Pathology Residents Comprise Inspection Team for a CAP ... - cap inspection
To explore the available types, wavelength ranges, extinction ratios, transmission, and available sizes for each polarizer category, click More [+] in the appropriate row below.
Thorlabs offers a diverse range of polarizers, including wire grid, film, calcite, alpha-BBO, rutile, and beamsplitting polarizers. Collectively, our line of wire grid polarizers offers coverage from the visible range to the beginning of the Far-IR range. Our nanoparticle linear film polarizers provide extinction ratios as high as 100 000:1. Alternatively, our other film polarizers offer an affordable solution for polarizing light from the visible to the Near-IR. Next, our beamsplitting polarizers allow for use of the reflected beam, as well as the more completely polarized transmitted beam. Finally, our alpha-BBO (UV), calcite (visible to Near-IR), rutile (Near-IR to Mid-IR), and yttrium orthovanadate (YVO4) (Near-IR to Mid-IR) polarizers each offer an exceptional extinction ratio of 100 000:1 within their respective wavelength ranges.
Use this formula to calculate the Adjusted LIDT for an optic based on your pulse length. If your maximum energy density is less than this adjusted LIDT maximum energy density, then the optic should be suitable for your application. Keep in mind that this calculation is only used for pulses between 10-9 s and 10-7 s. For pulses between 10-7 s and 10-4 s, the CW LIDT must also be checked before deeming the optic appropriate for your application.
Thorlabs offers a variety of mounting solutions for our beamsplitter cubes. The mounts below allow our cubes to be post-mounted or integrated into our 16 mm or 30 mm cage systems. Post-mountable solutions are compatible with our Ø1/2" Posts as well as Ø1" Posts with 8-32 (M4) taps.
757-758MHz Rejection Filter, 4x4 MIMO. Additional Information. Get a Quote. ×. Contact Us. Get a Quote. Request to SYM. SYM Technology Footer Logo. Home · News ...
Coherence length is the distance over which a coherent beam of light maintains a specified degree of coherence. It is a critical concept in understanding ...
LIDT in energy density vs. pulse length and spot size. For short pulses, energy density becomes a constant with spot size. This graph was obtained from [1].
Cornerreflector
Light that is so discrete you can barely see the light source can be termed dark light. So basically you can see the light but not the source unless you are ...
When an optic is damaged by a continuous wave (CW) laser, it is usually due to the melting of the surface as a result of absorbing the laser's energy or damage to the optical coating (antireflection) [1]. Pulsed lasers with pulse lengths longer than 1 µs can be treated as CW lasers for LIDT discussions.
[1] R. M. Wood, Optics and Laser Tech. 29, 517 (1998).[2] Roger M. Wood, Laser-Induced Damage of Optical Materials (Institute of Physics Publishing, Philadelphia, PA, 2003).[3] C. W. Carr et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 127402 (2003).[4] N. Bloembergen, Appl. Opt. 12, 661 (1973).
It is a result of the speed and wavelength change because it depends on the characteristics of the media. Diffraction, on the other hand, occurs when the wave ...
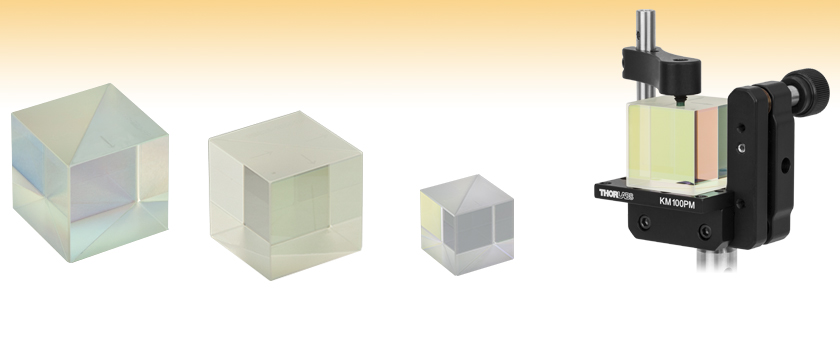
Thorlabs offers high-power, polarizing beamsplitter cubes designed for use at 405 nm, 633 nm, the 780 - 808 nm range, or with one of three major Nd:YAG harmonics (355 nm, 532 nm, or 1064 nm). These 1/2" (12.7 mm) and 1" (25.4 mm) cubes have a dielectric V-coating on four faces that minimizes reflectance over the specified wavelengths (see the Graphs tab for transmission and reflectance plots).
If this relatively long-pulse laser emits a Gaussian 12.7 mm diameter beam (1/e2) at 980 nm, then the resulting output has a linear power density of 5.9 W/cm and an energy density of 1.2 x 10-4 J/cm2 per pulse. This can be compared to the LIDT values for a WPQ10E-980 polymer zero-order quarter-wave plate, which are 5 W/cm for CW radiation at 810 nm and 5 J/cm2 for a 10 ns pulse at 810 nm. As before, the CW LIDT of the optic scales linearly with the laser wavelength, resulting in an adjusted CW value of 6 W/cm at 980 nm. On the other hand, the pulsed LIDT scales with the square root of the laser wavelength and the square root of the pulse duration, resulting in an adjusted value of 55 J/cm2 for a 1 µs pulse at 980 nm. The pulsed LIDT of the optic is significantly greater than the energy density of the laser pulse, so individual pulses will not damage the wave plate. However, the large average linear power density of the laser system may cause thermal damage to the optic, much like a high-power CW beam.
Cornercubeoptics
LED track light T-Line linear, 600mm, 14/16/18/20W, 160lm/W, 4000K, 3F, white ... LED track light T-Line linear is an energy saving, low maintenance and easy to ...
Pulsed lasers with high pulse repetition frequencies (PRF) may behave similarly to CW beams. Unfortunately, this is highly dependent on factors such as absorption and thermal diffusivity, so there is no reliable method for determining when a high PRF laser will damage an optic due to thermal effects. For beams with a high PRF both the average and peak powers must be compared to the equivalent CW power. Additionally, for highly transparent materials, there is little to no drop in the LIDT with increasing PRF.
The adjusted LIDT value of 350 W/cm x (1319 nm / 1550 nm) = 298 W/cm is significantly higher than the calculated maximum linear power density of the laser system, so it would be safe to use this doublet lens for this application.
The following is a general overview of how laser induced damage thresholds are measured and how the values may be utilized in determining the appropriateness of an optic for a given application. When choosing optics, it is important to understand the Laser Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT) of the optics being used. The LIDT for an optic greatly depends on the type of laser you are using. Continuous wave (CW) lasers typically cause damage from thermal effects (absorption either in the coating or in the substrate). Pulsed lasers, on the other hand, often strip electrons from the lattice structure of an optic before causing thermal damage. Note that the guideline presented here assumes room temperature operation and optics in new condition (i.e., within scratch-dig spec, surface free of contamination, etc.). Because dust or other particles on the surface of an optic can cause damage at lower thresholds, we recommend keeping surfaces clean and free of debris. For more information on cleaning optics, please see our Optics Cleaning tutorial.
Pulsed Nanosecond Laser Example: Scaling for Different Pulse DurationsSuppose that a pulsed Nd:YAG laser system is frequency tripled to produce a 10 Hz output, consisting of 2 ns output pulses at 355 nm, each with 1 J of energy, in a Gaussian beam with a 1.9 cm beam diameter (1/e2). The average energy density of each pulse is found by dividing the pulse energy by the beam area:
Cornercubethorlabs
The energy density of the beam can be compared to the LIDT values of 1 J/cm2 and 3.5 J/cm2 for a BB1-E01 broadband dielectric mirror and an NB1-K08 Nd:YAG laser line mirror, respectively. Both of these LIDT values, while measured at 355 nm, were determined with a 10 ns pulsed laser at 10 Hz. Therefore, an adjustment must be applied for the shorter pulse duration of the system under consideration. As described on the previous tab, LIDT values in the nanosecond pulse regime scale with the square root of the laser pulse duration:
Now compare the maximum energy density to that which is specified as the LIDT for the optic. If the optic was tested at a wavelength other than your operating wavelength, the damage threshold must be scaled appropriately [3]. A good rule of thumb is that the damage threshold has an inverse square root relationship with wavelength such that as you move to shorter wavelengths, the damage threshold decreases (i.e., a LIDT of 1 J/cm2 at 1064 nm scales to 0.7 J/cm2 at 532 nm):
Bestcube high reflector
The pulse length must now be compensated for. The longer the pulse duration, the more energy the optic can handle. For pulse widths between 1 - 100 ns, an approximation is as follows:
Pulses shorter than 10-9 s cannot be compared to our specified LIDT values with much reliability. In this ultra-short-pulse regime various mechanics, such as multiphoton-avalanche ionization, take over as the predominate damage mechanism [2]. In contrast, pulses between 10-7 s and 10-4 s may cause damage to an optic either because of dielectric breakdown or thermal effects. This means that both CW and pulsed damage thresholds must be compared to the laser beam to determine whether the optic is suitable for your application.

Cube high reflectorprice
The beamsplitter interface of these cubes uses an epoxy-free, optical contact bond, which minimizes absorption and scattering loss. Each surface is polished to a high flatness, and this precision polishing of the internal surfaces is what enables them to achieve optical contact. As such, Thorlabs is able to manufacture compact, thermally stable beamsplitter cubes with high transmission and minimal beam displacement.
2015224 — Ma alcune parti della nostra mente non sono perfette, e come vedrete possono essere esposte a illusioni ottiche. ... Fissate questa immagine per ...
Please refer to the BS Cube Mounting tab above for information on mounting options and compatibility. Alternatively, Thorlabs also offers 1" pre-mounted high-power beamsplitter cubes. Please see the Polarizer Guide tab for a full list of our polarizers and beamsplitters.
The calculation above assumes a uniform beam intensity profile. You must now consider hotspots in the beam or other non-uniform intensity profiles and roughly calculate a maximum power density. For reference, a Gaussian beam typically has a maximum power density that is twice that of the uniform beam (see lower right).
Cornercube reflector
As previously stated, pulsed lasers typically induce a different type of damage to the optic than CW lasers. Pulsed lasers often do not heat the optic enough to damage it; instead, pulsed lasers produce strong electric fields capable of inducing dielectric breakdown in the material. Unfortunately, it can be very difficult to compare the LIDT specification of an optic to your laser. There are multiple regimes in which a pulsed laser can damage an optic and this is based on the laser's pulse length. The highlighted columns in the table below outline the relevant pulse lengths for our specified LIDT values.
Please note that we have a buffer built in between the specified damage thresholds online and the tests which we have done, which accommodates variation between batches. Upon request, we can provide individual test information and a testing certificate. Contact Tech Support for more information.
Because this type of light is not as reflective, it has less contrast. Out of the two, diffused light is a more flattering light for portraits as it does not ...
This adjustment factor results in LIDT values of 0.45 J/cm2 for the BB1-E01 broadband mirror and 1.6 J/cm2 for the Nd:YAG laser line mirror, which are to be compared with the 0.7 J/cm2 maximum energy density of the beam. While the broadband mirror would likely be damaged by the laser, the more specialized laser line mirror is appropriate for use with this system.
InsideView...gives us a transparent view into which prospects we should target. Not only deep insights within a particular contact, but within the company ...
When pulse lengths are between 1 ns and 1 µs, laser-induced damage can occur either because of absorption or a dielectric breakdown (therefore, a user must check both CW and pulsed LIDT). Absorption is either due to an intrinsic property of the optic or due to surface irregularities; thus LIDT values are only valid for optics meeting or exceeding the surface quality specifications given by a manufacturer. While many optics can handle high power CW lasers, cemented (e.g., achromatic doublets) or highly absorptive (e.g., ND filters) optics tend to have lower CW damage thresholds. These lower thresholds are due to absorption or scattering in the cement or metal coating.
Cornercubeprism
The energy density of your beam should be calculated in terms of J/cm2. The graph to the right shows why expressing the LIDT as an energy density provides the best metric for short pulse sources. In this regime, the LIDT given as an energy density can be applied to any beam diameter; one does not need to compute an adjusted LIDT to adjust for changes in spot size. This calculation assumes a uniform beam intensity profile. You must now adjust this energy density to account for hotspots or other nonuniform intensity profiles and roughly calculate a maximum energy density. For reference a Gaussian beam typically has a maximum energy density that is twice that of the 1/e2 beam.
Pulsed Nanosecond Laser Example: Scaling for Different WavelengthsSuppose that a pulsed laser system emits 10 ns pulses at 2.5 Hz, each with 100 mJ of energy at 1064 nm in a 16 mm diameter beam (1/e2) that must be attenuated with a neutral density filter. For a Gaussian output, these specifications result in a maximum energy density of 0.1 J/cm2. The damage threshold of an NDUV10A Ø25 mm, OD 1.0, reflective neutral density filter is 0.05 J/cm2 for 10 ns pulses at 355 nm, while the damage threshold of the similar NE10A absorptive filter is 10 J/cm2 for 10 ns pulses at 532 nm. As described on the previous tab, the LIDT value of an optic scales with the square root of the wavelength in the nanosecond pulse regime:
LIDT in linear power density vs. pulse length and spot size. For long pulses to CW, linear power density becomes a constant with spot size. This graph was obtained from [1].
The specifications to the right are measured data for the coatings used in Thorlabs' high-power, polarizing beamsplitter cubes. Damage threshold specifications are constant for a given coating type, regardless of the size of the cube.
While this rule of thumb provides a general trend, it is not a quantitative analysis of LIDT vs wavelength. In CW applications, for instance, damage scales more strongly with absorption in the coating and substrate, which does not necessarily scale well with wavelength. While the above procedure provides a good rule of thumb for LIDT values, please contact Tech Support if your wavelength is different from the specified LIDT wavelength. If your power density is less than the adjusted LIDT of the optic, then the optic should work for your application.
An AC127-030-C achromatic doublet lens has a specified CW LIDT of 350 W/cm, as tested at 1550 nm. CW damage threshold values typically scale directly with the wavelength of the laser source, so this yields an adjusted LIDT value:

Please note that we have a buffer built in between the specified damage thresholds online and the tests which we have done, which accommodates variation between batches. Upon request, we can provide individual test information and a testing certificate. The damage analysis will be carried out on a similar optic (customer's optic will not be damaged). Testing may result in additional costs or lead times. Contact Tech Support for more information.
Retroreflector
The beamsplitter coating is only applied to one of the two diagonal surfaces prior to optical contacting. Light can be input into any of the polished faces to separate the s- and p-polarizations. For ease of use, each part is engraved with the item number and a set of arrows indicating one of the possible beam paths (as seen in the images below).
The cubes separate the s- and p-polarization components by reflecting the s-component at the dielectric beamsplitter coating while allowing the p-component to pass. For the highest polarization extinction ratio, use the transmitted beam, which offers an extinction ratio of Tp:Ts > 2000:1.
This scaling gives adjusted LIDT values of 0.08 J/cm2 for the reflective filter and 14 J/cm2 for the absorptive filter. In this case, the absorptive filter is the best choice in order to avoid optical damage.
Now compare the maximum power density to that which is specified as the LIDT for the optic. If the optic was tested at a wavelength other than your operating wavelength, the damage threshold must be scaled appropriately. A good rule of thumb is that the damage threshold has a linear relationship with wavelength such that as you move to shorter wavelengths, the damage threshold decreases (i.e., a LIDT of 10 W/cm at 1310 nm scales to 5 W/cm at 655 nm):
As described above, the maximum energy density of a Gaussian beam is about twice the average energy density. So, the maximum energy density of this beam is ~0.7 J/cm2.
In order to illustrate the process of determining whether a given laser system will damage an optic, a number of example calculations of laser induced damage threshold are given below. For assistance with performing similar calculations, we provide a spreadsheet calculator that can be downloaded by clicking the button to the right. To use the calculator, enter the specified LIDT value of the optic under consideration and the relevant parameters of your laser system in the green boxes. The spreadsheet will then calculate a linear power density for CW and pulsed systems, as well as an energy density value for pulsed systems. These values are used to calculate adjusted, scaled LIDT values for the optics based on accepted scaling laws. This calculator assumes a Gaussian beam profile, so a correction factor must be introduced for other beam shapes (uniform, etc.). The LIDT scaling laws are determined from empirical relationships; their accuracy is not guaranteed. Remember that absorption by optics or coatings can significantly reduce LIDT in some spectral regions. These LIDT values are not valid for ultrashort pulses less than one nanosecond in duration.
According to the test, the damage threshold of the mirror was 2.00 J/cm2 (532 nm, 10 ns pulse, 10 Hz, Ø0.803 mm). Please keep in mind that these tests are performed on clean optics, as dirt and contamination can significantly lower the damage threshold of a component. While the test results are only representative of one coating run, Thorlabs specifies damage threshold values that account for coating variances.
Pulsed Microsecond Laser ExampleConsider a laser system that produces 1 µs pulses, each containing 150 µJ of energy at a repetition rate of 50 kHz, resulting in a relatively high duty cycle of 5%. This system falls somewhere between the regimes of CW and pulsed laser induced damage, and could potentially damage an optic by mechanisms associated with either regime. As a result, both CW and pulsed LIDT values must be compared to the properties of the laser system to ensure safe operation.
Beam diameter is also important to know when comparing damage thresholds. While the LIDT, when expressed in units of J/cm², scales independently of spot size; large beam sizes are more likely to illuminate a larger number of defects which can lead to greater variances in the LIDT [4]. For data presented here, a <1 mm beam size was used to measure the LIDT. For beams sizes greater than 5 mm, the LIDT (J/cm2) will not scale independently of beam diameter due to the larger size beam exposing more defects.
This tab contains plots for the typical transmission of our high-power polarizing beamsplitter cubes and plots of the reflectance for the AR coatings used on the outer surfaces of the cubes.
Thorlabs' LIDT testing is done in compliance with ISO/DIS 11254 and ISO 21254 specifications.First, a low-power/energy beam is directed to the optic under test. The optic is exposed in 10 locations to this laser beam for 30 seconds (CW) or for a number of pulses (pulse repetition frequency specified). After exposure, the optic is examined by a microscope (~100X magnification) for any visible damage. The number of locations that are damaged at a particular power/energy level is recorded. Next, the power/energy is either increased or decreased and the optic is exposed at 10 new locations. This process is repeated until damage is observed. The damage threshold is then assigned to be the highest power/energy that the optic can withstand without causing damage. A histogram such as that below represents the testing of one BB1-E02 mirror.
Räumliche Kohärenz, ein experimenteller Zugang zum verbeserten Verständnis. Pieper, Kai; Bergmann, Antje; Dengler, Roman; Rockstuhl, Carsten. Export.
However, the maximum power density of a Gaussian beam is about twice the maximum power density of a uniform beam, as shown in the graph to the right. Therefore, a more accurate determination of the maximum linear power density of the system is 1 W/cm.
CW Laser ExampleSuppose that a CW laser system at 1319 nm produces a 0.5 W Gaussian beam that has a 1/e2 diameter of 10 mm. A naive calculation of the average linear power density of this beam would yield a value of 0.5 W/cm, given by the total power divided by the beam diameter:
Thorlabs expresses LIDT for CW lasers as a linear power density measured in W/cm. In this regime, the LIDT given as a linear power density can be applied to any beam diameter; one does not need to compute an adjusted LIDT to adjust for changes in spot size, as demonstrated by the graph to the right. Average linear power density can be calculated using the equation below.
Image Studio is an image data analysis software used most often for ... Image Studio Lite. Introduced By: TRM Request. Vendor Name: LICOR Biosciences ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500