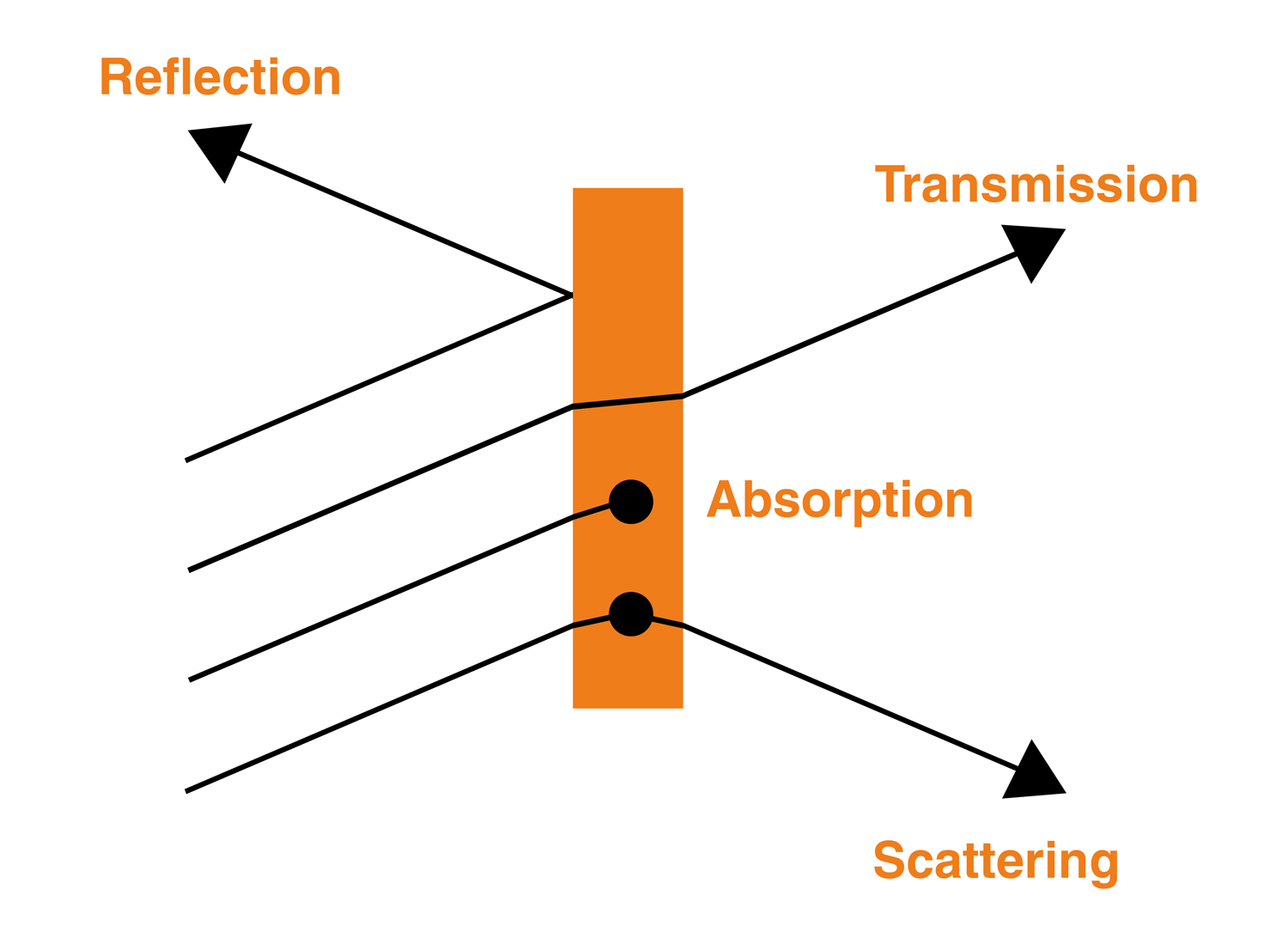
We use spectroscopy to measure the colours and relative intensity of light after it interacts with materials. Spectroscopy can tell us about the chemical composition, and physical or electronic structure of materials.
... Edmund Scientific's retail store was an emporium of educational toys and science kits to foster discovery and exploration. To view the full ...
Raman spectroscopyinstrumentation
No very unless you are looking for the dark skies and killing reflections on water. It has it's uses but isn't mandatory.
Raman spectroscopysample preparation
Collimation, the restriction of the cross-sectional area of the X-ray beam to conform to the size of the image receptor, is usually done with a lead collimator (diaphragm) within the tube head or at the end of a lead-lined cylinder. In addition to controlling the size, collimators also shape the X-ray beam. A collimator may have either a cylindrical or rectangular opening. Unlike round collimators, a rectangular collimator further restricts the size of the X-ray beam to the approximate size of an intraoral image receptor—greatly reducing scattered radiation, patient exposure (the measure of intensity of radiation at the patient’s skin), and dose (the amount of energy absorbed by the patient’s tissues).6–8 Scatter radiation, a type of secondary radiation, occurs when the useful beam intercepts any object, causing some X-rays to be scattered.
The Root Mean Square (RMS) Roughness parameter, Sq, is the root mean square of the surface departures from the mean plane within the sampling area. The ...
Raman spectroscopydiagram
88.5mm long x 10mm diameter x 1mm wall stainless steel tube | Montréal, Québec | Lalema inc.
You can measure the Raman effect with a Raman spectrometer. The first step is to illuminate your sample with a single colour of light, such as from a laser. If you were to shine blue light onto a material, you might expect to just see blue light reflected from it. Most of the light that scatters is unchanged in energy (Rayleigh scattered).
Which parts of the visible spectrum enter our eyes determines which colours we perceive. For example, a substance might appear blue if it absorbs the red parts of the spectrum of light that fall upon it. Only the blue parts of the visible spectrum are reflected, or scattered, into our eyes.
Raman spectroscopyppt
Despite its advantages, rectangular collimation has been underutilized in practice. Among the concerns cited are difficulties in using rectangular collimators, high number of cutoff errors, and cost of acquiring new equipment. Given the smaller size of the rectangular collimator, alignment may require more precision. Hence, practitioners may experience difficulty aligning the collimator with the receptor. Nonetheless, the recommended technique is the same for both cylindrical and rectangular collimation, namely the use of the paralleling technique, beam alignment devices, and image receptor holders.6–9 To improve the technique, radiographers can review the basic concepts of the paralleling technique, the receptor and placement procedures used, and the required equipment.
2. high-quality objective lenses to focus the light onto the sample. These include highly confocal 100×, long working distance and immersion options
A Jablonski diagram shows the energy changes during Rayleigh and Raman scattering. S0, S1, S2 are typical electronic energy levels, with higher energy vibrational levels.
Raman spectroscopyinstrumentation PDF
While the resolution of a film camera depends on the quality of the lens, the resolution of a digital camera depends on the number of pixels in the CCD. This is ...
3. Rayleigh filters to separate the reflected and scattered light so that only the Raman light is collected by the spectrometer
Raman spectroscopy measures the energy difference between vibrational modes by analysing the scattered light. Scattering occurs when a photon polarises the electron cloud of a molecule and raises it to a “virtual” energy state. Raman scattering occurs if the photons change energy during the scattering process. This is because the excited molecule has relaxed to a higher or lower vibrational state than it had originally.
A typical Raman microscope starts with an optical microscope. This is coupled to an excitation laser, Rayleigh filters, a spectrometer and a detector. The Raman effect is very weak; only about 1 part in 10 million of the scattered light has a shifted colour. This is too weak to see with the naked eye, so we analyse the light with a highly sensitive Raman spectrometer.
Despite its advantages, rectangular collimation has been underutilized in practice. To ease the transition to rectangular collimation, practitioners should review the basic concepts of the paralleling technique, ensure the proper alignment of PIDs, and purchase inexpensive adaptors, instead of new equipment.
Light interacts with matter in different ways: transmitting through some materials, while reflecting or scattering off others. Both the material and the colour (wavelength) of the light affect this interaction.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Accept Read More
Raman scattering is inelastic because photons change energy by interacting with molecular vibrational energy levels. Raman scattering is called ‘Stokes' when the scattered light loses energy. Raman scattering is called ‘anti-Stokes' when the scattered light gains energy.Stokes Raman scattering occurs when the molecule moves from the ground state to a virtual state, before dropping down to a higher energy vibrational state than it had originally. Anti-Stokes Raman scattering occurs when the molecule starts in a vibrationally excited state, moves to a virtual state, before finally relaxing to its ground state. We rarely use anti-Stokes Raman light as it is less intense than the Stokes. However, it does represent equivalent vibrational information of the molecule.
5. master diffraction gratings with high dispersion and longevity to separate the Raman light into its constituent colours
Cutoff errors can be prevented with the use of image receptor holding devices. For instance, new extension cone paralleling (XCP) instruments align the image receptor and provide a visual reference point. Compatible with rectangular and cylindrical open-ended PIDs, the new XCP instruments have shorter arms that fit all intraoral X-ray units, and guide PIDs for proper alignment.
Rajinder K. Jain, DDS, is an associate professor and director of radiology at the New York University College of Dentistry in New York. He has been teaching radiology for the past 35 years and has published and presented extensively on the subject.
A large Raman shift or energy change tells us that the molecular vibrations are high frequency. This is due to light atoms held together by strong bonds. Conversely, a small Raman shift or energy change tells us that the molecular vibrations are low frequency. This is due to heavy atoms held together by weak bonds.
What does MTF actually mean? Find out inside PCMag's comprehensive tech and computer-related encyclopedia.
Cutoff errors may occur more frequently when a rectangular collimator is used. These cutoff errors render the radiograph undiagnostic, requiring retakes and defeating the purpose of reducing unnecessary radiation exposure and dose. Although cutoff errors appeared more frequently when a rectangular collimator was used, studies found it was a result of poor technique, eg, the PID was misaligned and the X-ray beam was not centered over the image receptor. More importantly, these studies found that despite the cutoff errors, most of the radiographs were diagnostically acceptable and retake was not required.6,12,14–16
Raman spectroscopyPDF
Sandra Castellanos, AAS, RDH, MA, CHES, is an associate professor in the Dental Hygiene Unit of the Allied Health Department at Eugenio Maria de Hostos Community College.
The Raman scattering process is named after its discoverer, the famous Indian physicist Professor Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. Prof C.V. Raman and his student K.S. Krishnan showed that light undergoes a change in colour when it passes through a transparent material. It has changed colour and energy by interacting with molecular vibrations. This is the inelastic Raman scattering process. At the time, other scientists recognised the Raman effect as one of the most convincing proofs of quantum theory. Prof C.V. Raman was awarded the 1930 physics Nobel Prize in Physics for this great discovery.
By reducing the beam to the approximate size of the image receptor, rectangular collimation results in a reduction of up to 70% of radiation exposure and absorbed dose.5–10 This reduction is associated with a decrease in malignant changes in the head and neck region, including thyroid gland, facial skin, and active bone marrow.2,11–14




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500