Sign Charts - Caltrans - CA.gov - /- sign
Oxidisingin chemistry
To learn more about oxidizing agents and the part they play in oxidation-reduction reactions, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
As an electron acceptor – They are chemical substances whose atoms remove at least one electron from another atom in a chemical reaction. As per this definition, oxidizing agents are the reactants that undergo reduction in redox reactions. An illustration detailing the electron-accepting properties of oxidizing agents is provided below.
Eleven first picks have won the NBA Most Valuable Player Award: Oscar Robertson, Kareem Abdul-Jabbar (record six-time winner), Bill Walton, Magic Johnson (three-time winner), Hakeem Olajuwon, David Robinson, Shaquille O'Neal, Allen Iverson, Tim Duncan (two-time winner), LeBron James (four-time winner), and Derrick Rose (youngest winner).
Strongoxidisingagent meaning
In the example illustrated above, the Fe2O3 molecule acts as an oxidizer by transferring an electronegative oxygen atom to the carbon monoxide molecule.
Oxidizing agents normally exist in their highest possible oxidation states and, therefore, have a strong tendency to gain electrons and undergo reduction. Ions, Atoms, and molecules having a strong affinity towards electrons are considered to be good oxidizers. The stronger the electron affinity, the greater the oxidizing power.
An oxidizing agent is a compound or element that participates in a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction and accepts electrons from a different species. An oxidant is a chemical compound that easily transfers oxygen or another substance atoms in order to gain an electron.
Elemental fluorine is said to be the strongest elemental oxidizing agent. This is perhaps due to the fact that fluorine is the most electronegative element in the modern periodic table, and therefore exerts the strongest attractive force on electrons amongst all the elements. In fact, the oxidizing power of diatomic fluorine (F2) is strong enough to cause metals such as asbestos and quartz (and even molecules, such as water) to burst into flames when exposed to it.
An oxidizing agent (often referred to as an oxidizer or an oxidant) is a chemical species that tends to oxidize other substances, i.e. cause an increase in the oxidation state of the substance by making it lose electrons. Common examples of oxidizing agents include halogens (such as chlorine and fluorine), oxygen, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Oxidisingexamples
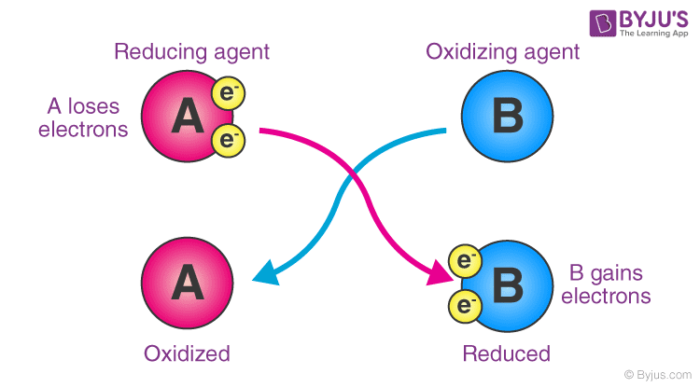
Here, substance ‘A’ undergoes oxidation, resulting in an increase in its oxidation number. On the other hand, the oxidation state of substance ‘B’ becomes smaller (since it gains electrons by undergoing reduction).
What isoxidisingagent
China's Yao Ming (2002), Italy's Andrea Bargnani (2006), France's Victor Wembanyama (2023) and Zaccharie Risacher (2024) are the only players without competitive experience in the United States to be drafted first overall. Eleven other international players with U.S. college experience have been drafted first overall—Mychal Thompson (Bahamas) in 1978, Olajuwon (Nigeria) in 1984, Patrick Ewing (Jamaica) in 1985, Duncan (U.S. Virgin Islands) in 1997, Michael Olowokandi (Nigeria) in 1998, Andrew Bogut (Australia) in 2005, Kyrie Irving (Australia) in 2011, Anthony Bennett (Canada) in 2013, Andrew Wiggins (Canada) in 2014, Ben Simmons (Australia) in 2016, and Deandre Ayton (Bahamas) in 2018. Duncan is an American citizen, but is considered an "international" player by the NBA because he was not born in one of the fifty states or the District of Columbia.[3] Ewing[4] had dual Jamaican-American citizenship when he was drafted, and Irving[5] and Simmons[6] had dual Australian-American citizenship when they were drafted.
Hydrogen peroxide is the chemical compound having formula H2O2. It appears to the human eye as a colourless liquid which has a greater viscosity than water. Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest compound having a peroxide functional group with an oxygen-oxygen single bond. It finds its uses as a weak oxidizing agent, disinfectant, and bleaching agent.
Some compounds that exhibit large oxidation states can also be considered good oxidizing agents. Ionic examples include the permanganate ion, the chromate ion, and the dichromate ion. Acidic examples of good oxidizers include nitric acid, perchloric acid, and sulphuric acid. The electronegativity of the molecules increases with the increase in the oxidation states of the atoms, increasing their ability to oxidize other substances.
Oxidisingchemicals
Oxygen is the element corresponding to the atomic number 8 and is denoted by the symbol ‘O’. It belongs to the chalcogen group of the periodic table and is a highly reactive non- metal with good oxidizing properties. In general, metals tend to form metal oxides by reacting with atmospheric oxygen, due to the strong oxidizing power of oxygen. Oxygen is observed to be a part of a majority of combustion reactions.
The group 17 elements of the periodic table are collectively referred to as Halogens. They are said to have a strong ability to gain electrons, attributed to their high electronegativities when compared to elements from other groups. This implies that they have the ability to easily attract electrons towards their respective nuclei. Examples of the halogens that are good oxidizing agents include iodine, bromine, chlorine, and fluorine. Fluorine is said to be the strongest elemental oxidizing agent due to its highest electronegativity, as discussed earlier.
Types ofoxidising
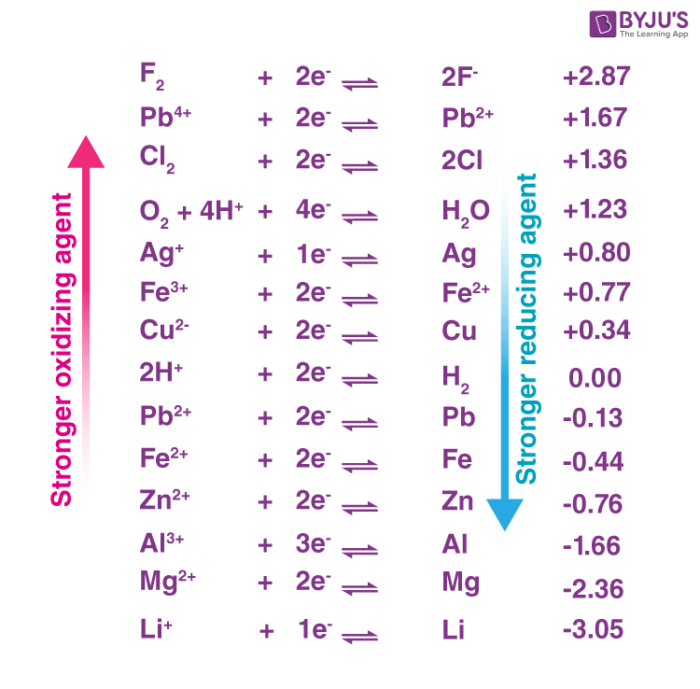
The standard electrode potential of a half-reaction in a redox process provides insight into the oxidizing power of the chemical substance. An illustration ranking some oxidizers in terms of their oxidizing powers is provided below.
Oxidisingprocess
As an atom-transferring substance – An oxidizing agent is a substance that transfers at least one electronegative atom to a chemical species in a chemical reaction. The transferred atom is typically an oxygen atom. Several combustion reactions and organic redox reactions involve the transfer of an electronegative atom between two reactants.
By accepting electrons from other substances, oxidizing agents cause their oxidation states to become more positive. Oxidizing agents are reduced as well.
The first overall pick in the National Basketball Association (NBA) is the player who is selected first among all eligible draftees by a team during the league's annual draft. The first pick is awarded to the team that wins the NBA draft lottery; in most cases, that team had a losing record in the previous season. The NBA team that garners the top overall draft pick selection generates significant media attention,[2] as does the respective player who eventually gets selected with that first pick.
Oxidisingsubstance symbol
Note that the drafts between 1947 and 1949 were held by the Basketball Association of America (BAA). The Basketball Association of America became the National Basketball Association after absorbing teams from the National Basketball League in the fall of 1949. Official NBA publications include the BAA Drafts as part of the NBA's draft history.
Many other oxidizing agents are commonly used industrially as well as in the day-to-day lives of humans. Examples include household bleach (NaClO), Potassium Nitrate (KNO3), and Sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
An oxidizing agent is a substance that causes oxidation by accepting electrons and thus becoming reduced. A reducing agent is a substance that causes reduction by losing electrons, causing it to be oxidized.
A few other examples of elemental oxidizing agents include diatomic oxygen (O2), diatomic chlorine (Cl2), and ozone (O3). These oxidizers are the elemental forms of the second and the third most electronegative elements (oxygen and chlorine respectively), making them good electron acceptors.
When it comes to electron transfers, an oxidizing agent gains electrons while oxidation is the process of losing electrons. Reduction, on the other hand, means gaining electrons. As a result, the oxidizing agent gains electrons from the species being oxidized, implying that it undergoes reduction (as it gains electrons).
Many organisms make use of electron acceptors, or oxidizers, to collect energy from the redox reactions such as in the process of hydrolysis of glucose.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500