Signal boxes DGM-SK - signals gas
NOTE: Specifications for biological safety cabinets are not included in the fire codes. Requirements for such cabinets are generally required in the health and safety legislation for cytotoxic drugs or biologically hazardous materials.
See the table below for examples of the maximum allowed quantity per fire compartment of Class IB flammable liquid that can be present ‘for use’ at different occupancies settings as stated in the National Fire Code of Canada. Note that some of the jurisdiction’s health and safety legislation or insurance companies may have lower maximum quantity requirements.
For example, the safety data sheet for substance A reports that it is classified as follows WHMIS Hazard class: Corrosive to Metals — Category 1 and TDG Class 8 Corrosive. Based on substance A’s corrosivity hazards, a “polyethylene corrosive and acid” cabinet should be selected.
Colour-coded cabinets are not required or specified in the National Fire Code of Canada, standards for storage safety cabinets, nor in health and safety legislation. Manufacturers produce storage safety cabinets in different colours for the following reasons:
A hazard and risk assessment needs to be done by a safety specialist to determine if the storage safety cabinets must be grounded. Generally speaking, if the cabinets are constructed of metal or other conductive material, they must be grounded when Class 1 flammable liquids are being dispensed in the cabinet.
A police officer who Tasered a 95-year-old woman with dementia symptoms at an Australian care home has been found guilty of her manslaughter.
If the cabinets are constructed of metal or other conductive material, they may need to be grounded as a precautionary measure when:
Select a location that does not block exits, walkways, evacuation routes, etc. Generally, manufacturers recommend that storage safety cabinets be located in well-ventilated and low-humidity environments that comply with the local fire code.
The trial in the New South Wales (NSW) Supreme Court heard that Mrs Nowland, while not formally diagnosed with dementia, had been displaying signs of cognitive decline in the months leading up to her death and had at times behaved aggressively towards healthcare workers.
At one point that night she had entered the room of another resident holding the knives, though he told the court he did not feel unsafe, and she had also later thrown one of the blades at a staff member.
(**) Fire compartment means an enclosed space in a building that is separated from all other parts of the building by enclosing construction providing a fire separation having a required fire-resistance rating.
Watch as the first day of the second Test between Australia and India is plunged into darkness due to floodlight failure - twice!
Marking and labelling requirements are required specifically for flammable liquid storage safety cabinets. The fire codes do not specify similar requirements for safety cabinets that are intended for other hazardous chemicals.
Police and paramedics were called to Yallambee Lodge - in the town of Cooma about 114km (71 miles) south of Canberra – around 04:00 on the day of the incident, after Mrs Nowland had been seen roaming the care home with two serrated steak knives.
The National Fire Code of Canada does not have specifications for other gasses. However, the National Fire Code instructs users to follow good practices such as the NFPA 55, “Compressed Gases and Cryogenic Fluids Code,” when it does not have requirements for specific situations. This standard is also cited in NFPA 1 for the storage of gases. The gas cabinet specifications are provided in Section 6.18 of the NFPA 55. Section 6.18 requires the gas cabinets to be ventilated and recommends that incompatible gases be stored in separate cabinets. The following maximum quantities for gas cabinets are recommended:
The need for ventilation depends on the type of hazardous chemicals stored in the cabinet. Storage safety cabinets for flammable liquids that are not toxic are not recommended to be ventilated as it has been shown that it is not necessary for fire protection. However, a cabinet will need to be vented according to the requirements of the local fire code or to good practices when it is used to store:
Watch the moment a fan with a beer snake distracts batter Marnus Labuschagne forcing bowler Mohammed Siraj to pull out of the delivery during the first day of Australia's second Test with India in Adelaide.
Most companies follow good practices and use specific colours for liquids that are a specific hazard. These colours are:
Copyright 2024 BBC. All rights reserved. The BBC is not responsible for the content of external sites. Read about our approach to external linking.
If there is no specification for a maximum allowed quantity in the local fire code or health and safety legislation, then for due diligence reasons, good practices need to be followed. For example, “NFPA 430 for the Storage of Liquid and Solid Oxidizers” specifies the maximum allowed quantities for different types of oxidizing chemicals.
Her death a week later caused public outcry, but White - a senior constable - argued at trial that his use of force was reasonable and proportionate to the threat.
Mitchell Starc claims career-best Test figures of 6-48 as Australia seize the initiative on day one of the second Test against India.
Mitchell Starc takes his best Test figures of 6-48 as Australia dismiss India for 180 on day one of the second Test in Adelaide.
Although every effort is made to ensure the accuracy, currency and completeness of the information, CCOHS does not guarantee, warrant, represent or undertake that the information provided is correct, accurate or current. CCOHS is not liable for any loss, claim, or demand arising directly or indirectly from any use or reliance upon the information.
Determine the type of storage safety cabinets needed by making sure the manufacturer’s technical data sheet or specifications match the chemical’s hazard(s) and local fire code requirements. Manufacturer information is generally available on their website.
White warned Mrs Nowland his weapon was aimed at her, before saying "bugger it" and firing it, while she was still 1.5m-2m away. She fell and hit her head, triggering a fatal brain bleed.
Prosecutors, however, said Mrs Nowland - who relied on a walker to get around and weighed under 48kg (105lb) - was not a danger and that the "impatient" officer had neglected his duty of care to her.
Yes, manufacturers offer different sizes of cabinets. Generally, the capacity of storage safety cabinets ranges from 15 L to 500 L.
When emergency services found Mrs Nowland, they repeatedly asked her to drop the knife in her right hand, and – using thick gloves – had tried to disarm her themselves, the court was told.
However in a written incident report, the officer - who had been stood down from duties while facing court - said he deployed his Taser because he felt a “violent confrontation was imminent”.
They must be placed at a location that meets the local fire code requirements, such as Part 2 in the National Fire Code of Canada, and as instructed by the manufacturer. Storage safety cabinets can be placed under a counter, along a wall, or be wall-mounted or stacked.
"The family will take some time to come to terms with the jury’s confirmation that Clare’s death at the hands of a serving NSW police officer was a criminal and unjustified act," they said in a statement issued by a lawyer, which also asked for privacy.
Storage safety cabinets for substance-specific hazards such as biohazardous or pyrophoric materials will need to meet additional requirements or standards.
Storage safety cabinets are generally selected based on the local fire code requirements, and manufacturer specifications. All types of cabinets (e.g., corrosive, oxidizers, toxic, flammable) must meet the required fire rating to protect the items stored. The fire-resisting material must be compatible with the hazardous chemicals in the containers in case of an unintentional spill.
In the moments before she was hit by the Taser, footage played to the jury showed the elderly woman using her walker to slowly shuffle forward - 1m (3.3ft) over the course of a minute - before stopping and raising the blade.
The storage safety cabinet must have an approval label, which meets the requirements of the standard it was manufactured to. When selecting cabinets, make sure it is certified by the appropriate organization. It is also a good practice to verify the cabinet’s certification by contacting the appropriate certifying organization in case the cabinet is counterfeit. In addition, the manufacturer will have a technical or specification document for their cabinets which should be compared to the requirements in the applicable Code or legislation.
He said White had used his weapon only three minutes after finding the woman: “He was fed up, impatient, not prepared to wait any longer.”
Yes. The maximum number of cabinets that can be present will vary for different occupancies and hazard classifications of the chemicals. For example:
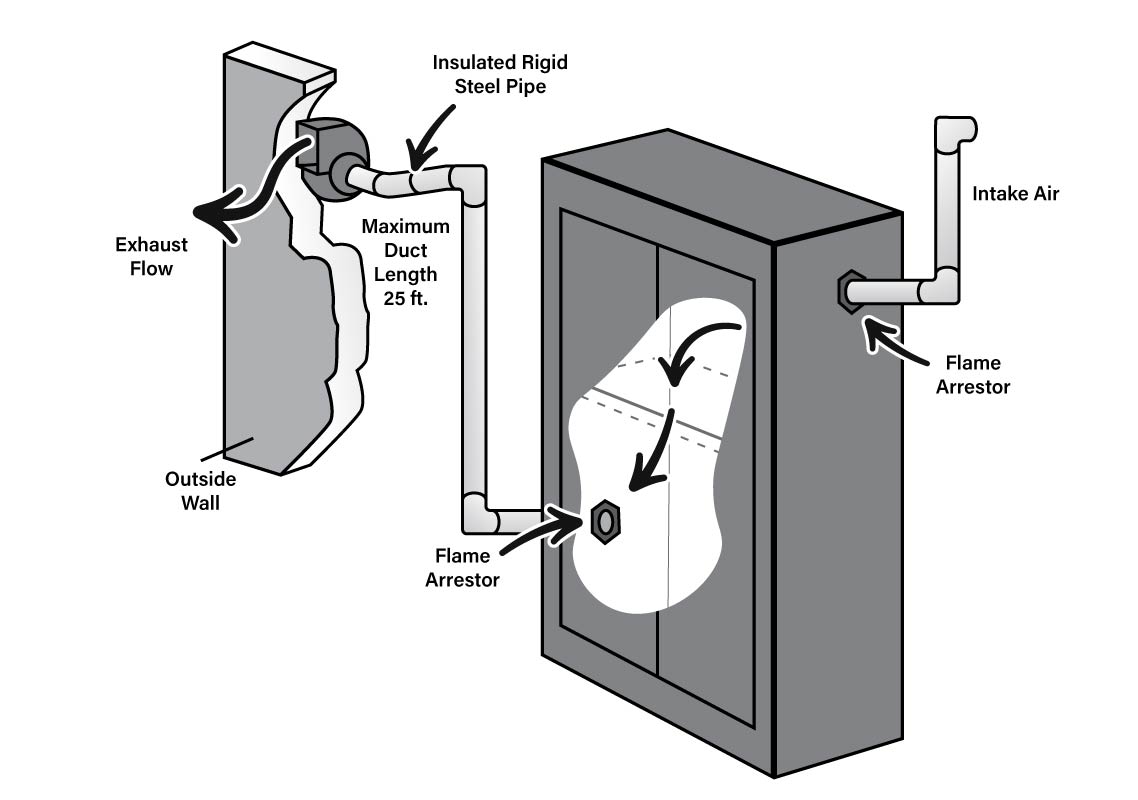
Generally, storage safety cabinets include dual vents. Depending on the hazardous chemical, the fire codes require vents to be:
Most jurisdictions have either adopted the National Fire Code of Canada or the Code with some modifications. The exceptions are Ontario, which has its own Fire Code, and Prince Edward Island (PEI) has adopted the “National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 1 Fire Code” and the “NFPA 101 Life Safety Code”.
Requirements may also be specified in the jurisdiction’s health and safety legislation and substance-specific regulations or standard. For example, British Columbia’s Occupational Health and Safety Regulations include mention of approved storage cabinets in Sections 5.33 to 5.35.
Kristian White, 34, used his weapon on Clare Nowland after the great-grandmother was found wandering with a small kitchen knife in the early hours of 17 May 2023.
Since the storage safety cabinet is tested in its original manufactured form with the original construction material per a standard stated in the fire code, any modifications will generally affect the cabinet's performance. When cabinets are modified, the certifying agency may require additional tests, inspections, examinations, or other evaluations that will demonstrate that the modified cabinet product continues to fulfill requirements. Unless the modifications have been determined to be insignificant to the structural integrity and fire performance of the cabinet, any other modification will generally void the approval of that product and the manufacturer’s warranty.
“Who could she have injured at that moment? No one,” Crown prosecutor Brett Hatfield said, summing up his case for the jury last week.
The defence pointed to evidence from one of the paramedics and White’s police partner, who both said Mrs Nowland had made them feel scared for their safety.
Storage safety cabinets are cabinets used to store hazardous chemicals such as acids, bases, oxidizers, flammable, and other types of chemicals. Many storage safety cabinets are manufactured to store specific types of hazardous chemicals. Their purpose is:
The National Fire Code of Canada, adopted by almost all jurisdictions (except PEI), sets the maximum amount of flammable and combustible liquid stored in a cabinet to be 500 L. However, Ontario’s Industrial Establishment Regulations limit the maximum to 235 L per cabinet. The maximum amount of flammable liquids for PEI is stated in the NFPA 1 Fire code, which is 120 gals (460 L) (same requirement as in NFPA 30 cited in NFPA 1).
Flammable liquid storage safety cabinets are cabinets that are specifically designed for the storage of flammable liquids. These cabinets provide temporary protection from a fire. For the cabinet to be effective, it must be used according to local fire code requirements and the manufacturer’s instructions.
In court he added that he didn’t think Mrs Nowland would be “significantly injured” and that he was “devastated” by her death.
The maximum amount of non-flammable hazardous chemicals in storage safety cabinets is not specified in the National Fire Code of Canada. Follow good practices such as those of NFPA to determine what the quantities should be for a specific occupancy.
Storage safety cabinets for other hazardous chemicals must also be labelled according to health and safety legislation, WHMIS requirements, or safe industry practices. Labels should state the type of hazardous chemical stored in the safety cabinet. For example, WHMIS pictograms can be used. This labelling informs workers and emergency responders of the hazards of the stored items in the cabinet.
NOTE: Avoid storing items on top of or near the cabinet including used or oily rags, wastepaper, or other flammable materials.
The National Fire Code of Canada requires that flammable liquid cabinets be labelled in conspicuous lettering to indicate that the cabinet contains flammable chemicals and that open flames must be kept away. Meanwhile, NFPA 1 and NFPA 30 require specific wording and font size, colour, as well location where they should be placed on the cabinet. See below for an example:
Incompatible materials, regardless of their physical form (e.g., gas, liquid, solid), must never be stored in the same cabinet, unless storage cabinets are designed with non-combustible or half-an-hour vertical fire barriers or partitions or as required by the fire code. For example:
Local fire codes will specify the standard that the storage safety cabinet must meet. The specification for cabinets may vary for different jurisdictions. The standards for storage safety cabinets in the different jurisdictions are as follows:
Yes. When the maximum allowed quantity outside a storage room is exceeded, gas cylinders can be stored in a gas safety cabinet. Note that this quantity varies for different occupancies and the hazard classification for the gas. For example, when gas cylinders contain a flammable gas that is lighter than air, according to the National Fire Code of Canada, the total quantity must not be more than:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500