Circular polarization - meaning of polarization of light
Optical fiber attenuation is sensitive to stress like encountered when bending fiber too tightly, especially with patchcords and fibers in tight enclosures. Stress causes light to exit the core of the fiber causing loss. A modification to the fiber index profile, adding a low index layer of glass around the core, usually called an optical trench, that guides or reflects light lost from the core back into the core can make fiber much less sensitive to bending losses. This can be done with both multimode and singlemode fibers.
Many fibers are now available as bend-insensitive fibers, including most multimode fibers. Singlemode fibers used in patchcords, small diameter high fiber count cables called micro cables and specialty cables are usually bend-insensitive fibers.
The main observation targets are transparent samples such as bacteria and blood cells. Light microscopes are also known as biological microscopes. They are used to observe organisms.

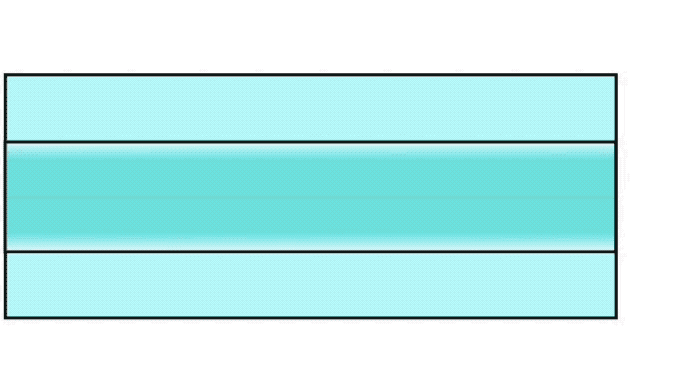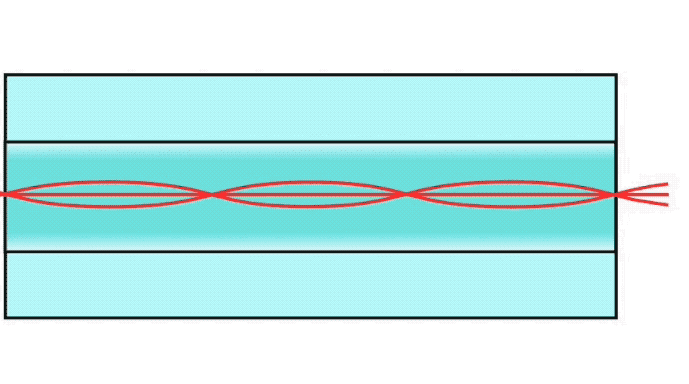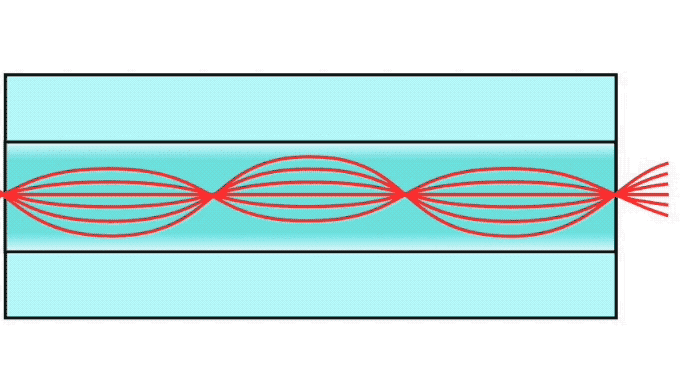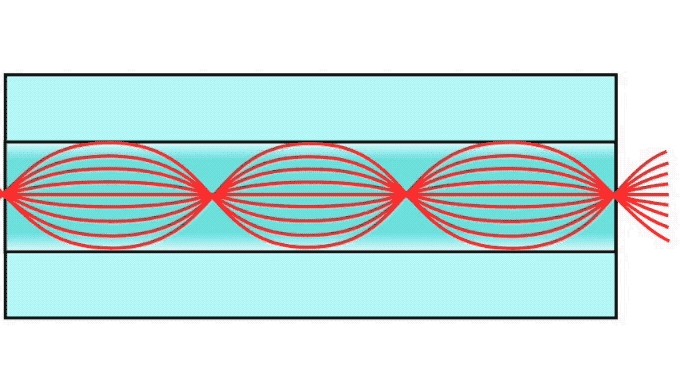
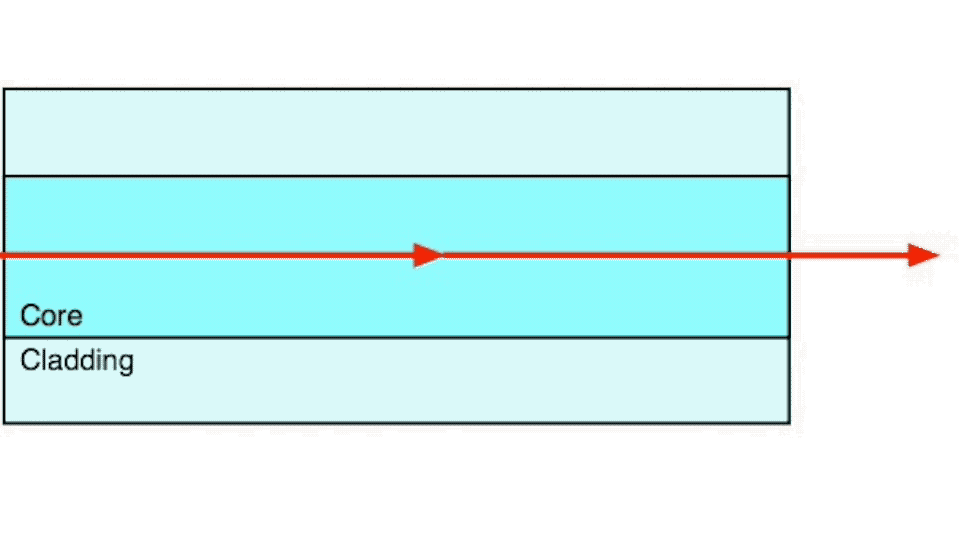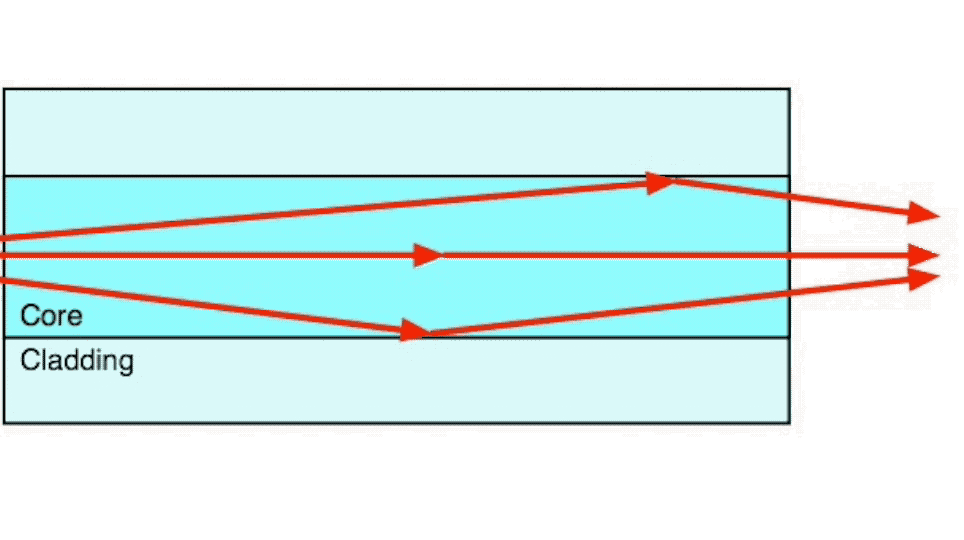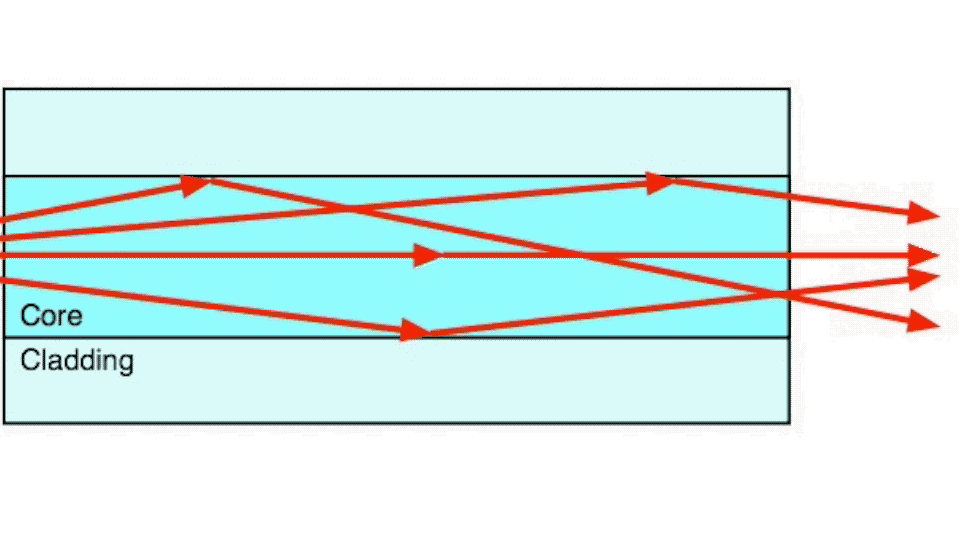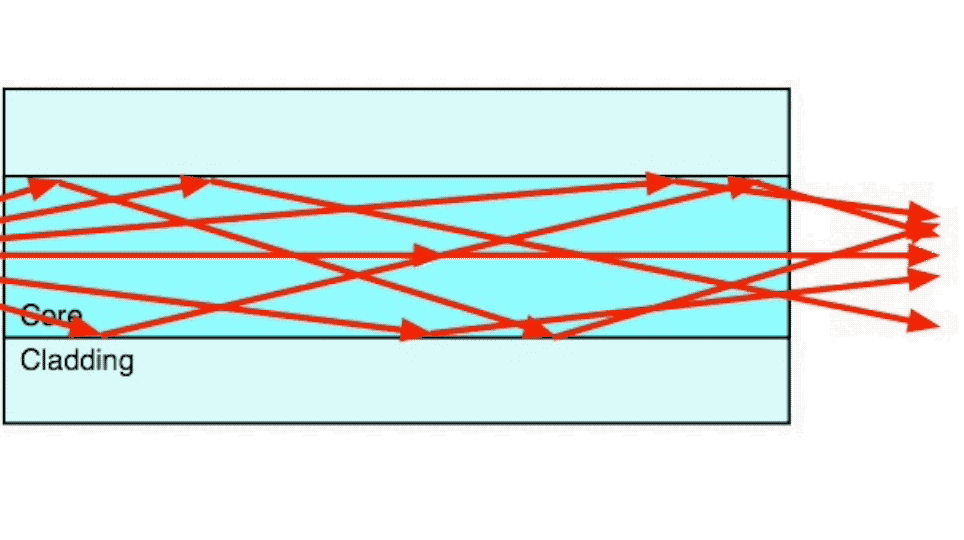
Step index multimode fiber was the first fiber design. The core of step index multimode fiber is made completely of one type of optical material and the cladding is another type with different optical characteristics. It has higher attenuation and is too slow for many uses, due to the dispersion caused by the different path lengths of the various modes traveling in the core. Step index fiber is not widely used - only POF and PCS/HCS (plastic or hard clad silica, plastic cladding on a glass core) use a step index design today. POF is mainly used for consumer audio and TV links.
Light microscopes are also called optical microscopes. They use light to perform magnified observation of microscopic targets such as bacteria and blood cells.
Visual light from the light source is condensed by the condenser lens and projected onto the microscopic, transparent sample. The light transmitted through the sample is once more condensed by a glass lens (the objective lens) for magnified observation. There are two types of light microscopes: simple light microscopes, which use a single lens, and compound light microscopes, which use multiple sets of lenses. Simple light microscopes are designed for low magnification. Compound light microscopes are designed for high magnification.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500