Infrared (IR) Laser Modules - Made in USA - infrared laser light
Microscope illumination techniquespdf
When using darkfield microscopy, no light from the illuminator will pass into the imaging system, only light diffracted by the structure is captured by the objective. This is what makes the structures appear rich in contrast, and very bright against a dark background. Darkfield microscopy is especially useful to detect tiny and isolated structural details, such as bacteria. When working with reflected light, darkfield illumination is used to identify grain boundaries in polished and etched metal sections, as well as to detect contaminants and flaws in surfaces.
When using a microscope with brightfield, some samples will have a natural contrast that is easily viewed, such as bright plants and flowers, metals, and pigments. Some samples can be stained to increase the microscope contrast. However, low contrast samples such as unstained bacteria, thin tissue slices, live cells, or reflective metal parts require the use of additional microscope contrast techniques in order to view the sample. Here we will explore each of these different microscopy contrasting techniques.
Köhlerillumination
Polarizing microscopes must be equipped with two crossed polarizers. In most cases at least one polarizer and one analyzer are used. Many materials, like most crystals and some biological structures such as muscle cells, are birefringent, meaning they have two refractive indices. This phenomenon fulfills an important diagnostic function in mineralogy, pharmacology, forensic microscopy, polymer research, or the quality control of textile fibers. Reflected light is used to visualize the contrasts in the origin of structure of opaque metals such as aluminum, zirconium, and others.
Your location is outside of our service area. Manufacturer restrictions prevent us from completing your request for the following item(s):
Magnification system ofmicroscope
Hoffman modulation contrast is a form of oblique transmitted light illumination in combination with a grayscale modulator comprising neutral gray absorbing layers mounted in the objective's back focal plane. The modulator consists of three grayscale strips that run vertically through the pupil of the objective. This results in this method's middle gray image background and modulates a relief contrast. iHMC is used in the live-cell microscopy of sperm and egg cells when conducting artificial insemination in human and veterinary medicine.
Our Studio41 home design showrooms are open to everyone - homeowners, contractors, designers, and architects. We welcome your business, no matter how large or small your project, whether you are buying a single item or for a whole house, we have the products, staff, service and convenient locations to meet your needs. If you're building or remodeling a home, we at Studio41 invite you to visit us for the products you need for your kitchen or bath, windows, and doors to complete the look you want. We have a full selection of quality products at affordable prices: kitchen and bath plumbing fixtures, kitchen and bath cabinetry, kitchen and bath accessories, windows, doors, door hardware and cabinet hardware.Click here to learn more about our process.
When using a brightfield microscope, thin and transparent samples have a very low contrast and can be barely visible. Phase contrast microscopy is the method of choice for viewing thin, unstained samples such as culture cells. Phase contrast uses a special condenser and objective lenses to enhance the contrast seen in the microscope image. Phase contrast is not useful for thick specimens such as plant or animal tissue sections.
Fluorescence is a low-energy form of radiation (emission) that results from a previous high energy illumination (excitation). As soon as the excitation stops, the fluorescence emission stops almost immediately. The particular advantages of fluorescence microscopy include a strong image contrast and its specificity; that is, its ability to specifically detect individual structures down to individual molecules. Fluorescence microscope illuminators often use gas discharge lamps such as HBO, XBO, HXP or long-life LED light sources. LEDs make it possible to change the excitation wavelengths extremely quickly. The downside to LED light sources is that they still exhibit rather low excitation intensity in certain spectral ranges.
Criticalillumination
What isilluminationinMicroscope
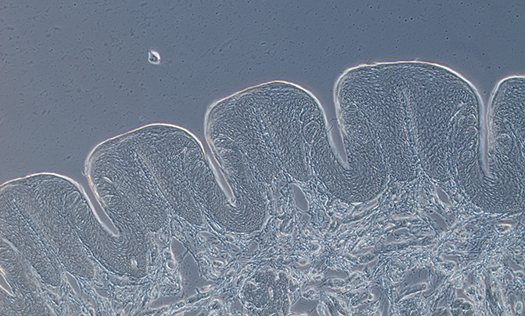
Oblique illumination is recommended to contrast objects that are too thick for alternative contrasting techniques. Oblique illumination directs light beams onto the specimen at different angles. As a result of highly directed one-sided illumination, the sample will have one side that appears bright and the other darker, which results in a shadow-casting relief image showing fine structural details. Oblique illumination microscopy is utilized to view thick tissue samples or solid samples that do not allow light to pass through them, such as automotive parts.
Microscopebase function
Welcome to our website! As we have the ability to list over one million items on our website (our selection changes all of the time), it is not feasible for a company our size to record and playback the descriptions on every item on our website. However, if you have a disability we are here to help you. Please call our disability services phone line at 877-472-2500 during regular business hours and one of our kind and friendly personal shoppers will help you navigate through our website, help conduct advanced searches, help you choose the item you are looking for with the specifications you are seeking, read you the specifications of any item and consult with you about the products themselves. There is no charge for the help of this personal shopper for anyone with a disability. Finally, your personal shopper will explain our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service, and help you place an order if you so desire.
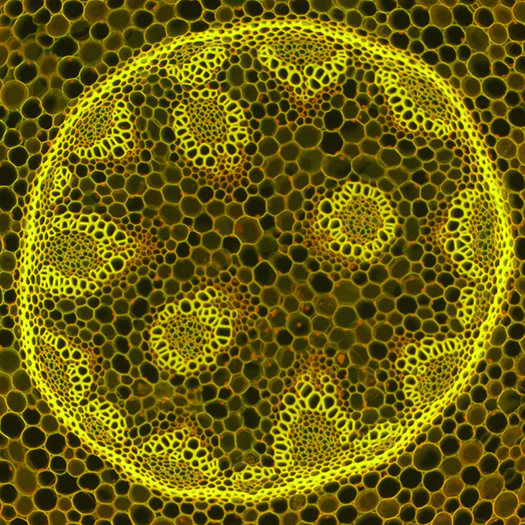
In interference contrast, previously split partial beams are combined as in phase contrast, interfering with each other as a result. Due to the interference of the two twin images in the intermediate image plane, a light-dark contrast is generated at the edges of objects. By laterally shifting the objective-sided DIC prism, also known as the DIC slider, the contrast can be adjusted in such a way that the light and dark object edges appear on a gray background. As the illumination appears darker on one side and brighter on the other side, a pseudo-relief image is perceived by our brain. This can - but does not have to - match the actual topography of the sample.
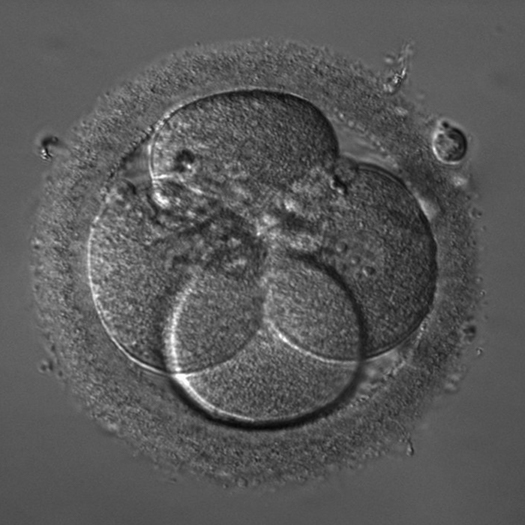
If you have any questions about microscope contrasting techniques or which microscope provides the best contrast for your application, please contact Microscope World.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500