Lichtvision Design | Home - light vision
Military and civilian applications include target acquisition, surveillance, night vision, homing, and tracking. Humans at normal body temperature radiate chiefly at wavelengths around 10μm (micrometers). Non-military uses include thermal efficiency analysis, environmental monitoring, industrial facility inspections, detection of grow-ops, remote temperature sensing, short-range wireless communication, spectroscopy, and weather forecasting.
A majority of migratory birds travel at night. Light pollution can draw these birds into bright cities. Finding themselves in a dense urban environment, and unable to perceive most types of glass, many of these birds collide with buildings and structures before finding their way back out of the city.
In optical communications, the part of the IR spectrum that is used is divided into seven bands based on availability of light sources transmitting/absorbing materials (fibers) and detectors:
The Descent
Infrared radiation extends from the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum at 700 nanometers (nm) to 1 millimeter (mm). This range of wavelengths corresponds to a frequency range of approximately 430 THz down to 300 GHz. Beyond IR is the microwave portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The C-band is the dominant band for long-distance telecommunication networks. The S and L bands are based on less well-established technology, and are not as widely deployed.
LightsOutimdb
Lights Out Salt Lake is a collaboration started by Tracy Aviary and the Utah Chapter of the International Dark Sky Association. Other partners and collaborators include National Audubon, Great Salt Lake Audubon, and Clark Planetarium.
The International Commission on Illumination (CIE) recommended the division of infrared radiation into the following three bands:
These divisions are not precise and can vary depending on the publication. The three regions are used for observation of different temperature ranges, and hence different environments in space.
Luckily, there are some simple solutions to help out our feathered friends. If we turn out lights at night - especially during peak migration - we will not draw as many birds into our dangerous cities. There are also many solutions to make windows visible to birds, from installing acopian curtains and bird tape to using bird-friendly glass.
Infrared radiation was discovered in 1800 by astronomer Sir William Herschel, who discovered a type of invisible radiation in the spectrum lower in energy than red light, by means of its effect on a thermometer. Slightly more than half of the energy from the Sun was eventually found, through Herschel’s studies, to arrive on Earth in the form of IR. The balance between absorbed and emitted IR radiation has an important effect on Earth’s climate.
Horror
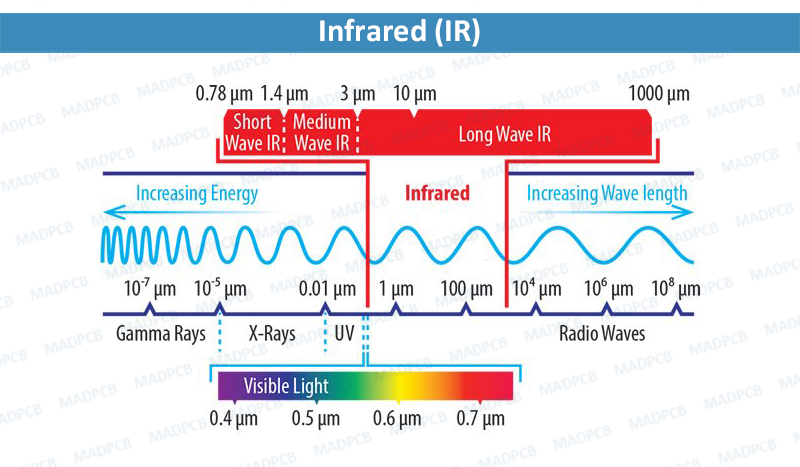
Infrared (IR), sometimes called Infrared Light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the huhttps://madpcb.com/glossary/electromagnetic-radiation/man eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (frequency 430THz) (although the longer IR wavelengths are often designated rather as terahertz radiation. Black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is almost all at IR wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, with properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.
NIR and SWIR together is sometimes called “reflected infrared”, whereas MWIR and LWIR is sometimes referred to as “thermal infrared”.
Infrared radiation is used in industrial, scientific, military, commercial, and medical applications. Night-vision devices using active near-IR illumination allow people or animals to be observed without the observer being detected. IR astronomy uses sensor-equipped telescopes to penetrate dusty regions of space such as molecular clouds, to detect objects such as planets, and to view highly red-shifted objects from the early days of the universe. IR thermal-imaging cameras are used to detect heat loss in insulated systems, to observe changing blood flow in the skin, and to detect the overheating of electrical components.
lights out中文
The most common photometric system used in astronomy allocates capital letters to different spectral regions according to filters used; I, J, H, and K cover the near-infrared wavelengths; L, M, N, and Q refer to the mid-infrared region. These letters are commonly understood in reference to atmospheric windows and appear, for instance, in the titles of many papers.
IR radiation is emitted or absorbed by molecules when changing rotational-vibrational movements. It excites vibrational modes in a molecule through a change in the dipole moment, making it a useful frequency range for study of these energy states for molecules of the proper symmetry. IR spectroscopy examines absorption and transmission of photons in the IR range.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500