Rate My Academy - my academy
The Executive Protective Service Training course is designed to prepare operators to perform both basics and advanced protective security details for domestic and international operations. Because of our unique training methodology, both veterans and rookies will greatly benefit from this course.
Floodplain
This course does not constitute a Security License in the Province of British Columbia. Upon successful completion of the course, participants will receive training material, a certificate, t-shirt, as well as photos. Please note that the course fee does not include transport, food or lodging.
Requirements: This course is completed in five demanding 8-12 hour days, plus an assessment day. This is an extremely demanding course; participants must be healthy, physically fit, 19 years of age or older, have good communication skills and be a team player. No previous experience is necessary.
FEMA floodway Map
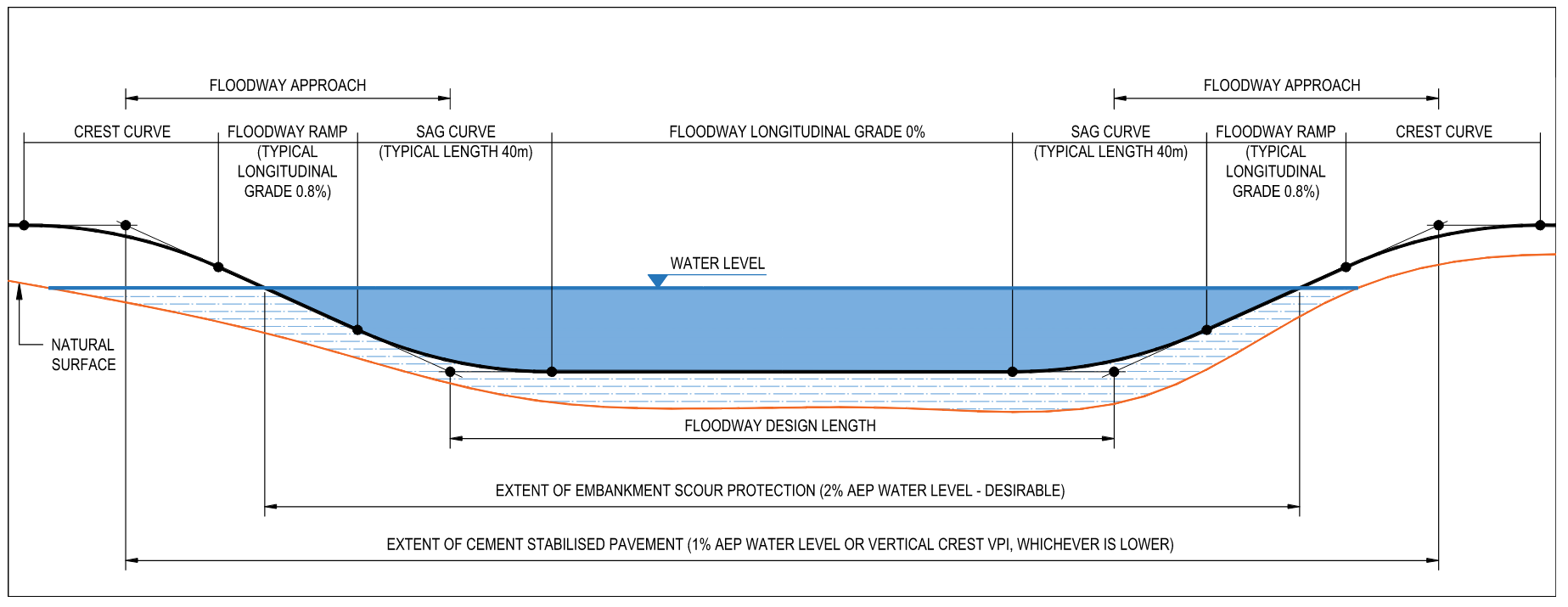
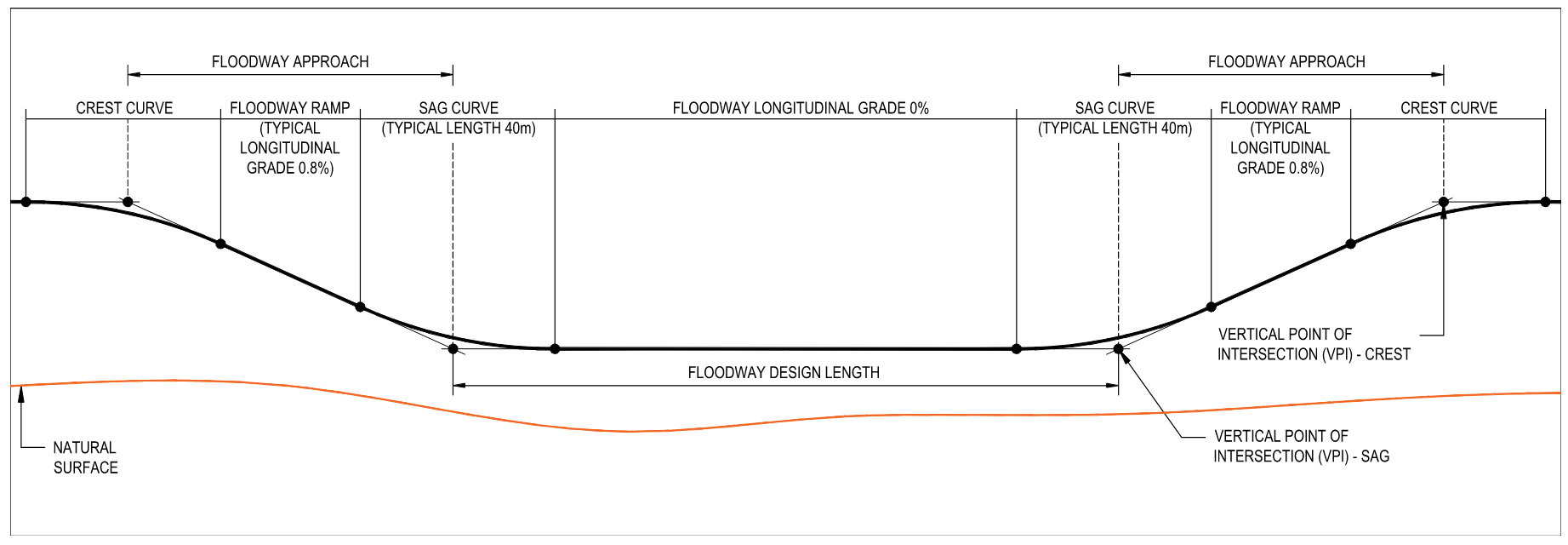
Sag vertical curves should be kept short in order not to encroach on the waterway in the floodway depression and not to increase the raised portion of the ramp more than is strictly necessary. Road embankments on the approaches to floodways are susceptible to scour and their length should be kept as short as possible. The angle of the ramp should therefore be as high as possible and consistent with other geometric requirements. A combination of 40m sag vertical curve with 0.8% longitudinal grade on floodway ramp is typically used, however, it should be noted that this combination will result in a very marginal deficiency in headlight criteria for a design speed of 110km/h with a reaction of 2.5 seconds. In this case, the length of sag vertical curve is expected to be increased slightly in order to meet the standard headlight criteria.
Design guidelines for pavement and embankment scour protection for floodways can be found in Main Roads Floodway Design Guide.
Floodway Map
These guidelines aim to ensure that all the design criteria have been considered for designing a floodway specifically from a road geometric design perspective. Guidelines for hydrological and hydraulics analysis and structural and civil engineering design of a floodway can be found in Main Roads Floodway Design Guide.
What is a floodway Zone
Floodways are commonly used on rural roads with relatively low traffic volume and where it is impractical or uneconomical to construct a bridge or culvert.The road geometric vertical alignment components of a floodway are outlined in Figure 1. The length of the floodway is generally taken to be the length between the intersection points of sag vertical curves, no account being taken of the extra capacity of floodway approaches or loss of capacity due to the sag vertical curves.
Floodway Pasig
The extent of cement stabilised pavement should be extended to 1% AEP water level or vertical crest VPI, whichever is lower.
In general, there are 5 typical floodway types and their guideline drawings are listed in Table 1. Each of the types varies in some ways from the others and their applications are explained in Main Roads Floodway Design Guide.
Floodway is designed such that it can be trafficable for all flows up to the design AEP and for all flows up to 2% AEP can be contained within the floodway approach without spilling out elsewhere along the road.
FEMA floodway
Course Topics Include: Legalities; Psychology of Violence; The Role of the Security Specialist; Team Formation and Dynamic; Equipment; Communications; Threat Assessment/Management; Close Protection Skills Acquisition; Weapons Handling; First Aid and Medical Training (includes CPR and Field Survival); Crowd Dynamics; Hotel, Airport, Residential and Vehicular Protection; Media and Public Relations; Escapes and Evasions; Health, Fitness and Wellbeing for Specialists; Tactical and Strategical Planning; Scenarios (and lots of them); and a Final Examination.
The extent of embankment scour protection should be extended beyond the floodway design length to the water level extent as shown in Figure 2. Consideration should be given to minimising the closure time by ensuring the road is not damaged after the design rainfall event. Road damage repair work is always difficult in a remote area and the fund for road repair work may not always be available for road damage caused by frequent events. The recommended desirable Annual Exceedance Probability (AEP) water level for the extent of embankment scour protection is 2%.
The Government of Western Australia acknowledges the traditional custodians throughout Western Australia and their continuing connection to the land, waters and community. We pay our respects to all members of the Aboriginal communities and their cultures; and to Elders both past and present.
Floodway vs floodplain
A relief culvert should be placed at the lowest point of the natural surface to drain the perennial or frequent flows. This prevents water from ponding upstream of the floodway, softening the embankment and subgrade which ultimately causes pavement failure.
You may wish to bring your own holster/carrying system (either concealed or exposed) and a training replica. We will otherwise supply.
Floodway should be on a straight horizontal alignment. When a floodway is on a horizontal curve and overtopped by water, the risks are listed below. Floodway and floodway approaches should not be located in either horizontal curves or plan/superelevation transitions.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500