The Smallest, Most Advanced LED Driver in the World - advanced led lights
Now in mounting our star boards to the heat sinks it is best to use a thermally conductive material to further take steps in optimal thermal performance. We recommend this Arctic Silver epoxy, it’s what we use here in the craft shop when we build all the LED kits we offer. We also have a very quick option in our HexaTherm Tape which is essentially just thermally conductive double sided tape in the exact shape of our LED star boards. The HexaTherm isn’t as thermally conductive as the epoxy but it will still do the trick. LEDSupply offers HexaTherm in 1-up and 3-up Star board tape sizes.
While exposure to UV light can lead to skin cancer, some skin conditions can be treated using UV light, according to Cancer Research UK. In a procedure called psoralen ultraviolet light treatment (PUVA), patients take a drug or apply a lotion to make their skin sensitive to light. Then a UV light is shone on the skin. PUVA is used to treat lymphoma, eczema, psoriasis and vitiligo.
Before diving into heat sinks you must know that when you purchase LEDs on our metal core printed circuit board LED stars this is already taking a good step to better thermal control. LEDs come in reels as bare emitters that are encapsulated in a transparent resin, which tends to be a poor thermal conductor, so when we mount them on an aluminum base it acts as a heat spreader and is an integral part of the circuit board that aids in thermal conductivity.
The guide goes on to state, "Radiations with wavelengths from 10 nm to 180 nm are sometimes referred to as vacuum or extreme UV." These wavelengths are blocked by air, and they only propagate in a vacuum.
The surface of your heat sink actually has a direct effect on thermal conductivity as well. A painted surface will actually work better than a bright, unpainted one. This also is the same for anodizing and etching heat sinks which will decrease the thermal resistance and make for an overall better heat sink.
LEDStrip lights
One of the most common ways of producing UV light is passing an electric current through vaporized mercury or some other gas. This type of lamp is commonly used in tanning booths and for disinfecting surfaces. The lamps are also used in black lights that cause fluorescent paints and dyes to glow. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs), lasers and arc lamps are also available as UV sources with various wavelengths for industrial, medical and research applications.
Many substances — including minerals, plants, fungi and microbes, as well as organic and inorganic chemicals — can absorb UV radiation. Absorption causes electrons in the material to jump to a higher energy level. These electrons can then return to a lower energy level in a series of smaller steps, emitting a portion of their absorbed energy as visible light. Materials used as pigments in paint or dye that exhibit such fluorescence appear brighter under sunlight because they absorb invisible UV light and re-emit it at visible wavelengths. For this reason they are commonly used for signs, safety vests and other applications in which high visibility is important.
Led lightstrip 24v
The ambient temperature and the drive current both affect the junction temperature of LEDs. Other influences are the nature of the light, whether it is steady state or pulsed, and then the one we are really interested in, LED wattage per unit area of heat sink (surface that dissipates heat).
Heat sinkmanufacturers
As the junction temperature of an LED increases, both the forward voltage and the lumen output decreases (see Picture 1). Not only is this decreasing the brightness and efficiency of your LED but this junction temperature affects the overall lifetime of the LED as well. LEDs don’t usually fail catastrophically (although some may, especially if you over heat them); instead, the lumen output of the LED will decrease over time. Higher junction temperatures lead to faster LED deterioration. This is why it is crucial to keep your LED junction temperature low. Also take note that if you are over driving your LED (putting more current to it than what it is rated) this will drive temperatures up so high that permanent damage can occur.
The thermal transfer takes place at the surface of the heat sink. That is why the best heat sinks have a large surface area. This can be achieved by straight up increasing the size of the heat sink, or by the use of fins. Finned heat sinks help as they provide many more surfaces for heat to transfer from. Whereas fins help, there still needs to be enough space in between fins for air to move through to generate a difference in temperature between the fins and the air. When fins are made too close together, the air in between wouldn’t cool and would become almost the same temperature as the fins which would stop thermal transfer all together. So more fins doesn’t automatically mean better cooling, you need well spaced fins.
A suntan is a reaction to exposure to harmful UVB rays. Essentially, a suntan results from the body's natural defense mechanism kicking in. This consists of a pigment called melanin, which is produced by cells in the skin called melanocytes. Melanin absorbs UV light and dissipates it as heat. When the body senses sun damage, it sends melanin into surrounding cells and tries to protect them from sustaining more damage. The pigment causes the skin to darken.
Recent research suggests that UV light may have played a key role in the origin of life on Earth, especially the origin of RNA. In a 2017 article in the Astrophysics Journal, the authors of the study note that red dwarf stars may not emit enough UV light to start the biological processes needed for the formation of ribonucleic acid, which is necessary for all forms of life on Earth. The study also suggests this finding could help in the search for life elsewhere in the universe.
Heatsinks for electronics
With high-power LEDs, it is crucial that you remove heat through efficient thermal management. Without good heat sinking, the junction (internal) temperature of the LED rises, causing the LED characteristics to change for the bad.
A number of artificial sources have been devised for producing UV radiation. According to the Health Physics Society, "Artificial sources include tanning booths, black lights, curing lamps, germicidal lamps, mercury vapor lamps, halogen lights, high-intensity discharge lamps, fluorescent and incandescent sources, and some types of lasers."
"Melanin is a natural sunscreen," Gary Chuang, an assistant professor of dermatology at Tufts University School of Medicine, told Live Science in a 2013 interview. However, continued exposure to UV radiation can overwhelm the body's defenses. When this happens, a toxic reaction occurs, resulting in sunburn. UV rays can damage the DNA in the body's cells. The body senses this destruction and floods the area with blood to help with the healing process. Painful inflammation occurs as well. Usually within half a day of overindulging in the sun, the characteristic red-lobster look of a sunburn begins to make itself known, and felt.
Electromagnetic radiation comes from the sun and transmitted in waves or particles at different wavelengths and frequencies. This broad range of wavelengths is known as the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The spectrum is generally divided into seven regions in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy and frequency. The common designations are radio waves,microwaves, infrared (IR), visible light, ultraviolet (UV), X-rays and gamma-rays.
Sometimes the cells with DNA mutated by the sun's rays turn into problem cells that don't die but keep proliferating as cancers. "The UV light causes random damages in the DNA and DNA repair process such that cells acquire the ability to avoid dying," said Chuang.
Heat sinkforLEDstrip
Marketing and technology enthusiast helping pave the way to a more energy-efficient society. Living in the beautiful state of Vermont and working for a company like LEDSupply that is helping provide LED products to save on energy is a great place to be to accomplish this. Always exploring and staying active outdoors while keeping a close eye on different trends and new technologies that could change the world for the better.
Stay tuned for more posts on LED heat sinks and choosing the right one, but this should get you started in setting up your LED system!
The most important part of LED cooling is the thermal path from the LED junction to the outside of the light fixture. Heat needs to be conducted away from the LED in an efficient manner, and then removed from the area by some sort of cooling or dissipation.
According to Robert Patterson, a professor of astronomy at Missouri State University, most observations are conducted using charge-coupled devices (CCD), detectors designed to be sensitive to short-wavelength photons. These observations can determine the surface temperatures of the hottest stars and reveal the presence of intervening gas clouds between the Earth and quasars.
Although LEDs are cool to the touch, within the devices themselves, there is plenty of unwanted heat. This heat comes from the inefficiency of the semiconductors that generate the light. The radiant efficiency (total optical output power divided by total electrical input power) of LEDs is typically between 5 and 40%, meaning that 60-95% of the input power is lost as heat. So what do you do with all this excess internal heat?!
Fluorescence can also be used to locate and identify certain minerals and organic materials. According to Thermo Fisher Scientific, Life Technologies, "Fluorescent probes enable researchers to detect particular components of complex biomolecular assemblies, such as live cells, with exquisite sensitivity and selectivity."
So there you have it, now you should know why you need an LED heat sink. When choosing your heat sink and finding which heat sink to use, remember to take into account all the factors that contribute to heat and the cooling process:
The result is skin cancer, the most common form of cancer in the United States. People who get sunburned repeatedly are at much higher risk. The risk for the deadliest form of skin cancer, called melanoma, doubles for someone who has received five or more sunburns, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
UV radiation has enough energy to break chemical bonds. Due to their higher energies, UV photons can cause ionization, a process in which electrons break away from atoms. The resulting vacancy affects the chemical properties of the atoms and causes them to form or break chemical bonds that they otherwise would not. This can be useful for chemical processing, or it can be damaging to materials and living tissues. This damage can be beneficial, for instance, in disinfecting surfaces, but it can also be harmful, particularly to skin and eyes, which are most adversely affected by higher-energy UVB and UVC radiation.

Live Science is part of Future US Inc, an international media group and leading digital publisher. Visit our corporate site.
Besides the sun, there are numerous celestial sources of UV radiation. Very large young stars shine most of their light in ultraviolet wavelengths, according to NASA. Because Earth's atmosphere blocks much of this UV radiation, particularly at shorter wavelengths, observations are conducted using high-altitude balloons and orbiting telescopes equipped with specialized imaging sensors and filters for observing in the UV region of the EM spectrum.
Ultraviolet light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that makes black-light posters glow, and is responsible for summer tans — and sunburns. However, too much exposure to UV radiation is damaging to living tissue.
In fluorescent tubes used for lighting, "ultraviolet radiation with a wavelength of 254 nm is produced along with the blue light that is emitted when an electric current is passed through mercury vapor," according to the University of Nebraska. "This ultraviolet radiation is invisible but contains more energy than the visible light emitted. The energy from the ultraviolet light is absorbed by the fluorescent coating inside the fluorescent lamp and re-emitted as visible light." Similar tubes without the same fluorescent coating emit UV light that can be used to disinfect surfaces, since the ionizing effects of UV radiation can kill most bacteria.
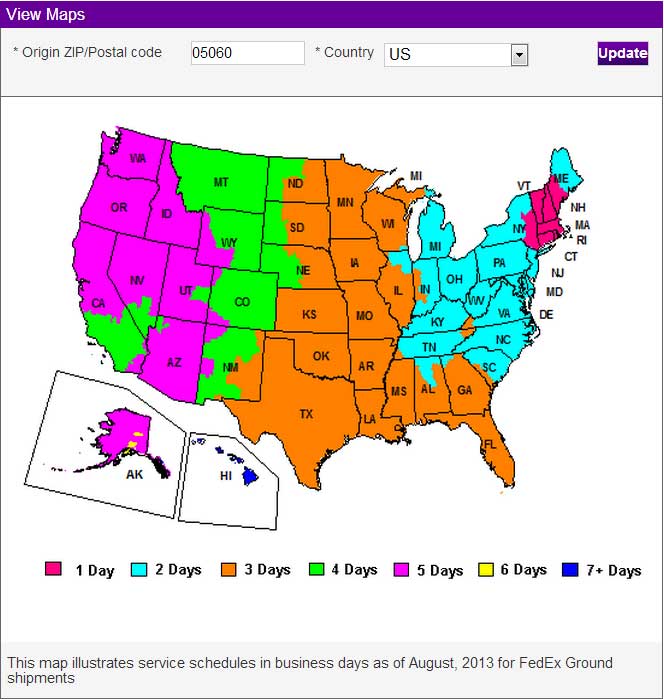
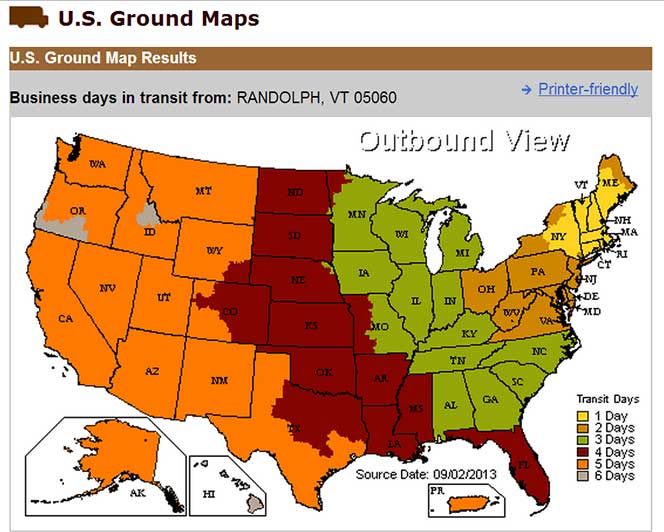
FREE SHIPPING on orders under 13oz - NO MINIMUM LEDSupply does NOT profit from the shipping or handling of your order! Orders received before 3PM EST will be safely packaged and quickly shipped the same business day. If your order is NOT shipped the same business day, LEDSupply will offer a 5% discount off your next order. All orders SHIP FROM: 44 Hull Street Suite 200 Randolph, Vermont 05060 See respective ZONE maps below for SPECIFIC delivery time to your location: Any order that does not qualify for free shipping, will by default include a discount of equal value to the free shipping offer. The shipping offered is meant to provide the widest variety of shipping options at the lowest price: FREE USPS First Class SHIPPING on orders under 13oz $5.99 USPS Priority SHIPPING on orders under 2lbs $7.99 FedEx GROUND SHIPPING on orders under 2lbs $8.99 UPS GROUND SHIPPING on orders under 2lbs $16.99 2-Day SHIPPING on orders under 2lbs $29.99 Standard Overnight SHIPPING on orders under 2lbs $39.99 Priority Overnight SHIPPING on orders under 2lbs Real-Time Rates are calculated for all International shipments *Base Rate + $1.99/lb for orders over 2lbs USPS Priority Delivery Zone Map: FedEX Ground Delivery Zone Map: UPS Ground Delivery Zone Map:
As I said previously, for larger LED arrays or lights that are in an enclosure where their isn’t much air flow you might want to consider some sort of ventilation system. This will help as the air surrounding your heat sink will in turn be cooler and allow for better thermal transfer from the heat sink surface to outside. Our MakersLED heat sink kits come with a fan included.
A frequently listed advantage of LEDs is that they do not produce heat. In a way, this is true, LEDs are cool to the touch because they usually do not produce heat in the form of infrared (IR) radiation. This obviously doesn’t go for IR specific LEDs.
LEDheatsink housing
Black-light tubes typically use mercury vapor to produce long-wave UVA light, which causes certain dyes and pigments to fluoresce. The glass tube is coated with a dark-purple filter material to block most of the visible light, making the fluorescent glow appear more pronounced. This filtering is not needed for applications such as disinfecting.
Most of the natural UV light people encounter comes from the sun. However, only about 10 percent of sunlight is UV, and only about one-third of this penetrates the atmosphere to reach the ground, according to the National Toxicology Program (NTP). Of the solar UV energy that reaches the equator, 95 percent is UVA and 5 percent is UVB. No measurable UVC from solar radiation reaches the Earth's surface, because ozone, molecular oxygen and water vapor in the upper atmosphere completely absorb the shortest UV wavelengths. Still, "broad-spectrum ultraviolet radiation [UVA and UVB] is the strongest and most damaging to living things," according to the NTP's "13th Report on Carcinogens."
Heat sinks are an important part of LED lighting because they provide the path for heat to travel from the LED light source to outside elements. Heat sinks are able to dissipate power in three ways: conduction (heat transfer from a solid to a solid), convection (heat transfer from a solid to a moving fluid, air in most cases), or radiation (heat transfer from two bodies at different temperatures through thermal radiation).
It may seem counterintuitive to treat skin cancer with the same thing that caused it, but PUVA can be useful due to UV light’s effect on the production of skin cells. It slows down the growth that plays a major role in the disease’s development.
IR radiation is what actually heats incandescent bulbs and other light sources, making them hot to the touch. Without IR radiation, LEDs are able to be placed in spots where the heat from other sources would cause a problem (grow lights, reef tank lights, illuminating food, etc.).
The thermal conductivity of the heat sink material directly affects how efficiently the heat dissipates through conduction. Copper is the best but because of its price point, aluminum is used more widely and is what the majority of the heat sinks we offer here at LEDSupply are. Thermoplastics, like our composite LED heat sink, can be used for smaller LEDs with lower heat dissipation requirements. The use of thermoplastics can be very useful as they can be molded in more shapes and are much more light weight.
Ultraviolet (UV) light falls in the range of the EM spectrum between visible light and X-rays. It has frequencies of about 8 × 1014 to 3 × 1016 cycles per second, or hertz (Hz), and wavelengths of about 380 nanometers (1.5 × 10−5 inches) to about 10 nm (4 × 10−7 inches). According to the U.S. Navy's "Ultraviolet Radiation Guide," UV is generally divided into three sub-bands:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500