Ultraviolet radiation - light spectrum ultraviolet
DIC is a very useful illumination technique for providing enhanced specimen features. DIC uses a Normarski prism along with a polarizer in the 90° crossed positions. Essentially, two light beams are made to coincide at the focal plane of the objective, thus rendering height differences more visible as variations in colour.
Advancedillumination
Machine vision lighting refers to the use of specific lighting techniques and equipment in the field of machine vision, which is a technology that enables machines to capture and interpret visual information from the surrounding environment. In machine vision applications, proper lighting is crucial for enhancing the quality and accuracy of image acquisition and analysis. Machine vision lighting is designed to optimize the illumination of objects or scenes being inspected or analyzed by machine vision systems.
Illuminationtechniques in slit lamp
Optical microscopy is a widely used technique for analysing metallographic specimens. The typical magnification range for optical microscopes is from ×50 to ×1000. Optical microscopes use a number of different optical techniques to reveal specific microstructural features, including the following illumination techniques: bright field (BF), dark field (DF), polarized light (POL), oblique (stereo) and Differential Interference Contrast (DIC):
Properly designed and implemented machine vision lighting plays a critical role in the success of machine vision systems, as it significantly impacts the system's ability to recognize and analyze objects, patterns, or defects in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, quality control, robotics, and more.
Eliminating glare: Minimizing unwanted reflections and glare on shiny or reflective surfaces to ensure accurate image analysis.
Dark field lighting
Dome LightMachine Vision
BF illumination is the most common illumination technique for metallographic analysis. The light path for BF illumination is from the source, through the objective, reflected off the surface, returning through the objective, and back to the eyepiece or camera.
Uniformity: Achieving consistent and even lighting across the entire field of view to reduce shadows and variations in image brightness.
Machine vision lighting can involve various lighting sources, such as LED lights, halogen lights, or laser sources, and different lighting techniques, including diffuse lighting, direct lighting, backlighting, and dark field lighting, among others. The choice of lighting method depends on the specific requirements of the machine vision application, the type of objects being inspected, and the desired outcome.
Contrast: Enhancing the contrast between objects and their backgrounds to make it easier for machine vision systems to detect, measure, or classify objects.
Machine visionBacklight
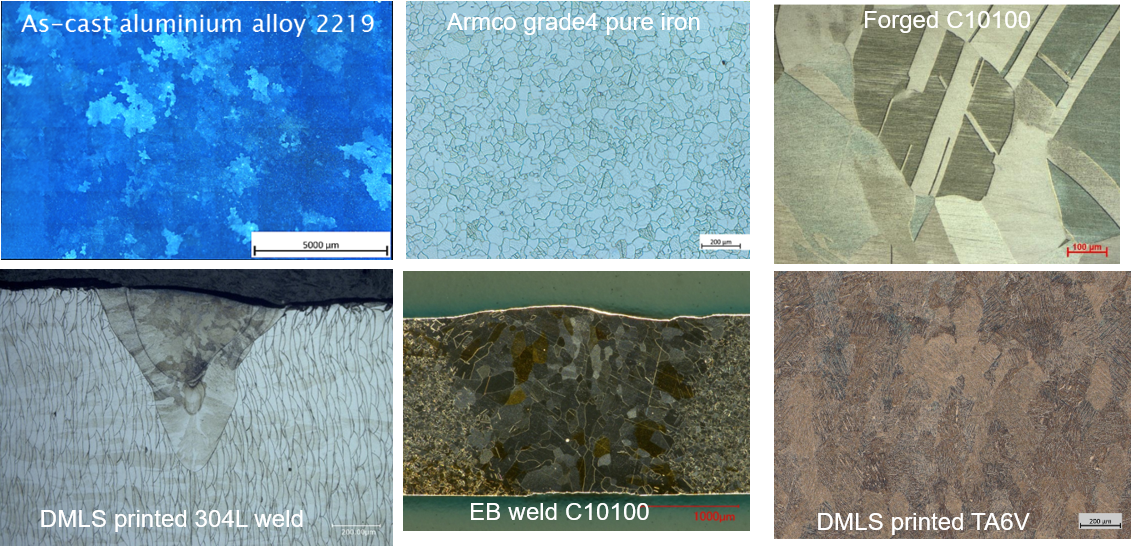

DF illumination is a lesser known but powerful illumination technique. The light path for DF illumination is from the source, down the outside of the objective, reflected off the surface, returned through the objective and back to the eyepiece or camera.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500