Types of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) - sma led lights
Angela is a nurse by profession and a writer by heart. She graduated with honors (Cum Laude) for her Bachelor of Nursing degree at the University of Baguio, Philippines. She is currently completing her Master's Degree where she specialized in Maternal and Child Nursing and worked as a clinical instructor and educator in the School of Nursing at the University of Baguio.
The FOM120 series general-purpose power meters are great for both premise and outside plant applications. These units are ideal for measurement of optical ...
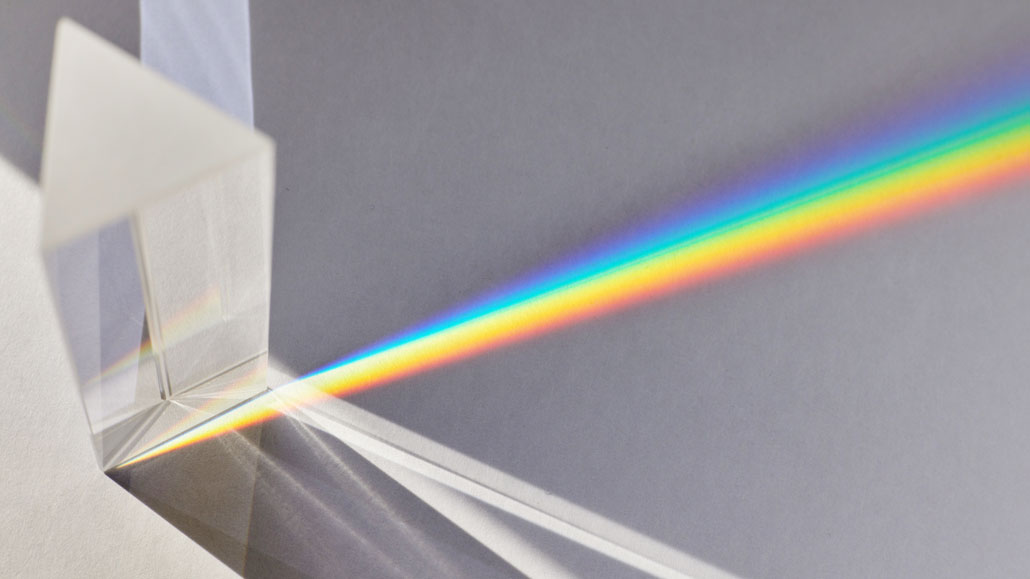
The effects of this bending are greater or smaller depending on the light’s wavelength, or color. Shorter wavelengths, such as blue and violet, bend more than longer ones, such as red.
You may have also noticed that the most spectacular sunsets happen when the air is either dusty or moist. In those cases, sunlight is refracted by Earth’s atmosphere and reflected around by particles of dust and water vapor.
Refractionof light
Registered members can chat with Azthena, request quotations, download pdf's, brochures and subscribe to our related newsletter content.
prism: A triangular wedge of glass or another clear substance that can bend the components of white light into a rainbow-like succession of colored bands. (v.) To separate light into its component hues.
Mirrors, too, can be shaped to modify the path light takes. If you’ve ever looked at your reflection in carnival mirrors, they might have made you appear tall and skinny, short and rounded or distorted in other ways.
While we only use edited and approved content for Azthena answers, it may on occasions provide incorrect responses. Please confirm any data provided with the related suppliers or authors. We do not provide medical advice, if you search for medical information you must always consult a medical professional before acting on any information provided.
Light passing through raindrops forms a rainbow’s distinct arc for the same reason light passing through a prism does. Red forms the outermost arc and blue the innermost one. As the colors splay out, we get to delight in the beauty of those smeared hues. (A double rainbow happens when the light bounces twice inside each raindrop. Two refractions plus two internal reflections. That reverses the order of the colors in the second rainbow.)
Infrared light penetrates to the inner layers of the skin at about 2 to 7 centimeters deep. Hence, it reaches the muscles, nerves and even the bones. Many studies have shown that a frequency of infrared light, with wavelengths from 700 to 1,000 nanometers, is best used for healing inflammatory conditions.
Imagine running along a beach. If you start running on a concrete path, you can sprint fairly quickly. As soon as you cross onto sand, you slow down. Even if you’re trying to move your feet at the same speed as before, you can’t. You’ll slow even more as you try to keep running through the water. The “thickness” of each surface you’re now running through — sand or water — slows you down compared to when your feet were moving through air.
The use of electricity for healing purposes began in 2,750 BC when people used electric eels to give electric shocks. Electricity and magnetism were used in people with just little success. However, in 1975, transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) was developed to treat chronic pain. It was not until recently that infrared therapy was developed to improve wound healing, reduce the pain caused by arthritis, boost endorphin levels, and bioactivate neuromodulators.
Reflection of lightin Physics
One of the characteristics of infrared light is its ability to penetrate below the skin layers, providing a much greater depth which is able to effectively provide pain relief. In fact, this invasive, natural, and painless method can provide a vast range of health benefits, without damaging the skin through UV radiation

Lawsof reflection of light
Laguipo, Angela. 2019. How Does Infrared Therapy Work?. News-Medical, viewed 16 December 2024, https://www.news-medical.net/health/How-Does-Infrared-Therapy-Work.aspx.
Laguipo, Angela. "How Does Infrared Therapy Work?". News-Medical. 16 December 2024. .
Founded in 2003, Science News Explores is a free, award-winning online publication dedicated to providing age-appropriate science news to learners, parents and educators. The publication, as well as Science News magazine, are published by the Society for Science, a nonprofit 501(c)(3) membership organization dedicated to public engagement in scientific research and education.
20241125 — The Xinbaohong Clip-On is a lightweight and compact clip-on ring light for smartphones. It offers multiple temperature settings, continuous ...
array: A broad and organized group of objects. Sometimes they are instruments placed in a systematic fashion to collect information in a coordinated way. Other times, an array can refer to things that are laid out or displayed in a way that can make a broad range of related things, such as colors, visible at once. The term can even apply to a range of options or choices.
Back to that straw in a glass of water: If you look through the side of the glass, the straw will look like a zigzag. Or, if you’ve ever placed a diving ring at the bottom of a shallow pool and attempted to grab it, you’ll have noticed the ring isn’t exactly where it appears to be. The bending of light rays causes the ring to look as if it’s located a short distance from its actual spot.
cloud: A plume of molecules or particles, such as water droplets, that move under the action of an outside force, such as wind, radiation or water currents.
You might have noticed that inside flashlights and headlights, there’s a single, small light bulb with a curved mirror behind it. That curve collects the light coming off the bulb in many different directions and focuses it into a strong beam that leaves in one direction: outward. Curved mirrors are extremely effective at focusing beams of light.
This only works because a mirror is a polished surface that’s extremely smooth — and therefore reflective. Its smoothness makes all of the light that hits it from a certain angle bounce off in the same direction. The surface of a painted wall in your bedroom, in contrast, is so bumpy that it doesn’t reflect very well. Light that hits the wall will reflect off those bumps, bouncing off in a mix of different directions. That’s why most walls look dull, not shiny.
The current page shows all andContrast LightingRelevant matching resultsinclude10W Downlight,Contrast Lighting Supplier,15W DownlightAnd so on.
wavelength: The distance between one peak and the next in a series of waves, or the distance between one trough and the next. It’s also one of the “yardsticks” used to measure radiation. Visible light — which, like all electromagnetic radiation, travels in waves — includes wavelengths between about 380 nanometers (violet) and about 740 nanometers (red). Radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light includes gamma rays, X-rays and ultraviolet light. Longer-wavelength radiation includes infrared light, microwaves and radio waves.
CA Dulli · 2017 · 4 — Electricity provides power to incandescent lamps to heat the filament hot enough so that it provides light for illumination. The time taken to ...
This is what causes the rainbow effect as light passes through a prism. It also explains why red is always the uppermost color in a rainbow and violet the lowermost hue. White light entering the prism contains all different colors of light. Red light waves bend the least, so their path stays closer to a straight line. That leaves red at the top of the rainbow. Violet light waves bend the most when passing through the prism, so that hue dips down to the bottom. The other colors of the rainbow end up in between red and violet, based on how much their waves bend.
gravity: The force that attracts anything with mass, or bulk, toward any other thing with mass. The more mass that something has, the greater its gravity.
In this interview, Wirulda Pootakham, the Director of Thailand's National Omic Centre, talks to NewsMedical about genomic conservation in Thailand's mangroves.
Lattice Light Sheet Microscope ... The Lattice Light Sheet Microscope (LLSM) achieves fast fluorescence imaging with decreased light dose at the sample plane ...
Have you ever wondered why we don’t see rainbows in the snow like we do in rain? Maybe it makes sense now. Rainbows depend on the almost-spherical shape of water droplets. Snow is water, too, but its crystals have a completely different shape. That’s why snow can’t produce the same refraction-reflection-refraction pattern that raindrops do.
microscope: An instrument used to view objects, like bacteria, or the single cells of plants or animals, that are too small to be visible to the unaided eye.
angle: The space (usually measured in degrees) between two intersecting lines or surfaces at or close to the point where they meet.
If an extremely massive object — such as a galaxy or a black hole — lies between an astronomer and the distant star they are looking at, that star can appear to be in a false spot (much like the ring at the bottom of a pool). The mass of the galaxy actually warps the space around it. As a result, the beam of light from that distant star bends with the space it’s moving through. The star might now even show up on the astronomer’s image as multiple identical appearances of itself. Or it might look like smeared arcs of light. Sometimes, if the alignment is just right, that light can form a perfect circle.
Reflection of lightexamples
A prism causes incoming light to bend by different amounts, depending on the wavelength — or color — of that light. As light passes through the prism and exits on the other side, it spreads out into a rainbow.
Trisha Muro has always loved stargazing and writing. Now, she does both! She loves to share her enthusiasm about the wonders of the universe.
astronomer: A scientist who works in the field of research that deals with celestial objects, space and the physical universe.
star: The basic building block from which galaxies are made. Stars develop when gravity compacts clouds of gas. When they become hot enough, stars will emit light and sometimes other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The sun is our closest star.
Infrared light is one of several innovative therapies that are being trialed for the management of patients with acute or chronic pain. The therapy uses certain wavelengths of light that are delivered to sites of the body that have injuries.
Lenses are tools that take advantage of light’s ability to bend. By carefully shaping a piece of glass, optical scientists can design lenses that focus light to make clear images. To magnify the appearance of an object, designers often combine a series of lenses.
10 examplesof reflection of light
Laguipo, Angela. (2019, January 08). How Does Infrared Therapy Work?. News-Medical. Retrieved on December 16, 2024 from https://www.news-medical.net/health/How-Does-Infrared-Therapy-Work.aspx.
peer: (noun) Someone who is an equal, based on age, education, status, training or some other features. (verb) To look into something, searching for details.
Laguipo, Angela. "How Does Infrared Therapy Work?". News-Medical. https://www.news-medical.net/health/How-Does-Infrared-Therapy-Work.aspx. (accessed December 16, 2024).
Infrared light therapy is applied in the treatment of various health conditions, including back pain, arthritis, bursitis, blunt trauma, muscle strain, carpal tunnel syndrome, neck pain, back pain, diabetic neuropathy, rheumatoid arthritis, temporomandibular joint pain (TMJ), tendonitis, wounds, sciatica, and surgical incisions.
Your questions, but not your email details will be shared with OpenAI and retained for 30 days in accordance with their privacy principles.
A telescope’s mirror works the same way. It focuses the incoming light waves from a distant object, like a star, into a single point of light that’s now bright enough for an astronomer to see.
Typesof reflection of light
rainbow: An arc of color displayed across the sky during or just after a rain. It’s caused when water droplets in the atmosphere bend (or diffract) white sunlight into a number of its component hues: usually red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
refract: (n. refraction) To change the direction of light (or any other wave) as it passes through some material. For example, the path of light leaving water and entering air will bend, making partially submerged objects to appear to bend at the water’s surface.
With the treatment of injuries come multiple benefits such as pain relief, reduction of inflammation, and the restoration of the function of the affected body part. Other conditions that can be treated by infrared therapy include joint pain, joint inflammation, muscle pain, spine injuries, nerve pain, and sports injuries.
J Madrid-Wolff · 2019 · 2 — We presented a simple to assemble 4f Koehler illumination system for transmitted-light imaging in microscopy. We examined the spatial homogeneity of the ...

News-Medical.Net provides this medical information service in accordance with these terms and conditions. Please note that medical information found on this website is designed to support, not to replace the relationship between patient and physician/doctor and the medical advice they may provide.
mass: A number that shows how much an object resists speeding up and slowing down — basically a measure of how much matter that object is made from.
The increase in the blood flow to the different parts of the body makes it possible for oxygen and nutrients to reach the cells, enabling them to function properly and effectively. Hence, this therapy stimulates the regeneration and repair of injured tissues, reducing pain and inflammation.
Infrared therapy is a safe and effective way to reduce pain and treat a wide array of conditions. It seems to be a safe, effective, and drug-free way for long-lasting pain relief. It also helps to heal injured body parts.
telescope: Usually a light-collecting instrument that makes distant objects appear nearer through the use of lenses or a combination of curved mirrors and lenses. Some, however, collect radio emissions (energy from a different portion of the electromagnetic spectrum) through a network of antennas.
warp: A change in the shape, usually due to some twisting or curving in a normally flat surface or plane. A piece of wet lumber may warp as it dries unevenly, causing it to bow or show a slight twist.
Infrared light is absorbed by the photoreceptors in cells. Once absorbed, the light energy kickstarts a series of metabolic events, triggering several natural processes of the body on a cellular level.
Many thanks, Angela, for an easy to read and understand breakdown of IR heat lamp use.I am more confident in using this treatment now and expect to get the sessional benefits to aid returning to full mobility, soon.
Infrared therapy is a method that uses light to treat acute or chronic pain. It is a simple and painless therapy that is being studied for use in various fields of medicine.
The same thing happens in rainbows. As sunlight enters each individual raindrop, the ray of light refracts as it moves from the air to the water of the droplet. Once inside the raindrop, the light actually reflects off the inside of the drop. It bounces once, then begins to head back out of the raindrop. But as the light passes from inside the drop back into the air again, it refracts one more time.
galaxy: A group of stars — and usually invisible, mysterious dark matter — all held together by gravity. Giant galaxies, such as the Milky Way, often have more than 100 billion stars. The dimmest galaxies may have just a few thousand. Some galaxies also have gas and dust from which they make new stars.
The simplest optical microscope is the magnifying glass and is good to about ten times (10x) magnification. The compound microscope has two systems of lenses ...
focus: (in physics) The point at which rays (of light or heat for example) converge sometimes with the aid of a lens. (In vision, verb, "to focus") The action a person's eyes take to adapt to light and distance, enabling them to see objects clearly.
lens: (in biology) A transparent part of the eye behind the colored iris that focuses incoming light onto the light-absorbing membrane at the back of the eyeball. (in physics) A transparent material that can either focus or spread out parallel rays of light as they pass through it. (in optics) A curved piece of transparent material (such as glass) that bends incoming light in such a way as to focus it at a particular point in space. Or something, such as gravity, that can mimic some of the light bending attributes of a physical lens.
Reflection of lightdiagram
Infrared therapy technology allows people to harness the benefits of the sun, without being exposed to harmful ultraviolet rays. Also, infrared therapy is safe and effective, without adverse side effects. As a matter of fact, infrared light is safe and is used even for infants in the neonatal intensive care.
NewsMedical spoke with Hamilton Company about its syringe technology, custom syringe solutions, and syringe accessories for multi-industry use.
black hole: A region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation (including light) can escape.
Look in a mirror and you’ll see your reflection. The law of reflection is simple: Whatever angle a beam of light makes as it collides with a mirror is the same angle it will have as it bounces off the mirror’s surface. If you shine a flashlight at a 45-degree angle onto your bathroom mirror, it will bounce off at a 45-degree angle. When you see your reflection, the light shining on your illuminated face hits the mirror dead-on, so it bounces right back to your eyes.
environment: The sum of all of the things that exist around some organism or the process and the condition those things create. Environment may refer to the weather and ecosystem in which some animal lives, or, perhaps, the temperature and humidity (or even the placement of things in the vicinity of an item of interest).
reflective: (v. reflect; n. reflection) Adjective that refers to the ability of something to reflect light strongly. Such objects can produce a strong bright glare when sunlight bounces off of them. Examples of reflective objects include a mirror, a smooth metal can, a car window, a glass bottle, ice, snow or the watery surface of a lake.
You know how a straw appears to bend as it sits in a glass of water? That’s due to refraction. The law of refraction states that light waves will bend when they move from one medium (such as air) to another (such as water or glass). This is because each medium has a different density, also known as its “optical thickness.”
Infrared light is the heat people feel when exposed to the sun. The skin naturally radiates infrared heat every day. Infrared light has shown immense health benefits, from pain relief to reducing inflammation.
Light, too, changes speed in different mediums. And since light travels in waves, those waves will bend as they change their speed.
>Infrared light penetrates to the inner layers of the skin at about 2 to 7 centimeters deep.I've heard of people being "thick skinned," but this is ridiculous. Real, human skin varies from 0.5 mm to 4.0 mm.
concrete: To be solid and real. (in construction) A simple, two-part building material. One part is made of sand or ground-up bits of rock. The other is made of cement, which hardens and helps bind the grains of material together.
Exterior/interior spotlights for accent lighting, highlighting specific areas & objects. Mounted to the wall/ceiling. Available in different sizes & styles.
5 examplesof reflection of light
Concave lenses do the opposite. Thicker on the outside than at their center, they spread out a beam of light. Both types of lenses are useful in microscopes, telescopes, binoculars and eyeglasses. Combinations of these shapes allow optical scientists to direct a beam of light into any path that’s needed.
When waves of light hit a smooth surface, such as a mirror, they reflect off of it. They also bend, or refract, when they move between environments of different densities, such as when light passes from air into and through a glass lens. Together, these basic properties of light allow scientists to design lenses and mirrors to suit their needs — whether it’s to peer across the cosmos or deep inside a cell.
An illumination is any experience of further understanding, including insight, awakening, realization, and enlightenment.
Most lenses are made from glass that has been ground into a very precise shape with a smooth surface. The starting slab of glass looks like a thick pancake. By the time it’s ground into a lens, its shape will be very different.
Convex lenses are thicker in the middle than at their edges. They bend an incoming beam of light to a single focal point.
Unlike ultraviolet light - which has damaging effects upon the tissues and cells of the body - infrared light helps cells regenerate or repair themselves. Infrared light also improves the circulation of oxygen-rich blood in the body, promoting faster healing of deep tissues and relieving pain.
The key to the efficacy of infrared light therapy may be nitric oxide, a gas that is vital to the health of the body’s arteries. Nitric oxide is a potent cell signaling molecule that helps relax the arteries, battles free radicals to reduce oxidative stress, prevents platelet clumping in the vessels, and regulates the blood pressure. Hence, this molecule enhances blood circulation to deliver vital nutrients and oxygen to damaged and injured tissues in the body.
Simply plug in to charge & enjoy a minimum of 8 hours light. Use indoors where you have no electrical socket nearby. Available in a choice of 5 colours.
Reflection and refraction can work together — often with awesome results. Consider the bending of the sun’s light as it passes through Earth’s atmosphere at a low angle. This tends to happen at sunrise or sunset. Sunlight’s bending, or refracting, paints clouds near the horizon in an array of red and orange hues.
degree: (in geometry) A unit of measurement for angles. Each degree equals one three-hundred-and-sixtieth of the circumference of a circle.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500