Light Box Room Sign Tiki Bar - Tropical home bar accessory - lights for tiki bar
Spectroradiometry. In KonicaMinolta.us: Radiometry, Spectroradiometry and Photometry Retrieved from: https://sensing.konicaminolta.us/learning-center/light-measurement/radiometry-spectroradiometry-photometry/
Light intensityunit
4. Luminance - Measured in candela per square meter or nit, luminance is the total light emitted or reflected from a surface in a given direction. It indicates how bright we perceive the result of the interaction of the incident light and the surface.
luminous intensity中文
2. Luminous intensity - Measured in candela, luminous intensity is the amount of light emitted by a source in a particular direction.
Experienced Application Development Manager at Lumitex with a demonstrated history of working in the electrical and electronic manufacturing industry. Skilled in Research and Development (R&D), Engineering Management, Process Engineering, Engineering, and Statistical Process Control (SPC). Strong program and project management professional with a Bachelor of Science (BS) focused in Chemical Engineering from Youngstown State University.
Spectrometry is known for the science and utilization of spectrometers for measurement and analysis. It is the study of interactions between light and matter, and the reactions and measurements of radiation intensity and wavelength.
Photometry is a subset of radiometry that only applies to the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. While radiometry focuses on measuring radiant energy in terms of absolute power, photometry takes into account the response of the human eye and focuses on measuring light in terms of perceived brightness.
Understanding the measurement of light helps us, as a lighting solutions provider, meet the brightness and uniformity requirements of your specific applications.
Flux (Luminous Flux) - Originating from the Latin word 'Fluxus,' meaning flow, flux is the amount of energy a light emits per second, measured in lumens (lm).
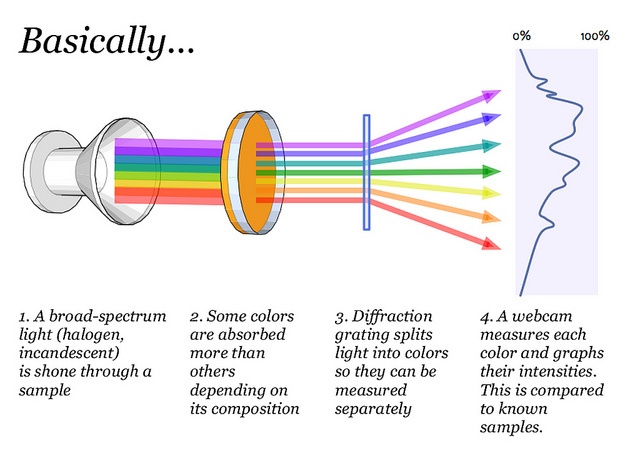
image credit: By publiclaboratory Spectrometry diagram [CC BY 2.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/), from flickr
Think of it like this – IL-Luminance, IL, I = Incident Light. Illuminance is measuring the incident light. Luminance is what’s leaving the surface – L = leaving. Illuminance measures incident, luminance measures what’s leaving.
There are many terms and technologies used when it comes to the power of light and light measurement. It is key to understand how all of these unique aspects come together.
When it comes to lighting, you need to consider watts (W) (energy used) versus lumens (lm) (brightness). Or electricity consumption versus light output. Lumens are weighted for human perception where as watts are not.
How islight intensitymeasured
3. Illuminance - Measured in lumens per unit area, illuminance refers to the amount of light incident on a surface. Illuminance can also be referred to in foot-candle.
A photometer is an instrument that measures light intensity. It can be defined as an instrument that measures visible light.
Photometry is distinguished from radiometry in which each separate wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum is detected and measured, including the ultraviolet and infrared." Photometry. In EDU.photonics.com/Photometry: The Answer to How Light is Perceived Retrieved from https://www.photonics.com/a25119/Photometry_The_Answer_to_How_Light_Is_Perceived
The diagram below shows how spectrometry is used to analyze a sample. The sample is shown in Step 2. Spectrometry can also be used to analyze the wavelengths present in a given light source. In this instance, there would be no sample between the source and diffraction grating.
The biomedical use of light consists of diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Read more on Spectroscopy in Biomedical Services.
What matters the most in terms of measuring light intensity is the actual number of lumens falling on a particular surface.
"An integrating sphere collects electromagnetic radiation from a source completely external to the optical device, usually for flux measurement or optical attenuation."
"The basic function of a spectrometer is to take in light, break it into its spectral components, digitize the signal as a function of wavelength, and read it out and display it through a computer.”
Radiantintensity

Spectral Irradiance - the irradiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. The SI units for spectral irradiance is Watt/cubic meter.
Opticalintensity
As with radiometry, applications of photometry are also diverse. It is used in a number of industries to test the intensity of light produced by displays, instrument panels, night-vision devices and more.
Spectroradiometry is the "measurement of light energy at individual wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum. It can be measured over the entire spectrum or within a specific band of wavelengths."
Spectral Radiance - the radiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength. The SI units for spectral radiance is Watt/square meter Steradian nanometer.
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the radiant power emitted by an object in a particular direction and is dependent on the wavelength of light being emitted.
lightintensity中文
Calculating the intensity of light depends on the light source and the direction in which it radiates light. The amount of light falling on a surface is known as illuminance and is measured in lux.
4. Radiance - Measured in watts per square meter Steradian, radiance is the measure of radiant intensity emitted from a unit area of a source.
1. Luminous flux - Measured in lumens, luminous flux is the measurement of total perceived power emitted in all directions by a light source.
Luminousintensity
In an article written by ATA Scientific Instruments, What is Spectrometry and What is it Used For, they detail modern ways we use spectroscopy:

Photometry is the "science of the measurement of light intensity, where 'light' refers to the total integrated range of radiation to which the eye is sensitive.
Light intensityformula
Sciencing wrote a step by step article/experiment on How to Calculate Light Intensity with the intensity of light around a bulb that radiates light equally in all directions. The conclusion detailed that "the light intensity at your point on the sphere is equal to the number of watts that the bulb radiates divided by the surface area of the sphere." The full calculations can be found here.
As noted above, flux is the total light output. With watts referring to absolute power and lumens being weighted for human perception.
1. Radiant Flux/Power - Expressed in watts, radiant flux can be defined as the total optical power of a light source. It can also be defined as the rate of flow of radiant energy. You can think of it as the total amount of light emitted from a light bulb.
Overall, radiometry is the science of measuring electromagnetic radiation. In regards to optics, it refers to the detection and measurement of light waves in the optical portion the electromagnetic spectrum (infrared, visible, and ultraviolet). Radiometry also includes characterizing the distribution of the radiation's absolute power.
It's important to understand the different terms used to characterize light. From the measurement of light in the electromagnetic spectrum, to understanding perceived brightness to the human eye, light intensity and the tools used to measure light, this guide covers it all.
2. Radiant Intensity - Also measured in watts, radiant intensity is the amount of flux emitted through a known solid angle.
3. Irradiance - Measured in watts per square meter, irradiance is the measurement of radiant flux on a known surface area.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500