Home | The Light Adjustable Lens from RxSight - lens light
While both provide 3D sensing, ToF cameras are generally more compact, power-efficient, and cost-effective for shorter ranges, while LiDAR systems offer higher accuracy and longer range for applications like autonomous vehicles.
AdvanceLEDSupply
Modern ToF cameras can achieve millimeter-level accuracy in ideal conditions, though real-world accuracy may vary based on environmental factors and the specific camera model.
LED Advanced
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Developed in exclusive collaboration with NVIDIA, our ToF camera systems are also listed in Jetson AGX Orin. This productive collaboration allows us to empower several industries such as IoT, automotive visual applications, robotics, deep learning, visualization, and edge IT.
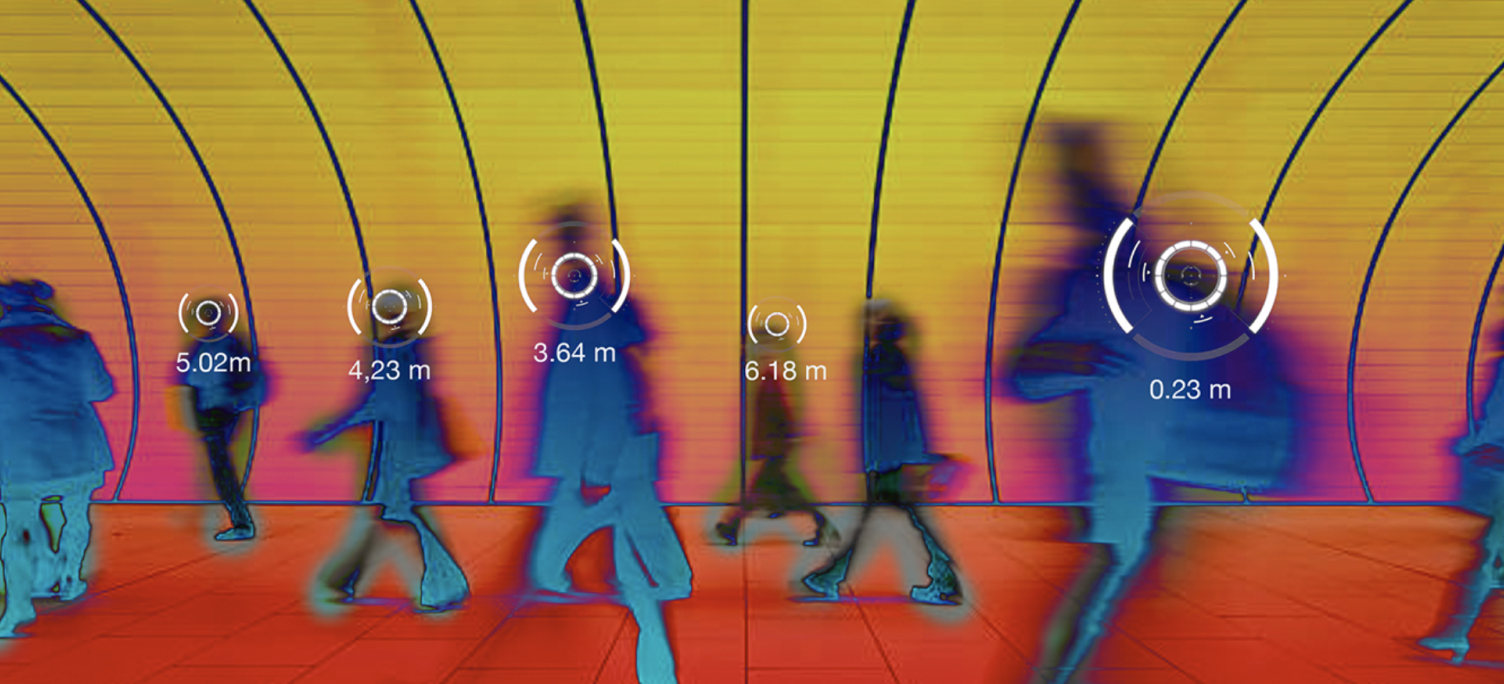
A ToF camera is an advanced imaging device that measures the time it takes for light to bounce off objects in a scene, creating depth maps and 3D representations of the environment.
We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Advanced LEDgrowlights
ToF cameras emit light pulses and measure the time taken for the light to return after reflecting off objects. This time measurement is used to calculate distances, creating a detailed 3D map of the surroundings.
Often referred to as ‘depth cameras’, our robust ToF camera systems offer the best-in-class performance while consuming less computing power. This enables power-efficient ToF camera systems to be deployed on a mass scale. A proud member of the NVIDIA Partner Network, Leopard Imaging focuses on developing ToF cameras for imaging solutions that are compatible with the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier platform. We offer hardware and software development as well as fine-tuning services for both developers and customers.
A ToF camera measures how long it takes for light to bounce off an object. Using this principle, the camera calculates the distance to all objects in a scene. This point cloud data is used to compute and create a three-dimensional (3D) map of the object space. Thus, ToF cameras are also referred to as “depth cameras.” Unlike stereo 3D methods, no image contrast is necessary, and ToF systems exhibit excellent mechanical robustness.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500