LED Tunnels - tunnel led
Regular astigmatism refers to a change in refraction from one principle meridian of the eye to the other, the two meridians always being at right angles [13]. We refer to “with the rule” astigmatism when the steepest axe (meridian with the greatest refractive power) tends to be vertical (around 90º), and “against the rule” astigmatism when the steepest axe tends to be horizontal (around 180º). The wave aberration associated with regular astigmatism has a cylindrical shape.
Opticalaberration
Im Fach Physik wird kohärentes Licht noch enger definiert. Kohärentes Licht ist eine elektromagnetische Strahlung, wobei die Wellenfronten eine festen räumlichen und zeitlichen Zusammenhang aufweisen. Die räumliche Kohärenz liegt vor, wenn alle Wellenfronten die gleiche Ausbreitung haben (feste Phasenbeziehung), während zeitliche Kohärenz vorliegt, wenn alle “Wellenfronten” die gleiche Wellenlänge haben. Erst dann wird in der Physik von kohärentem Licht gesprochen.
Both LASIK and PRK increase wavefront aberrations of the cornea, particularly increasing coma and spherical aberrations [5,26]. Oshika T. et al. [5] showed that conventional LASIK induced more SA than PRK when dealing with large pupil, but considered that this might be the consequence of a smaller transition zone of the laser ablation in LASIK.
Correspondence to: Tătaru Călin, MD, PhD Emergency Eye Hospital Bucharest 1 Alexandru Lahovari Square, District 1, Bucharest, Romania Phone: +4021 319 27 51, E-mail: calintataru1@yahoo.com
Coma makes the image rays to “flare out” from the image point in a fashion reminiscent of a comet’s tail. The wave aberration has the shape of a lounge chair [13]. Coma is pupil independent and is increased when multiple optical elements do not share the same optical axes [23]. Vertical and horizontal come are described by third-order Zernike polynomials.
Kohärentes Licht beschreibt eine Lichtquelle, bei der die Lichtwellen in einer konstanten Phase zueinander stehen. Das bedeutet, die Phasenverschiebung zwischen den Wellen ändert sich nicht mit der Zeit.
Kohärentes Licht ist die Voraussetzung, um Interferenz zu erzeugen (und alle damit verbundenen physikalischen “Phänomene”). Oft wird kohärentes Licht mit monochromatischem Licht gleichgesetzt, was nicht ganz korrekt ist. Kohärentes Licht ist eine elektromagnetische Welle mit nur einer bestimmten “Wellenlänge” (=> einfarbiges Licht). Im Gegensatz zu monochromatischem Lichtbesteht zwischen den einzelnen Wellen (zusätzlich) eine feste Phasenverschiebung.
Licht, so wie wir es von der Sonne oder Glühlampen kennen, sendet keine kohärente Strahlung aus. Dies liegt daran, dass diese Lichtquellen Licht in alle Richtungen aussenden und nicht nur Licht einer Wellenlänge aussenden, sondern vieler Wellenlängen. Die bekannteste Quelle für kohärentes Licht ist der Laser. Jede “Laserstrahlung” weist eine zeitliche und räumliche Kohärenz auf.
In der Kommunikation, besonders in der Faseroptik, ermöglicht kohärentes Licht die Übertragung von Daten über große Entfernungen ohne signifikanten Signalverlust.
Kohärentes Licht ist für die Datenübertragung effizienter, weil das Signal stärker und zentriert ist, es ermöglicht eine schnellere und klarere Übertragung von Informationen.
Laser refractive surgery represents one of the most remarkable inventions in eye surgery. Since 1990 when the first laser in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK) procedure was described by Pallikaris [1], people worldwide have turned to refractive surgery and gave up glasses or contact lenses. Nowadays the most used refractive procedures are lamellar (LASIK) and surface (like photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)) ablations of the cornea who aim to achieve an uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA) of 20/20 Snellen. Despite the good UDVA results there are patients unsatisfied with their surgery outcome and one of the reasons blamed might be the increase in high -order optical aberrations. Some of the most frequent complications after refractive surgery are glare and halo, especially if the surgeon deals with large pupils or uses a small ablation diameter [2]. Many studies regarding changes in corneal [3] and wavefront aberrations [4,5] show that best corrected image quality decreases after refractive surgery.
Spherical aberration
Kohärentes Licht findet Anwendung in Laser-Chirurgie, Laser-Druckern, Laser-Scannern und in der Faser-Optik-Kommunikation.
Other higher-order aberrations (HOA) as trefoil, trefoil and other aberrations that don’t have a name, but are described only in mathematic terms by Zernike polynomials, have a lower impact on visual quality.
The purpose of this review is to describe optical aberrations and their impact on vision and how refractive surgery outcomes are influenced by them. The review is divided in three parts: one regarding optical aberrations, the second regarding laser refractive surgery and the last concerning the impact refractive surgery has on eye’s optical aberrations and quality of vision.
1) The cornea is not spherical and flattens towards the periphery (it has a prolate shape); therefore there is less refractive power at the periphery resulting in a reduction in refraction of peripheral rays of light [7].
According to Dr J. Holladay [6] good vision is more than 20/20 on a Snellen visual chart. The modern ophthalmologist should understand that contrast sensitivity, near and distance vision, performance under light and dark conditions, and the brain’s interpretation of input from the sensory apparatus, are all important elements in patients’ quality of vision [6]. Quality of vision is influenced by the presence of aberrations in the eye’s optical system.
Kohärentes Licht findet Anwendung in der Laseraugen-Chirurgie, bei der präzise Schnitte in der Netzhaut gemacht werden müssen.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
The main optical aberrations of the eye are as follows: spherical aberration, chromatic aberration, oblique astigmatism and high order aberrations. When the patient undergoes various types of surgeries (cataract surgery, corneal refractive surgery) the properties of the eye change and the eye doctor must take into account the correction of optical aberrations to improve vision quality.
Astigmatism of oblique incidence is described by a fourth-order Zernike polynomial; it shouldn’t be confused with regular astigmatism.
Ein Laser ist ein Gerät, das kohärentes Licht erzeugt, indem es eine stimulierte Emission von Photonen aus einem angeregten Medium erzeugt, wodurch eine einheitliche Wellenfront mit gleichbleibender Phase entsteht.
Chromatic aberration
Kohärentes Licht hat Wellen, die in einem konstanten Phase-Verhältnis zueinander stehen, während bei inkohärentem Licht die Phasenbeziehungen zufällig sind und das Wellenmuster unregelmäßig ist.
3) Foveal cones are excited more strongly when the light incident upon them enters through the center of the pupil rather than through the periphery [21]. The Stiles Crawford’s effect and its consequence is that peripheral light rays that are refracted more due to SA will be perceived less [7].
In 2014 Am J Ophthalmology published a study [29] comparing also wavefront-guided and wavefront-optimized LASIK for myopia where wavefront-guided treatment platforms appeared to offer significant advantages in terms of residual refractive error, uncorrected distance acuity and contrast sensitivity. The study found no differences in levels of residual astigmatism or in HOA.
Wie eingangs erwähnt, handelt es sich bei kohärentem Licht um eine elektromagnetische Strahlung mit einer bestimmten Wellenlänge und einer bestimmten Phasenverschiebung. Darin besteht auch der Unterschied zwischen monochromatischem Licht und kohärentem Licht. Dies lässt sich auch durch das Fremdwort “kohärent” ableiten. Die Bezeichnung “kohärent” leitet sich aus dem Lateinischen und bedeutet sinngemäß “zusammenhängend”. Bei einem kohärenten Licht liegt also ein “Zusammenhang” zwischen den einzelnen Wellenfronten bzw. Wellenzügen vor (=> feste Phasenverschiebung)
Only hyperopia, myopia and regular astigmatism are correctable by spectacles or contact lenses, so in the past they were the only aberrations of clinical interest [13]. However the eye suffers from other optical imperfections (called high-order aberrations) which cannot be corrected by conventional means. Like defocus, optical aberrations blur the retinal image, reducing image contrast and limiting the range of spatial frequencies available to further stages of the visual processing. The contribution of aberrations to optical degradation is typically smaller than is that of defocus or astigmatism; the blurring effect of aberrations becomes more noticeable for large pupils [14].
1) The laser in situ keratomilieusis (LASIK) uses a lamellar procedure in which the excimer laser ablation is done under a partial thickness lamellar corneal flap [2]. The flap could be done by a microkeratome or by a femtosecond laser and is repositioned at the end of the surgery.
A study about pupil sizes and visual acuity has shown that a normal daytime pupil size (this mean 3-3.2 mm) is the optimum pupil size for achieving best UCVA in a normal emetropic eye, balancing the diffraction effect that appears at small pupil sizes (especially below 2mm), against the aberrations let in by a large pupil [22].
The aberrations of an optical system, such as the eye, prevent a spherical wavefront from remaining spherical as it passes through the system. This aberration of wavefront can be compared with an ideal spherical wavefront, whose center of curvature on the image side of the system is at the ideal image position. The difference between the actual wavefront and the ideal wavefront is the wave aberration [13]. (Image reproduced with approval of Jie Shen [31])
Kurz nochmal zum Unterschied monochromatisches und kohärentes Licht: Positionieren wird vor einer Glühlampe einen Farbfilter, der nur noch elektromagnetische Strahlung einer Wellenlänge durchlässt, so erhalten wir monochromatisches Licht. Das “einfarbige” Licht ist nun zeitlich kohärent (gleiche Wellenlänge), die Ausbreitung der Wellenlängen im Raum hat aber noch keine feste Phasenbeziehung. Daher gilt, dass kohärentes Licht auch monochromatisches Licht darstellt, während monochromatisches Licht nicht immer kohärent sein muss. Dies kann man aber bei monochromatischen Licht auch erreichen, beispielsweise, indem man eine Blende vor den Farbfilter positioniert und somit die Wellenzüge (der ausbreitenden Wellen) in Phase bringt.
Aberration in Optics pdf
The main aberrations of the eye could be classified as low-order (defocus, regular astigmatism) and high-order aberrations (spherical aberration, distortion, coma, astigmatism of oblique incidence, other higher-order aberrations), as monochromatic (measured at a single wavelength) and chromatic aberrations [15]. Since the 19th century scientists know about the presence of high-order aberrations, but only recently in the 1990s wavefront sensors were developed to allow routine estimation of these ocular aberrations [16].
Seidelaberrations
Optical aberrations lead to defects in image-forming, the image obtained being imperfect and thereby decreasing the quality of vision. When an optic system is not perfect, as happens with the eye, the rays of light that pass through the system produce optical aberrations.
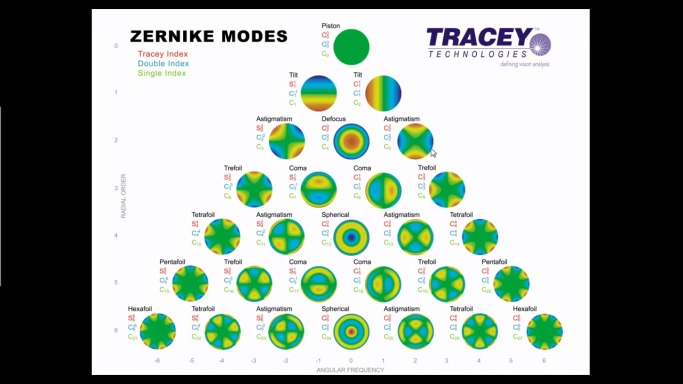
This figure shows the most common shapes of aberrations when a wavefront of light passes through an eye with imperfect vision. A theoretically perfect eye is represented by an aberration-free flat plane, named piston (top). Wavefront aberrations can be mathematically represented as the sum of a series of polynomial functions of different orders to show the departure from perfection and classify the shape of aberration maps. The most used are Zernike polynomials, each polynomial represent a particular mode of optical aberration, reconstructed here as a wavefront map. The 2nd order terms represent sphere and cylinder. The 3rd order terms and higher represent higher order aberrations. Here are shown the Zernike aberrations till the 6th order (Image reproduced with courtesy of Tracey Technologies, Inc.).
1) First of all, the optic and visual axis do not coincide as they should for a perfect vision in order that the image with the highest resolution to project on the retina with the highest resolution (fovea centralis) [8]. The angle between the optic and visual axes is called angle alpha. It measures about 5 degrees for humans and it was considered the most reliable reference in refractive surgery because it had the lowest variability between patients [6]. However there is a high debate on where to best center refractive surgery procedures and devices according to the visual axis or to use the line of sight [8,9,10].
A prospective study published in 2013 sustains better visual performance after wavefront guided LASIK compared to conventional LASIK for myopia, especially for eyes with high-magnitude root mean square [27].
2) Secondly, the human eye is not a fixed optical system; the pupil center is not static due to modifying its refractive state by accommodation and light [12].
Feng et al. [27,28] reviewed the outcomes for wavefront-guided and wavefront-optimized LASIK for myopia. He included 930 eyes in the meta-analysis, but found no statistically significant differences in the eyes achieving uncorrected distance visual acuity of 20/20, nor did the HOA differ between the two groups unless the preoperative root mean square of higher order aberrations (RMS) was higher than 0.3 μm. This meta-analysis suggested that both wavefront-guided and wavefront-optimized LASIK have excellent efficacy, safety, and predictability.
Das Licht von einer Glühbirne ist nicht kohärent, weil die Lichtwellen in zufälligen Phasenbeziehungen zueinander emittiert werden.
Types of aberration in optics
Defocus refers to both myopia and hyperopia. The wave aberration has a paraboidal or bowl shape. For myopia the corresponding wave aberration is called positive defocus (even though myopia is corrected by minus lenses), while for hyperopia is called negative defocus (even though hypeopia is corrected by positive lenses).
Skiamoto et al. [2] reviewed the results for wavefront-guided versus conventional laser ablation for myopia. The review revealed that in wavefront guided LASIK 89% of patients achieved 20/20 or better uncorrected distance visual acuity, whereas only 72% of patients with conventional LASIK did. The same review also approached the FDA studies for patients with hyperopia – their findings suggest that although wavefront-guided treatments might prevent some worse outcomes, they do not improve the chances of obtaining the best outcomes; wavefront-guided ablation do not solve the problems of unpredictable wound healing and biomechanics, which are important determinants in the outcome of hyperopic LASIK.
2) The crystalline lens has a varying refractive index and curvature; the central nucleus has a higher refractive index than the cortex so that the central rays are refracted more, and SA is reduced overall [7].
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Abbreviations: LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis), PRK (photorefractive keratectomy), UDVA (uncorrected distance visual acuity), SA (spherical aberrations), HOA (higher-order aberrations), RMS (root mean square)
Also the lens and cornea are slightly tilted and decentered relative to each other [11]. As a consequence the eye functions only at about 40% of the performance it could theoretically achieve [6].
In Spherical aberration (SA) rays of light entering the eye near the pupil edge are focused in front of the retina (positive SA), while rays near the pupil center are focused further behind (negative SA). The distance between these focal points is known as the axial spherical aberration. Point objects form a retinal blur circle. The SA is about 2 D and is maximum at 2-4 mm from the visual axis [19]. SA is the reason for night myopia. In low light conditions the pupil enlarges, more peripheral rays enter the eye and the focus shifts anteriorly, making the patient more myopic. The effect of spherical aberration increases as the fourth power of the pupil diameter. Doubling pupil diameter increases spherical aberration 16 times [20]. The human eye has innate adaptations that minimize SA:
An optical aberration is defined as an optical phenomenon resulting from the failure of an optical system to produce a good image; the image of an object is distorted due to the presence of optical aberrations while the rays of light do not obey the laws describing perfect optical systems [7]. The human eye is not a perfect optical system, especially for large pupil diameters:
Until recently the surgeon could only decide where to do the laser ablation, choosing either LASIK or a surface ablation to correct the sphere and cylinder error. With the help of wavefront aberrometry which measures the more subtle, high order aberrations of the eye [24], the surgeon has options on the method he uses: standard ablations versus wavefront ablations.
Opticallens
Acknowledgement: This paper is partly supported by the Sectorial Operational Programme Human Resources Development (SOPHRD), financed by the European Social Fund and the Romanian Government under the contract number POSDRU 141531.
1) Wavefront-optimized ablations – try to preserve the eye’s pre-existing optical aberration (the adjustments are done on average population data and the ablation profile is based on an ideal model, without evaluating the patient’s own aberrometry). Its aim is to optimize the asphericity of the cornea, to precompensate for the expected 4th-order spherical aberration and higher-order astigmatism in the average eye [13,25].
Optical aberrationsof the eye
Myopia, hyperopia and regular astigmatism represent low-order aberrations, but in terms of Zernike polynomials they are classified as second-order aberrations. Lower order aberrations make up about 85 per cent of all aberrations in the eye [18].
A recent study [30] comparing the refractive outcome of wavefront-guided LASIK and wavefront-guided PRK in patients with high preoperative HOA (root mean square more than >0.35 μm) showed similar efficacy, safety and predictability, though wavefront guided - PRK induced less HOA.
The purpose of this review is to describe optical aberrations and their impact on vision and how refractive surgery outcomes are influenced by them.
These new surgical procedures have proved their benefit and efficacy. Some of the techniques are very new and need to be further tested and observed in time. However, at a close look we see that the need and demand for laser surgery is increasing every day, patients expect very good results and is our duty to offer them the best that we can. Taking into consideration the studies presented here, the benefit of using wavefront-guided ablations seems to matter for myopic eyes that have preoperative HOA with a RMS more than 0.3 μm. The results seem to be better when comparing wavefront-guided ablations with wavefront-optimized ablations, so for good outcomes the surgeon should take into account the presence of HOA before laser eye surgery. Further studies should also focus on hyperopic patients and the results of wavefront ablations on such eyes. For the moment conventional laser surgery offers good and stable results, but advancements in technology push forward the development in laser eye surgery, the hopes and expectations of both surgeons and patients.
2) Wavefront –customized ablations (also known as wavefront guided ablations) – take into consideration the patient’s own aberration profile aiming to correct not only the spherocylindrical error but also the pre-existing HOA or those HOA that might be induced by conventional laser corrections [4].
2) Photorefractive keratectomy is the most used of the surface ablations nowadays. In this procedure the excimer laser ablates the most anterior portion of the corneal stroma after the epithelium was removed. The corneal healing occurs from the surrounding epithelial cells which migrate and divide to correct the epithelial defect. Compared to LASIK the wound-healing might associate greater stromal haze and scarring [2].
In order to measure optical aberrations we must understand the concept of wavefront aberration. The aberrations of an optical system, such as the eye, prevent a spherical wavefront from remaining spherical as it passes through the system (Fig. 1). This aberrated wavefront can be compared with an ideal spherical wavefront, whose centre of curvature on the image side of the system is at the ideal image position. The difference between the actual wavefront and the ideal wavefront is the wave aberration [13]; the most convenient position for comparing the two wavefronts is at the exit pupil of the system [15]. If the actual wavefront is ahead of the ideal one, the wave aberration is considered positive, otherwise is negative. Wave aberrations are small quantities and are usually expressed in micrometres or wavelengths. At a wavelength of 500 nm, one micrometre (pm) is equivalent to two wavelengths [15]. Wavefront aberrations can be mathematically represented as the sum of a series of polynomial functions of different orders to show the departure from perfection and classify the shape of aberration maps. The most used polynomial functions are the Taylor and Zernicke polyn omial series [17] (Fig. 2). With their use we can compare and standardize different models of aberration and reproduce them in order to correct them by laser surgery.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500