The FOA Reference For Fiber Optics - Optical Fiber - light fiber cable
What ispolarizationinPhysics
It means that the light emitted by the sun travels in all the given directions, i.e. on different polarized lights. And when it is transmitted over a distance, it has a slight separation, and is separated only when its measuring angle is equal to the angle of separation. Because sunlight is everywhere, it is said that light is not polarized. When uninterrupted light falls on an exposed surface with an incident angle equal to the angle of division of the earth or also called Brewster's angle, it is called polarized-polarized. When uncollected light is transmitted through a separating sheet, it is separated.
Polarization of light refers to the alignment of the light waves so that they vibrate in a single direction. Light waves normally osciilate in all directions as they move. But when the light is polarized, these vibrations are restricted to one direction only thereby making the light very much organized.
Polarization definition
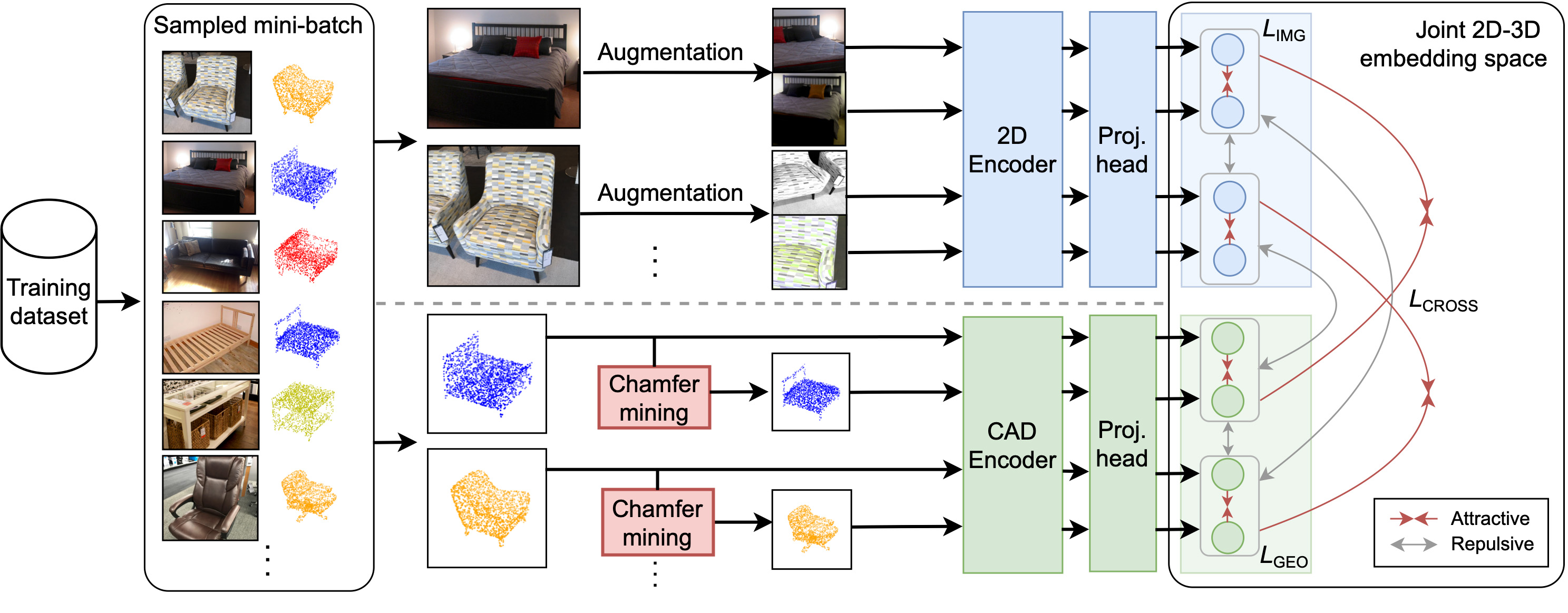
Learning Geometric-aware Properties in 2D Representation Using Lightweight CAD Models, or Zero Real 3D Pairs
Our method can generate multiple plausible chrome balls by varying the initial noise map of diffusion sampling. Note that the average of these variations captures the overall lighting reasonably well. This average is utilized by our "iterative inpainting" algorithm to enhance the quality and consistency of light estimation. Hover over these videos to pause.
Circularly polarizedlight
Polarization of light is the act of arranging radiation waves so that they oscillate in a single direction only. In general terms, light waves are free to vibrate in any direction while polarized light waves only vibrate in one specific plane or direction. Polarization is used in different applications including designing of sunglasses that reduce glare, enhancing photography, and investigating of properties of different materials. Read the below article for a better understanding of the polarization of Light.

Polarization by Refraction: Light is passed through certain crystals (like calcite or quartz) and splits into two beams with perpendicular polarization directions (birefringence).
Polarisation meaning inPhysicsElectrostatics

Polarisation angle is the angle at which unpolarized light or other electromagnetic radiation must be incident upon a nonmetallic surface for the reflected radiation to acquire maximum plane polarization.
If light strikes an interface so that there is a 90-degree angle between the reflected and refracted rays, the reflected light will be linearly polarized. The special angle of incidence that produces a 90-degree angle between the reflected and refracted rays is called the Brewster angle.
Polarization of light
$$ \mathbf{E}=E_0 \cos (k z-\omega t) \hat{i} $$ Where: $E_0$ : Amplitude $k$ Wave number $\omega$ : Angular frequency $t$ : Time $\hat{i}$ : Unit vector along the $\boldsymbol{x}$-axis
Separation is also possible by re-emitting light. Procrastination occurs when light rays pass from one information to another. On top of these two things, the path of the pole changes where it goes. The pointed beam receives a certain degree of separation.
polarization中文
Polarization by Transmission: This method utilizes Polaroid sheets which only allow vibrations in one direction to pass through.
Elliptical polarization: It is the type of polarization where the tip of the electric field vector defines an ellipse in any fixed plane traversing, as well as is normal to the direction of propagation.
Polarization of lightnotes PDF
Polarization by Reflection: When unpolarized light is reflected at a Brewster's angle, the reflected light is Polarized light.
Circular polarization: It is the type of polarization in which at every point, the electromagnetic field has a constant magnitude, but its direction rotates with a constant value in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
Linear polarization: Linearly polarized light wave means that the electric field vibrates in a certain linear direction perpendicular to the wave axis, and the magnetic field vibrates in a direction which is perpendicular to both, the advancement axis and direction of the electric field.
Our technique can estimate lighting for a variety of input images, such as indoor and outdoor scenes, close-up shots, paintings, and photos of human faces. Here, we show our predicted chrome balls in a normally exposed version (EV0) and an underexpoed version (EV-5). These input images are from Unsplash.com.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500