Signs | The Official Ministry of Transportation (MTO) Bus ... - stop sign on bus
Class 3flammable liquids transportation
As a trusted voice in the aviation community, we can help raise your profile and ensure you are seen by the audience that really matters to you. Our offers are customizable to your needs, whether on our websites, our events or in our manuals.
While dangerous goods storage and handling occur throughout the proceeding, the loading process comes next. It is important not to store or load certain dangerous goods next to one another and never next to food items. All packaging must be secured, as well as other items being shipped so that they do not shift during transport and fall into the dangerous goods causing damage to their packaging. (9.3.5)
In the 1930s, the British Royal Navy developed a primitive, radio-controlled UAV: the Queen Bee. The Queen Bee could be landed for future reuse and could reach ...
As mentioned previously, proper dangerous goods packaging is of great concern for safely shipping hazardous material. Making certain that the dangerous goods’ packaging is well assembled and sturdy enough to be handled is a priority. But when packaging hazmat for shipping, shippers must meet other guidelines regarding their classes and the degree of danger per substance. This is why dangerous goods shipments have been further broken down into Packing Groups.
Next, the operator must go over the Dangerous Goods Checklist and ensure all regulations are met within those guidelines (see IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) for more information.
Class 3 dangerous goodslist
Download the DGR Quick Reference CardConsult the card, print it and keep it handy to assist with basic information on dangerous goods handling.
Out of the over 1.25 million packages of hazmat shipped each year, three types of dangerous goods stand out. These are items that are most commonly shipped, being flammable liquids, dry-ice, and lithium batteries. Dry ice is widely used as a refrigerant for goods such as frozen foods and pharmaceuticals, including vaccines.
It’s important to know what a dangerous good is before you ship. According to IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) Manual, “Dangerous goods (also known as hazardous materials or hazmat) are articles or substances which are capable of posing a hazard to health, safety, property or the environment and which are shown in the list of dangerous goods in the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations or which are classified according to those Regulations.” Because IATA participates in strict regulatory process, dangerous goods can be transported by air safely and securely when these guidelines are closely followed.
Because safety is IATA’s number one concern, dangerous goods training is required for all persons across the entire supply chain who prepare, offer, accept and handle dangerous goods. This dangerous goods training must be renewed every two years. IATA makes obtaining this training easy and accessible to everyone who needs it by offering courses and yearly manuals so that stakeholders can be up-to-date on the most current rules and regulations. IATA’s desire to keep aviation safe is the driving force behind ensuring the regulations are met by adequately training all parties involved in the transport of dangerous goods . Whether you are shipper, freight forwarder, a cargo acceptance agent, cabin crew member or anything in between you can find up-to-date information on training for dangerous goods in our training section.
Fly Net Zero is the commitment of airlines to achieve net zero carbon by 2050, bringing air transport in line with the Paris agreement to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulation Manual (DGR) contains a list of approximately 3,000 articles and substances that are commonly shipped by air. This list includes names for listed entries such as paint and ethanol as well as generic “not otherwise specified” (n.o.s.) entries that cover a chemical family or group of related substances, such as alcohols, n.o.s. and environmentally hazardous substance, liquid, n.o.s.. (4.0.2.1)
Class 3Hazardous materials divisions
For hazmat to be shipped by air, there are specific procedures to be met. First, the shipper must meet their criteria, such as declaring the shipment as dangerous goods, properly completing the Dangerous Goods Declaration, and adequately preparing the shipment for transport. Then the cargo acceptance procedures are carefully enacted. Using the Dangerous Goods Checklist will make sure that what the shipper has submitted complies with the Dangerous Goods Regulations.
Proper safety for the transport of hazardous material begins with shippers and ends with the operators. The shippers have specific responsibilities that must be closely adhered to for their goods to be accepted by the airlines. They are responsible for every aspect of the packaging of their dangerous goods as well as explicitly following these guidelines: (Sec 5)
Class8dangerous goods
Axon Body 3 is the newest in Axon's industry-leading body-worn camera series. Featuring enhanced low-light performance, advanced audio capabilities, reduced ...

Lithium batteries are one of the most commonly transported dangerous goods. The rules and regulations regarding the transport of lithium batteries need to be addressed specifically, so IATA created a unique manual geared specifically to shippers of lithium batteries. The manual further breaks down how to safely transport lithium batteries for companies and individuals who may not be familiar with the dangerous goods process. The IATA Lithium Battery Shipping Regulations (LBSR) can better assist with the regulations for shipping lithium batteries and items that contain lithium batteries.
Warning signs alert you to possible dangers ahead. They are usually yellow with black diagrams. They may indicate the presence of people (e.g. children, ...
Every year more than 1.25 million dangerous goods shipments are transported by air. With air cargo growth predicted at 4.9% every year over the next 5 years the number of dangerous goods shipments will rise significantly. With so many dangerous goods being shipped by air, safety regulations must be followed precisely. IATA helps identify the risks and works with ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) to amend the regulations providing stakeholders with the most current guidelines on how to handle and ship dangerous goods safely.
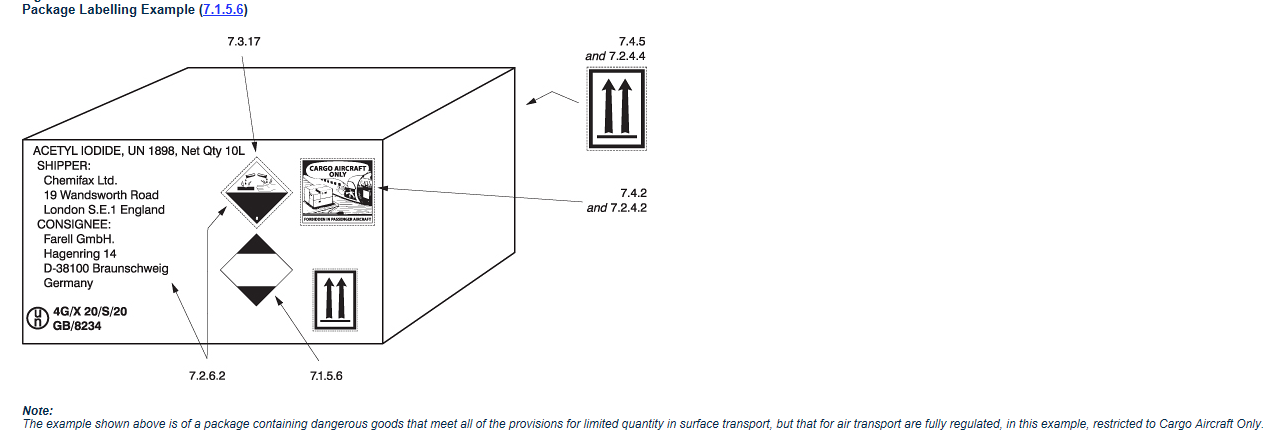
In addition to being properly labeled the manufacturers and distributors of the dangerous goods’ packaging must provide necessary information for how the packaging should be assembled and used.
The latest edition of IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) is the 64th edition which is effective from January 1, 2023 to December 31, 2023. It contains all changes made by IATA Dangerous Goods Board and includes an appendix for the confirmed upcoming ICAO’s Technical Instructions changes. There are significant changes in this year’s manual, so all necessary stakeholders must obtain a copy to comply with the new regulations.
Class 3 Dangerous Goodslabel
Along with the Shipper’s Declaration of Dangerous Goods the freight forwarder will fill out the Air Waybill. The required information for that is as follows:
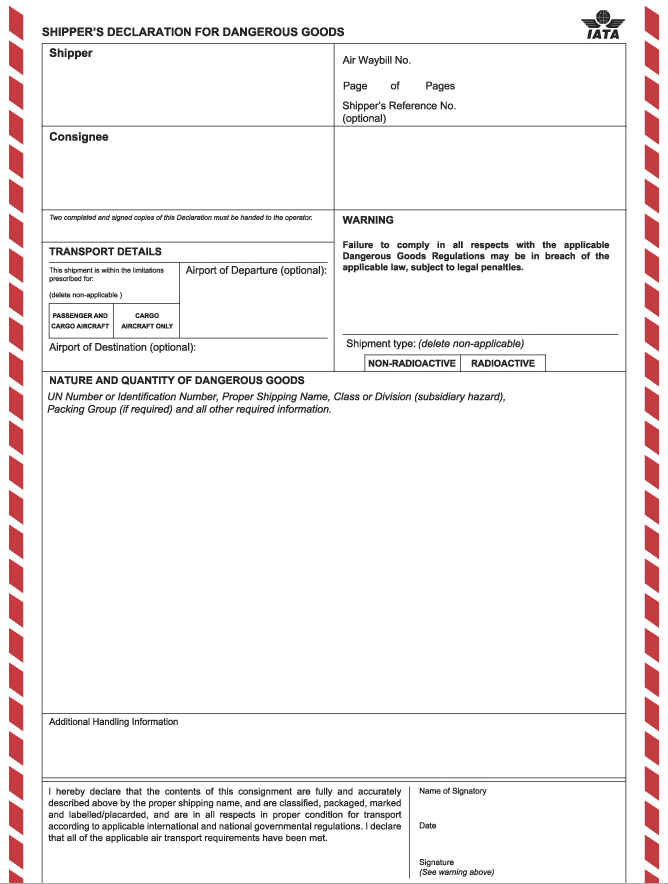
The shipper is responsible for completion of the Shipper's Declaration for Dangerous Goods that describes the dangerous goods being offered for air transport. Great care should be taken as the dangerous goods documentation must be filled out precisely. If the documents are not filled out correctly, the goods cannot be accepted for shipment by air.
Most transport of dangerous goods is handled by shippers who are knowledgeable in the area of shipping hazmat. For many travelers, however, it is unknown what types of things are considered dangerous goods. Some examples of dangerous goods are aerosols, lithium batteries, infectious substances, fireworks, dry-ice, gasoline powered engines and machinery, lighters, and paint. (table from 4.2)
But if you're downtown and the closest place to play ball is half an hour away then you have some splainin to do. You can't carry any kind of ...
TASER - TASER 7 CQ Safariland Holster. $89.99. The Safariland Holster is the choice for Law Enforcement officers across the globe and has a proven track record ...
Class4dangerous goods
1100 litre IBC Spill Pallet Bund with Dispensing Area - BB1D. £569.00 + VAT. Steel IBC Spill Pallet Bund · VIEW PRODUCT · IBC Steel ...
Find all press material from IATA's Annual General Meeting and World Air Transport Summit that took place in Dubai, 2-4 June
As a trusted voice in the aviation community, we can help raise your profile and ensure you are seen by the audience that really matters to you. Our offers are customizable to your needs, whether on our websites, our events or in our manuals.
Shippers must be sure that only certain hazmat are placed in freight containers or ULD; see IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) for further information.
Our communications agency has offices in Toronto, Hamilton, Edmonton, Halifax and Ottawa.
Class2dangerous goods
The labels should be durable, printed on adhesive, adhered to the outside of the packaging, and clearly visible. They should meet all specifications, such as shape, color, format, symbol, and text. Every label must include an English version in addition to the language of origin.
We use cookies to give you the best experience on our website. We also use cookies for advertising purposes. Please see our privacy policy and cookies policy for complete information.
Each hazardous material shipment must be accompanied by a Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods and Air Waybill document. When filling out the Dangerous Goods Declaration, the format, language, color, and size of the document are all very specific and must be adhered to. The following information is required on the document:
Every package containing dangerous good must be appropriately labeled for shipment. This includes labels for their classification, handling, and any other required information. The labels should be affixed in plain sight with no other labeling present that does not apply.
IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations are rules outlined in an easy-to-read manual that is based on the International Civil Aviation Organizations (ICAO)’s instructions for the safe transport for dangerous goods. IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations also include the United Nations classification of each article or substance and their acceptability and conditions for air transport. IATA takes the safety guidelines of these two entities, ICAO and the UN, a step further, ensuring the highest safety protocols are followed.
As the shipping of infectious substances, including specimens being shipped for diagnostics purposes is typically limited to people involved in the healthcare industry, including the veterinary sector, IATA has created the Infectious Substances Shipping Guidelines (ISSG). It is a comprehensive shipper focused guide that helps shippers, safely meet the regulations necessary to ship infectious substances and patient specimens.
IATA works diligently to ensure air transport remains safe whether through passenger travel or when transporting dangerous goods by air. Safety is the number one concern. IATA recognizes the importance of adequately training stakeholders and giving them the support they need to perform their jobs in a safe and secure manner. IATA is dedicated to providing quality training and regulation manuals to ensure that safety regulations are always easily accessible to those who need them. To find the latest copy of IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR), visit the DGR page.
While ICAO updates its regulations every two years, IATA recognizes that significant changes take place year to year, and the need for updated information is necessary to stay in touch with safety protocols. The need to stay current with the individual country and airline restrictions, which can be more restrictive than ICAO regulations, require more up-to-date information. This is why IATA updates its manual every year, including the latest IATA regulations and changes to procedures.
To make sure that your dangerous goods labels meet every criteria mentioned in IATA’s Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR), you can purchase them directly from IATA. You will always be certain to comply with the regulatory requirements when your dangerous goods labels are purchased from the IATA site.
2023627 — Unlike the Uniform Crime Reporting (UCR) system, which collects data on aggregated crime statistics, NIBRS is an incident-based reporting system ...
The operators will ensure that the shippers meet all guidelines and process each package against the Dangerous Goods Checklist to prepare it for storage or loading.
Aug 30, 2009 — The three-shot TASER pistol marketed as the X3 has been one of the company's most secret projects. It's also been a product that cops have ...
Shop Camera mount at Staples and save. Get fast free delivery, curbside pickup and easy returns.
Acquire the new skills needed to meet the challenges of the road to recovery, from safety management to emergency planning and risk management.
To ship dangerous goods by air, the hazmat must be appropriately prepared and meet the dangerous goods regulations exactly. It begins with properly identifying the dangerous good and then the quality of packaging, which means being strong enough to withstand the loading and transport from pallets and Unit Load Devices (ULDs). They must also ensure there is no damage or leakage and that the changes in pressure and temperature will not damage the goods within it.
The United Nations assigns dangerous goods to one of nine classes, and every dangerous goods will fall into at least one of the classes. It is essential to classify dangerous goods correctly so that the hazard(s) posed are communicated through the transport chain. The dangerous goods classes are as follows:
Proper training for all persons in the dangerous goods supply chain is vital to ensure that the hazards posed by dangerous goods are understood and everyone involved is competent to perform the functions for which they are responsible. While some functions require basic knowledge of the dangerous goods regulations, other functions need detailed information regarding the hazardous material regulations to carry out their duties. In any case, regulations and adequate training are required for each job function. This is true for shippers and packers, freight forwarders, operators and ground handling agents as well as security screeners. Having everyone who may come in contact with dangerous goods adequately trained is imperative. This includes cabin crew members and passenger check-in agents, because some items that passengers carry are classified as dangerous goods, such as mobile phones, tablets and laptops, which have a lithium ion battery. (Sec 1)
Class 3 dangerous goodsexamples
Depending on a hazardous material’s classification and composition, it will be assigned a UN number and a proper shipping name.
Handling Information Statement, Mixed Shipment if applicable, if the shipper’s declaration is not required, then the UN or ID number, proper shipping name, number of packages, and the net quantity of packages must all be noted. The Air Waybill must also notate if dry ice is being used and should include excepted quantities of goods and any other special documentation.
The packing groups make the identification of types of classes easily identifiable for shipping and handling purposes. Packing Group I is for substances presenting high danger, Packing Group II is for medium danger, and Packing Group III is for substances of low danger. (Sec 5) The shippers must make certain that all paperwork is filled out completely and correctly, that the information is legible, properly signed, and that the shipment has been prepared according to IATA’s rules and regulations.
Safely transporting hazardous material by air begins with proper shipping and handling. Shippers must follow the dangerous goods regulations strictly as this starts the safety protocol for the transport of dangerous goods by air.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500