Reflected Collimator for Light Guide - collimator light
Seriously, if i am not grateful, i am lying. This note is really helpeful to me to differet ways to different methology.
When the sun is at a low angle in the sky, the sunlight reflecting off the surface of water is nearly 100% horizontally polarized because the angle of incidence is close to the Brewster angle. Glare-reducing sunglasses are coated with a polarizer with a vertical transmission axis and therefore block the reflected light.
Thanks for helping me to know the parts and functions of a light microscope. THANKS AGAIN AND I HOPE THAT I WILL DRAW IT IN MY EXAM
1. which objective lens focuses closest to object 2. what controls the light entering the binocular lenses 3. how can you enhance the resolving power of a microscope 4. what is useful and false magnification PLEASE CAN YOU HELP ME IN ASWERING THOSE QUESTIONS
Thanks a lot for this wonderful note: It is really helpful, Really appreciate the way all the detail about microscope have been explained
An ideal polarizer is a material that passes only EM waves for which the electric field vector is parallel to its transmission axis. The electric field is a vector and can be written in terms of the components parallel and perpendicular to the polarizer's transmission axis. E = Eparallel + Eperpendicular. An ideal polarizer passes Eparallel and absorbs Eperpendicular.If E0 is the incident field vector and the angle between E0 and the transmission axis is θ, then the magnitude of transmitted field vector is E0 cosθ and its direction is the direction of the transmission axis. The intensity I of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to the square of the magnitude of the electric field vector. We therefore haveItransmitted = I0 cos2θ. This is called the law of Malus. If θ = 90o the transmitted intensity is zero.
Ans. Rack stop is included in the microscope for preventing the specimen slide from coming too far up and hitting the objective lens.
Condensermicroscope function
A polarizer produces linearly polarized light. It is often convenient to orient the transmission axis of a polarizer vertically or horizontally to produce light with vertical or horizontal linear polarization.
Some materials turn birefringent when stressed. By placing transparent materials between two polarizers, we can perform stress analysis tests.
Ans. The coarse adjustment knob moves the stage up and down to bring the specimen into focus. The fine adjustment knob brings the specimen into sharp focus under low power and is used for all focusing when using high-power lenses.
Objective lensmicroscope function
I did NOT like this website sourse. Wanna know why I didn’t like it??? I don’t like it BECAUSE my school wants me to use this website sourse. My new science teacher wants us to answer those 10 questions. I think its pretty dumb. No Offensen to anyne out there, because I am a nice person not a mean one.
When unpolarized light passes through a polarizer, the intensity is reduced by a factor of ½. The average of cos2θ, averages over all angles θ is ½. Itransmitted = I0all angles = ½I0.

Stage clipsmicroscope function
An unpolarized electromagnetic wave traveling in the x-direction is a superposition of many waves. For each of these waves the electric field vector is perpendicular to the x-axis, but the angle it makes with the y-axis is different for different waves. For unpolarized light traveling in the x-direction Ey and Ez are randomly varying on a timescale that is much shorter than that needed for observation.
Thanks alot of your help and knowI can draw it well in my exams and write the functions.Thankyou very much for your help
Armmicroscope function
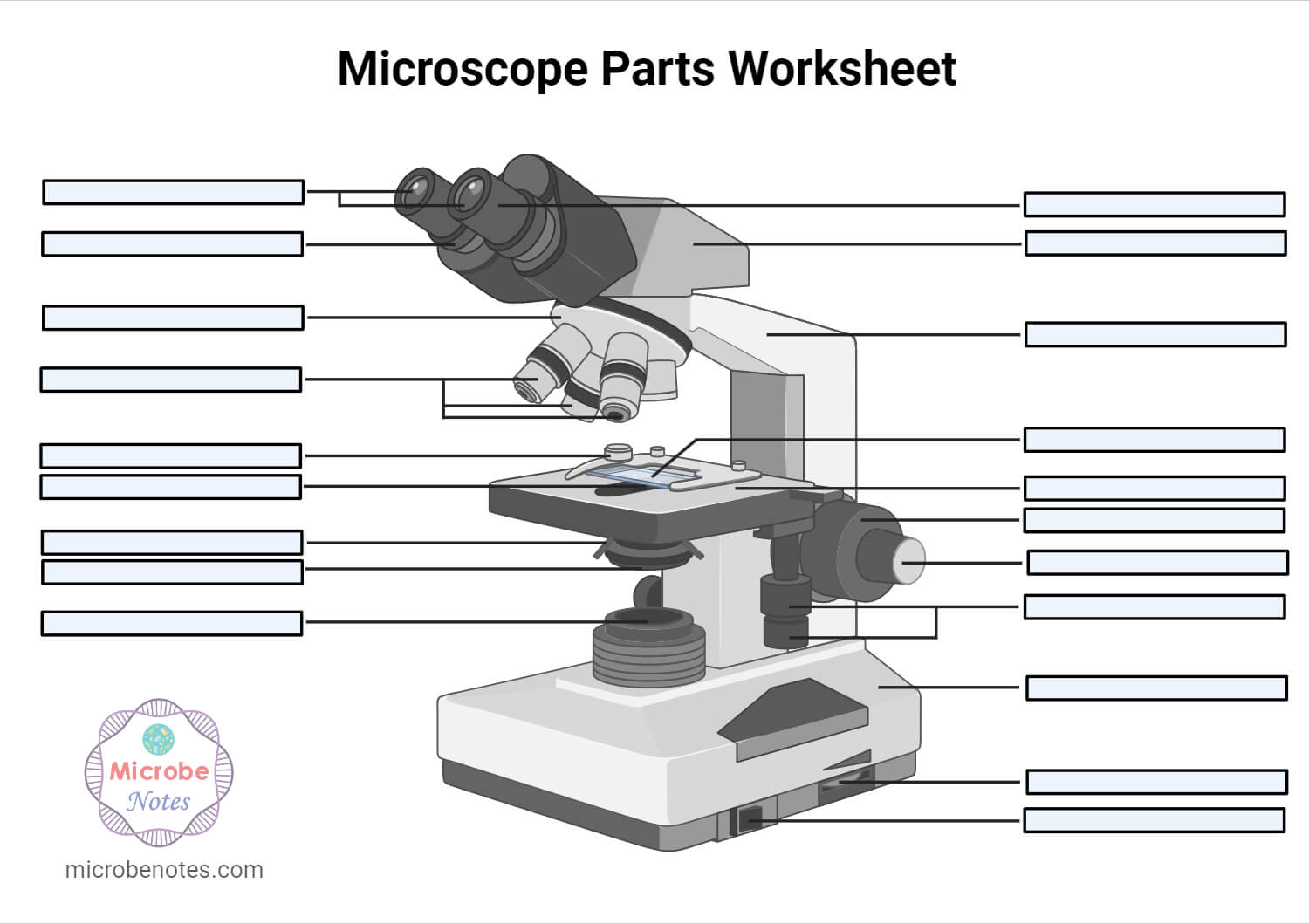
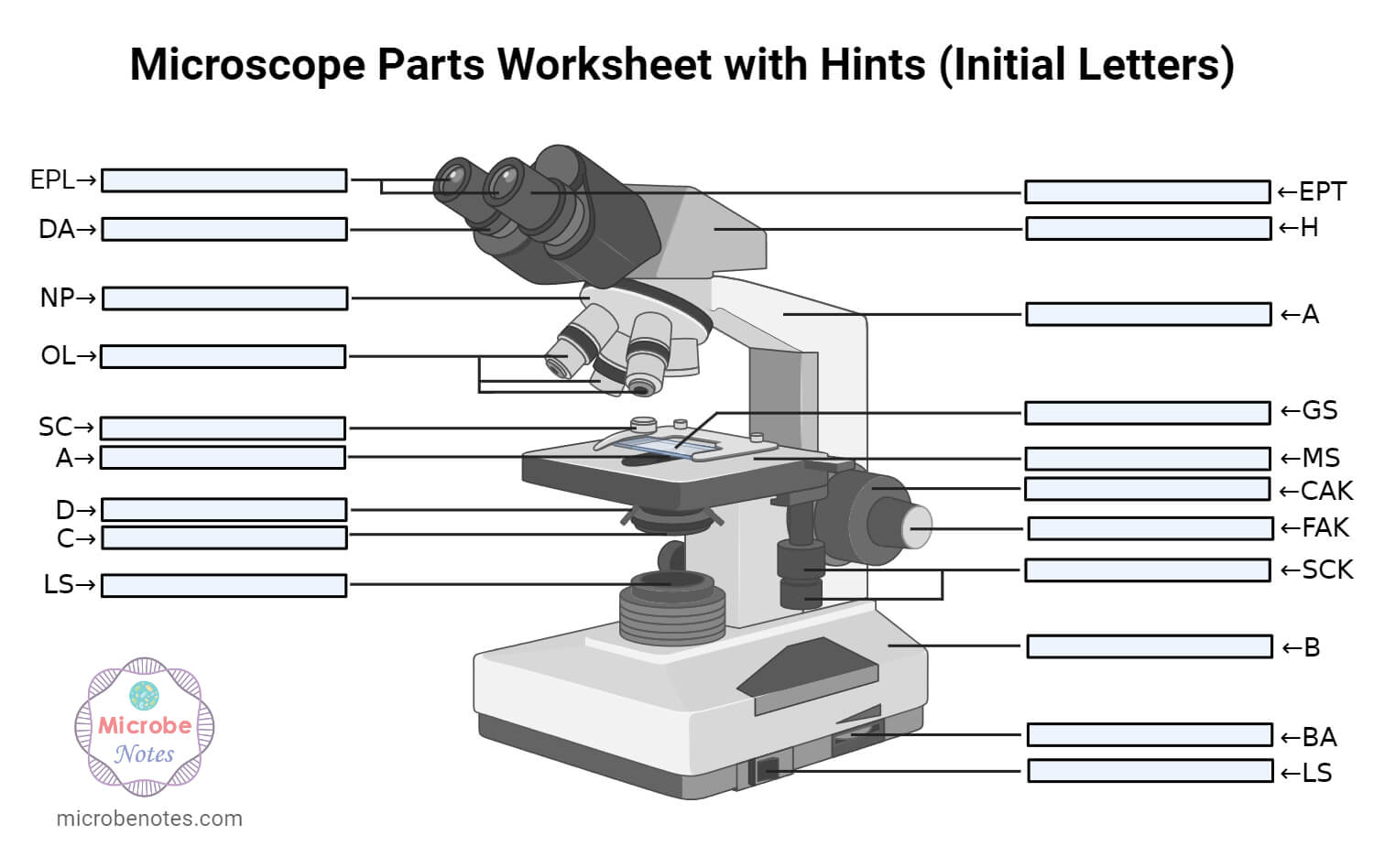
1. Ocular Lens (Eye Piece)2. Diopter Adjustment3. Head4. Nose Piece5. Objective Lens6. Arm (Carrying Handle)7. Mechanical Stage8. Stage Clip9. Aperture10. Diaphragm11. Condenser12. Coarse Adjustment13. Fine Adjustment14. Illuminator (Light Source)15. Stage Controls16. Base17. Brightness Adjustment18. Light Switch
Thanks very much dear and please continue doing so, am Gerald M from Uganda East Africa doing diploma in nursing at Mulago school of nursing and midwifery
Thank you very much it really helped me with my science home work since i in 8th grade and this my home work to draw a microscope label all the parts and the function thank may the holy father of holy spirits bless you and give more wisdom thanks love you all keep up the good work and thank you again bye.
Thanks much for this. We just did microscopy as a topic and the write-up has really helped me to understand better. Thanks again
There are different types of microscopes like light microscope, dark-field microscope, phase contrast microscope, electron microscope, fluorescent microscope, etc.
Having been constructed in the 16th Century, microscopes have revolutionized science with their ability to magnify small objects such as microbial cells, producing images with definitive structures that are identifiable and characterizable.
Thank you so much for the note that you have given to me i was so grateful to know that you are so bright people that extend your help to a student
Their ability to function is because they have been constructed with special components that enable them to achieve high magnification levels. They can view very small specimens and distinguish their structural differences, for example, the view of animal and plant cells viewing microscopic bacterial cells.
Ans. Condensers are lenses that are used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen. They are found under the stage next to the diaphragm of the microscope. They play a major role in ensuring clear sharp images are produced with a high magnification of 400X and above. Abbe condenser is a condenser specially designed for high-quality microscopes, which makes the condenser to be movable and allows very high magnification of above 400X. High-quality microscopes normally have a high numerical aperture than objective lenses.
Ans. The magnification of a lens is defined as the ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object. Microscope magnification measures the total enlargement of the image of an object. Magnification power is the product of eyepiece lens power and objective lens power.
A beam of unpolarized light of intensity I0 passes through a series of ideal polarizing filters with their transmission axis turned to various angles, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the light intensity (in terms of I0) in regions A, B, and C? (b) If we remove the middle filter, what will be the light intensity at point C?
Thank you for the support u have done may the Holy Spirit from the Almighty shine upon you to have more knowledge 2 continue making more notes from various topics in microbiology????✍️
Basemicroscope function
this is a really good artical i used it to study my science i just wanted to point out to you that tere are a few spelling errors but other than that it is a 100% rating from me
Microscopes are made up of lenses for magnification, each with its own magnification powers. Depending on the type of lens, it will magnify the specimen according to its focal strength.
There are different polarization mechanisms. The most common method of producing polarized light is to use polaroid material, made from chains of organic molecules, which are anisotropic in shape. Light transmitted is linearly polarized perpendicular to the direction of the chains. The transmission axis is perpendicular to the chains.
Microscopeparts and functions
Stagemicroscope function
Optically active or circular birefringent materials rotate the direction of polarization of linearly polarized light. The amount of rotation depends on the wavelength of the light. Sugar molecules have a handedness (chirality) and in solution are optically active. If we polarize white light and pass it through sugar syrup, the direction of polarization of the light emerging from the syrup will be different for the different color components. If the light then passes through a second polarizer, its color changes with the orientation of the transmission axis of this polarizer.
A beam of light is passed through the condenser to the specimen. The light transmitted from the specimen enters the objective lens. While passing through the objectives, the transmitted rays are spread so that they appear to come from the bigger objects.
When unpolarized light is incident on a boundary between two dielectric surfaces, for example on an air-water boundary, then the reflected and transmitted components are partially polarized. The reflected wave is 100% linearly polarized when the incident angle is equal to an angle called the Brewster angle. For water this angle is is ~53o with respect to the normal or 37o with respect to the water surface. For are considerable angular range around the Brewster angle the reflected light is highly polarized in the horizontal direction.
The light is then focused on the eyepiece lens. This lens further magnifies the pre-magnified image coming from the objectives.
Ans. The eyepiece, also known as the ocular is the part used to look through the microscope. Its found at the top of the microscope. Its standard magnification is 10x with an optional eyepiece having magnifications from 5X – 30X. Objective Lens are the major lenses used for specimen visualization. They have a magnification power of 40x-100x. There are about 1- 4 objective lenses placed on one microscope, in that some are rare facing and others face forward.
Polarization is a phenomenon peculiar to transverse waves. Longitudinal waves such as sound cannot be polarized. Light and other electromagnetic waves are transverse waves made up of mutually perpendicular, fluctuating electric and magnetic fields. In the diagram below an EM wave is propagating in the x-direction, the electric field oscillates in the xy-plane, and the magnetic field oscillates in the xz-plane. A line traces out the electric field vector as the wave propagates.
Diaphragmmicroscope function
1. Illuminator (Light Source)2. Diaphragm (Iris)3. Condenser4. Condenser Focus Knob5. Rack Stop6. Stage7. Stage Control Knobs8. Nose Piece9. Objective Lens10. Tube (Head)11. Eyepiece (Ocular Lens)12. Diopter Adjustment13. Adjustment Knobs (Fine Adjustment Knob and Coarse Adjustment Knob)14. Arm15. Base16. Light Switch17. Brightness Adjustment
For a linearly polarized electromagnetic wave traveling in the x-direction, the angle the electric field makes with the y-axis is unique.
Certain birefringent crystalline substances bend light trough an angle that depends upon the state of incident polarization. The have an optic axis. Unpolarized light entering a birefringent crystal not along the optic axis of the crystal is split into beams which are bend by different amounts.
Ans. A microscope is an optical instrument with one or more lens systems that are used to get a clear, magnified image of minute objects or structures that can’t be viewed by the naked eye.
Microscopes are generally made up of structural parts for holding and supporting the microscope and its components and the optical parts that are used for magnification and viewing of the specimen images. Modern microscopes have additional electronics and display devices. This description defines the parts of a microscope and the functions they perform to enable the visualization of specimens.
Microscopes are instruments that are used in science laboratories to visualize very minute objects, such as cells and microorganisms, giving a contrasting image that is magnified.
The optical parts of the microscope are used to view, magnify, and produce an image from a specimen placed on a slide. These parts include:
it very good website i use in 4 grade right after i plai amog us and they vote me out using orang strat witch mad me sad 🙁




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500